
24 Apr Limiting the Spread: 6 Core Infection Control Principles That Apply to any Healthcare Environment
Healthcare workers save thousands of lives a day with infection control. Hospitals and nursing homes are breeding grounds for germs. Infections start when germs enter the body, multiply, and cause a reaction. That’s why workers, including doctors and nurses, must use standard infection control principles.
Infection Control Starts With Knowledge
Everyone who works in a healthcare environment must follow infection control protocol. There are some tools that make the job easier. For instance, Isolation carts Infection Control should be standard in every facility. Nurses have to be prepared when they answer a call. Isolation carts are designed to carry all the tools to protect themselves and the patient from infection.
Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is the main infection control measure. The major weapons used are hand washing and alcohol-based hand sanitizers. A hand sanitizer should contain between 60 to 95 percent alcohol. Sanitizer is preferred except when hands are visibly dirty or when a patient has infectious diarrhea. Healthcare workers wash their hands a lot. Hands should be washed before and after patient contact. Further, wash your hands, even if wearing gloves, after contact with blood, bodily fluids, broken skin, membranes, and contaminated items.
Additionally, hands should be washed after gloves are removed. The CDC recommends washing hands for at least 20 seconds using soap and water. Remember to wash between fingers and under nails. Moreover, nurses should teach patients and their families the correct hand washing technique.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
 PPE includes gowns, face shields, gloves, and anything used to protect the body from infectious organisms. Gloves should be worn when touching blood, membranes, wounds, and contaminated items. Face shields protect the eyes, nose, and mouth. Additionally, a gown should be worn if the body may come in contact with bodily fluids. Everyone with patient contact should be taught how to use PPE properly.
PPE includes gowns, face shields, gloves, and anything used to protect the body from infectious organisms. Gloves should be worn when touching blood, membranes, wounds, and contaminated items. Face shields protect the eyes, nose, and mouth. Additionally, a gown should be worn if the body may come in contact with bodily fluids. Everyone with patient contact should be taught how to use PPE properly.
Training should include how to put on PPE and take it off to avoid contamination. There are several things workers should not do while wearing PPE. These include:
- touching the face
- touching surfaces
- removing PPE when leaving the work area
- using hand hygiene.
Safe Injection Methods and Waste Disposal
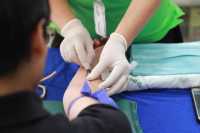 Gloves should be worn when giving an injection. Sharps units must be used for uncapped needles and other sharp instruments. These objects should be placed in the disposal unit immediately after being used. The sharps unit should be disposed of according to state and local regulations.
Gloves should be worn when giving an injection. Sharps units must be used for uncapped needles and other sharp instruments. These objects should be placed in the disposal unit immediately after being used. The sharps unit should be disposed of according to state and local regulations.
Respiratory Hygiene
Respiratory Hygiene and cough etiquette are used because pathogens can be airborne. Patient education is key in this area. They should be taught to cover the mouth with a tissue when coughing and sneezing. Patients should place the used tissue in the trash and then clean their hands. The government wants healthcare facilities to have ample supplies of tissue and hand sanitizer available. That’s why hand sanitizer is placed near the entrance of most facilities. Ideally, patients with respiratory infections should wear a mask.
Environmental Cleaning
Medical equipment and surfaces must be disinfected to stop the spread of bacteria. Reusable equipment like stethoscopes and scissors must be cleaned after each use. Healthcare facilities must use a “broad-spectrum” anti-microbial substance for disinfecting. The cleaning and nursing staff should work together to ensure rooms are thoroughly cleaned between patients.
It only takes a second for an infection to start. That’s why medical professionals must use standard precautions to prevent infections. These standards protect workers and patients.
[subscribe]
[last-modified]
The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on May 12, 2020 by Marie Benz MD FAAD

