02 Nov Infrared Non-Contact Thermometers vs. Traditional Ones: Comparing Accuracy, Speed and Convenience

Body temperature measurement plays a crucial role in healthcare. Fluctuations in temperature often indicate the presence of disease and monitoring it also helps medical practitioners assess the effectiveness of treatments.
To get accurate measurements, healthcare professionals use thermometers. These devices are designed to measure body temperature in different ways, including oral, rectal, axillary, tympanic, and temporal methods. These areas are known for maintaining stable temperatures, and the accuracy and reliability of readings largely depend on the point of measurement. Therefore, selecting the appropriate thermometer for a healthcare facility is critical.
This article compares infrared non-contact thermometers with traditional thermometers. Understanding their advantages and disadvantages will help decide which best suits your needs.
Infrared Thermometers

These thermometers are non-contact devices that measure a person’s temperature by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by the skin, typically from the forehead. Infrared non-contact thermometers allow for a quick, accurate and safe temperature measurement, making them a popular option in medical facilities.
Furthermore, the non-contact nature of these devices helps reduce the risk of cross-contamination. This is another factor that contributes to their popularity in healthcare settings.
Accuracy
When used correctly and according to the manufacturer’s instructions, infrared thermometers deliver consistent and reliable results, making them an excellent tool for monitoring fevers and other temperature-related health conditions.
Speed
With these devices, you get instant temperature readings. This makes them perfect for situations where quick measurements are required, such as in healthcare facilities.
Convenience
In addition to being lightweight and portable, these temperature-measuring devices also come with user-friendly interfaces that make them easy to operate. The non-contact feature of these thermometers also allows for the temperature measurement of patients without disturbing them.
Traditional Thermometers
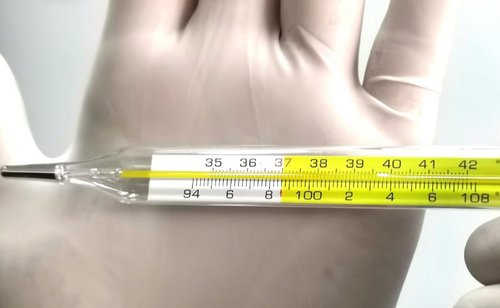
There are two types of traditional thermometers: mercury and digital.
Mercury Thermometers
Mercury thermometers have been used for generations and were once considered the gold standard for temperature measurement. These thermometers consist of a glass tube filled with mercury that expands or contracts in response to temperature changes, with the mercury level displayed on a calibrated scale.
Accuracy
Mercury thermometers are known for being highly accurate, delivering precise temperature readings due to mercury’s consistent expansion and contraction with temperature changes.
Speed
These medical tools can take up to 5 minutes to deliver accurate results, which could be an issue for busy healthcare facilities.
Convenience
The convenience of mercury thermometers lies in their simplicity—no batteries or complex setups are required, and the temperature can be easily read by observing the mercury level against the scale. However, despite these benefits, their use has diminished due to safety concerns around mercury toxicity, leading to a shift toward safer digital alternatives.
Digital Thermometers
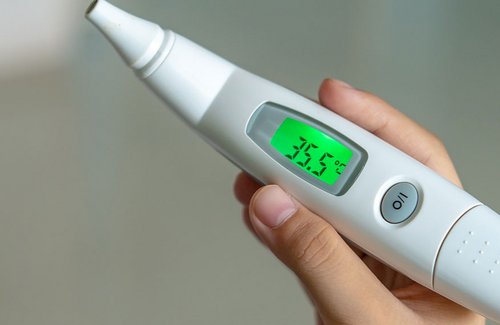
The safety and ease of use of digital thermometers have made them a better option than mercury. Instead of mercury, these tools use electronic sensors to measure temperature, which are then displayed on a digital screen.
Accuracy
Digital thermometers are fitted with advanced sensors that ensure precise measurements.
Speed
Digital thermometers typically provide a temperature reading within 10 to 30 seconds. The exact time may vary depending on the type and brand of the thermometer, as well as the method of measurement (oral, rectal, or underarm).
Convenience
The easy-to-read displays and simple operation of digital devices make them convenient for anyone to use. Many digital options feature memory recall, automatic shutoff, and flexible tips that contribute to improved comfort and efficiency.
Despite the many advantages of traditional options, such as their accuracy and ease of use, infrared thermometers have become a favourite option among healthcare facilities. This preference is mostly due to their non-contact design, which minimises the risk of cross-contamination. Their quicker readings also make them a better option for busy medical environments.
How to Choose an Infrared Thermometer?
If you decide to go for an infrared option, here is what you’ll need to consider.
Accuracy and Precision
Medical-grade infrared thermometers need to provide highly accurate readings. Accuracy is crucial in a healthcare environment where even small temperature variations can indicate serious medical conditions. Look for a model with a minimal margin of error, typically ±0.2°C (±0.4°F) or better. High-precision options also often feature advanced sensor technology to reduce interference from environmental factors like ambient temperature.
Measurement Speed
In busy medical settings, thermometers need to deliver readings quickly and efficiently. Look for models that can capture accurate temperatures in one second or less. This is particularly useful in situations where multiple patients need to be screened rapidly, such as during flu seasons or pandemics. Fast readings minimise the time between uses, increasing efficiency.
Ease of Use
In a fast-paced medical environment, thermometers must be intuitive and simple to use. Look for models with clear digital displays that are easy to read, even in low-light conditions. Features like backlighting, large fonts, and audible alerts when a reading is complete are helpful for quick assessments. Additionally, a user-friendly design that offers one-button operation ensures that staff can easily take temperature readings, regardless of their technical skill level.
Memory and Data Logging
Some infrared thermometers offer memory storage to track multiple temperature readings. This can be particularly useful for monitoring trends in a patient’s temperature over time, which helps in assessing their response to treatments. A thermometer that stores at least 20 readings can reduce the need for manual recording and streamline patient documentation.
Durability and Battery Life
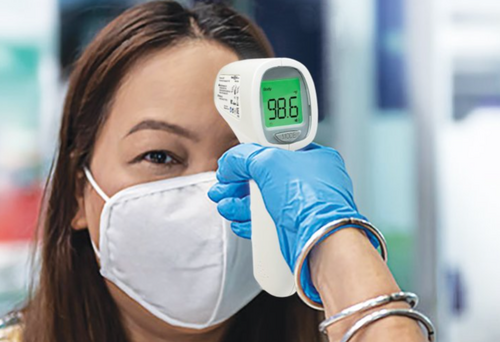
Medical settings require durable devices that can withstand frequent use. Choose a model that is built from high-quality materials and can handle being dropped or used frequently.
Additionally, look for thermometers with long battery life or rechargeable options to minimize disruptions during patient care.
Hygiene and Safety Features
Some infrared thermometers include built-in hygiene and safety features, such as antimicrobial materials or disposable covers. These help maintain a sterile environment, which is critical in preventing the spread of infections in a healthcare setting.
The Importance of Calibration and How It Can Be Done
Infrared thermometer calibration is crucial for ensuring accurate temperature measurements. This typically involves comparing the infrared device’s readings to a known reference standard, such as a calibrated thermometer or thermal camera, at specific temperature points. This process can be performed in-house using calibration kits or by sending the device to a professional calibration service.
———
The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition.
Some links are sponsored. Products and services are not warranted or endorsed.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on November 2, 2024 by Marie Benz MD FAAD
