08 Oct Autologous Stem Cell Treatments: A New Era in Personalized Medicine
The world of medicine is experiencing a significant shift, thanks to the revolutionary potential of autologous stem cell treatments. These therapies represent the dawn of a new era in personalized medicine, where doctors can do more than just manage symptoms—they can actively engage in healing the body from within. Autologous stem cell treatments use the patient’s own stem cells to repair damaged tissues, offering a natural and effective way to promote recovery.
In contrast to traditional medical treatments, which often focus on masking pain or facilitating healing through external interventions, stem cell therapy allows doctors to directly initiate and support the healing process at the cellular level. This groundbreaking approach holds the promise of transforming how we address injuries and degenerative conditions, placing the patient’s own cells at the heart of recovery.
Medicine’s Evolution: From Managing Symptoms to Initiating Healing
For centuries, medicine has largely focused on managing symptoms rather than directly healing the root cause of injuries or diseases. Pain relief medications, for example, are designed to mask discomfort, while other interventions, such as casting a broken bone, put the body in a position to heal itself. Though these methods are often effective, they rely on the body’s natural healing process, which can be slow, imperfect, and sometimes incomplete.
Stem cell therapy, however, changes this paradigm. For the first time in the history of medicine, doctors have a tool that allows them to actively initiate the healing process. Stem cells, with their unique ability to transform into various types of specialized cells, offer an unprecedented opportunity to regenerate damaged tissues, reduce inflammation, and promote faster recovery. This shift from simply supporting healing to actually driving it marks a new chapter in medical treatment.
The Power of Autologous Stem Cells
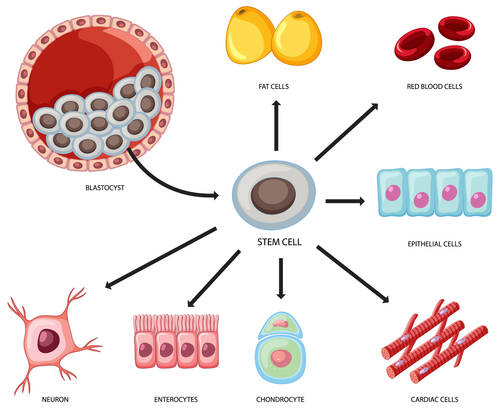
Stem cells are versatile, undifferentiated cells that can become many different types of cells in the body, such as muscle, bone, cartilage, or nerve cells. This ability makes them a powerful tool for regenerative medicine. But not all stem cell therapies are created equal. One of the most important distinctions to understand is the difference between autologous stem cells (stem cells taken from the patient’s own body) and donor stem cells (stem cells harvested from another individual).
Autologous stem cell therapy uses the patient’s own cells, which are typically collected from areas rich in stem cells, such as fat tissue (adipose tissue) or bone marrow. Once harvested, these stem cells can be processed and reintroduced into the patient’s body, where they help repair damaged tissues and promote healing. Because the cells come from the patient’s own body, there is a decreased risk of immune rejection, and the process is safer and more natural than using donor cells.
The Risks of Donor Stem Cells: Why Autologous Is Safer
For years, the idea of using donor stem cells—cells harvested from young, healthy individuals—has been widely advertised. Many believed that using cells from younger donors would provide more potent and effective treatments, based on the notion that younger cells may have greater regenerative potential. However, this approach ignores the inherent risks associated with introducing foreign cells into the body.
The primary risks of using donor stem cells include:
- Disease Transmission: Donor cells carry the potential for transmitting infectious diseases or other unknown pathogens. Even with rigorous screening, there’s always a small chance that harmful agents could be introduced into the recipient’s body.
- Immune Rejection: Because donor cells do not carry the recipient’s DNA, the body’s immune system may recognize them as foreign and attack them. This immune response can cause inflammation, rejection of the treatment, and in some cases, may lead to serious complications.
- Unintended Side Effects: The use of donor cells introduces variables that are outside the control of both the patient and the medical team. These cells may behave unpredictably or fail to integrate properly with the patient’s tissues.
In contrast, autologous stem cell therapy minimizes these risks. Since the stem cells are taken from the patient’s own body, there is a decreased risk of disease transmission, and because the cells share the patient’s DNA, there is a decreased risk of immune rejection. This makes autologous therapy not only safer but potentially more effective, as the cells are more suited to interact with the patient’s tissues and promote healing.
Personalized Medicine: Tailored for Your Unique Biology
The power of autologous stem cell therapy lies in its personalization. Every person’s body is unique, and so are their health needs. With autologous treatments, doctors can tailor the therapy to the individual patient, using their own cells to target specific areas of damage or degeneration. This personalized approach ensures that the treatment is biologically compatible with the patient, maximizing the chances of successful recovery.
Because the stem cells used in autologous therapy come from the patient’s own body, they are already programmed to communicate effectively with the patient’s tissues. This seamless integration allows the cells to home in on areas of injury, reduce inflammation, and promote regeneration. By working with the body’s natural healing processes, autologous stem cell therapy offers a more efficient and effective solution for treating injuries and degenerative conditions.
Transforming the Future of Medicine
Autologous stem cell treatments represent a major leap forward in medicine, offering new hope for patients with conditions that were previously difficult to treat. Whether it’s an aging joint, a chronic injury, or a degenerative disease, autologous stem cell therapy works provide a safer and potentially more effective way to harness the body’s own healing power.
As more research and clinical experience continue to validate the benefits of stem cell therapies, we are likely to see these treatments become an integral part of mainstream medicine. In fact, many doctors and researchers believe that stem cell therapy could soon become the standard of care for treating a wide range of injuries and degenerative diseases.
To learn more about how autologous stem cell treatments are transforming patient care, visit Cell Surgical Network, where leading experts in regenerative medicine are pioneering the future of healthcare.
In this new era of personalized medicine, autologous stem cell therapy stands as a beacon of hope, offering a safer, more effective, and more natural way to heal the body and restore quality of life.
For more information:
- https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/autologous-stem-cell-transplant
- https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/autologous-stem-cell-transplant
The information on MedicalResearch.com and other sites referenced on this platform, is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition.
Some links may be sponsored. Products and services, including those referenced in this post, are not tested, warranted or endorsed.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on November 25, 2024 by Marie Benz MD FAAD
