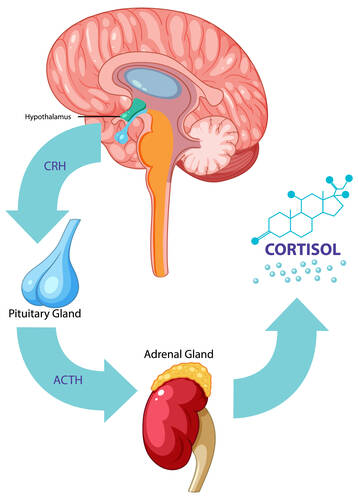
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones. These hormones control many vital body functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. As we age, the efficiency of this system declines, leading to various age-related diseases and conditions. Understanding how the endocrine system impacts longevity can help us develop strategies to live longer and healthier lives.
The Role of Endocrine Health in Aging
Endocrine health is integral to aging because hormones regulate processes like cell regeneration, immune function, and energy metabolism. For example, a decline in growth hormone levels is associated with decreased muscle mass and bone density, while imbalances in insulin can lead to type 2 diabetes, a condition that significantly shortens lifespan.
The Endocrine Theory of Aging
The endocrine theory of aging posits that the aging process is largely regulated by hormones, which act as messengers coordinating various physiological processes. According to this theory, as we age, the production and regulation of hormones change, leading to the deterioration of bodily functions. For instance, the decline in growth hormone and sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone are associated with muscle wasting, reduced bone density, and increased fat accumulation—all hallmarks of aging. By understanding and potentially manipulating these hormonal changes, it might be possible to slow down or mitigate some aspects of aging.
(more…)