Author Interviews, OBGYNE, Radiology / 22.07.2024
Uterine Fibroids: Weill Cornell Radiologist Discusses Implications and Treatment Options
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Nicole Lamparello, M.D
Interventional Radiologist
Assistant Professor of Radiology
Weill Cornell Medicine
Assistant Attending Radiologist
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you briefly describe the condition of Uterine Fibroids?
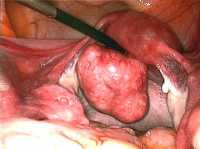
Response: A uterine fibroid (leiomyoma) is a type of tumor that grows in the uterus.. Most fibroids are benign growths that do not spread to other regions of the body. However, fibroids can cause a variety of symptoms that severely impact a woman’s quality of life, including pelvic pressure or pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, abdominal bloating, urinary urgency/retention and infertility.
Often, women with uterine fibroids are presented with hysterectomy as a treatment option, and are not informed about less-invasive options, such as Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), a non-surgical procedure performed by an interventional radiologist.
(more…)