Author Interviews, Hematology, Pain Research, Pediatrics / 10.12.2023
ASH23: Nemours Study Links Pain Scores with Return ED Rates in Children with Sickle Cell Disease
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
David Brousseau, MD, MS
Chair of Pediatrics
Nemours Children’s Health, Delaware and the
Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
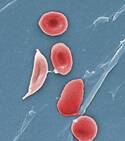
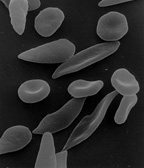
Response: Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an inherited red blood cell disorder – the most common genetic disorder in the United States, affecting about 100,000 Americans (1 of every 365 Black births and 1 of every 16,3000 Hispanic-American births) (source: CDC).
Pain is its most common symptom. Patients may experience acute or chronic pain or both. Acute episodes of pain, or pain crises, can vary in duration and severity. Many are treated at home; however when the pain is excruciating and cannot be treated at home, they lead to Emergency Department (ED) visits and even hospitalization.
Reducing pain through prompt administration of pain medication in the ED is a core principle of national guidelines for SCD care. However, little data exists on how pain scores and changes in pain scores in the ED are associated with the patient’s disposition and the odds of a return visit.
(more…)