11 Aug Microneedles Enhance Treatment of Keloids
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Hong Liang Tey MBBS, FRCP
Head of Research Division and Senior Consultant, National Skin Centre, Singapore
Adj Assoc Prof., Yong Loo Ling School of Medicine, National University of Singapore
Asst Prof., Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
We developed dissolving microneedles embedded with a medication, triamcinolone, as a novel treatment option for patients with keloids and evaluated its efficacy and safety in a clinical trial.
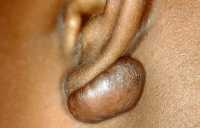
Background: Keloids are a common skin disorder and itch and pain afflicts up to 80% of patients. The first-line and typically the only treatment option is multiple repeated intra-lesional corticosteroid injections by dermatologists or specially-trained nurses. However, many patients are unable to undergo this treatment. Typically, such patients
- Are unable to tolerate the pain of conventional intra-lesional injection, as keloids are inherently hypersensitive. The problem is exacerbated by the fact that repeated monthly injections are required to achieve a response. In addition, children cannot tolerate pain and cannot undergo such injections.
- Have keloids on the mid facial region, where injection carries a risk of causing blindness.
- Are unable to afford the time and cost of repeated travelling to see a dermatology doctor or nurse for the injections. These include patients residing or working overseas.
- Have mid-sternum protrusive scars after cardiac arterial bypass surgery, and painful injections may trigger another heart attack.
MedicalResearch.com: What did you do?
Response: We designed dissolving microneedles embedded with triamcinolone, a steroid currently used as the first-line treatment of keloids (figure 1). These microneedles are composed of hyaluronic acid, a naturally-occurring ground substance in normal skin, which dissolves upon insertion into the skin. We performed preclinical studies in cell cultures, mice, guinea pigs and rabbits, comprising sterility, cytotoxicity, systemic toxicity, skin irritation, delay contact sensitization and phototoxicity tests, which demonstrated safety of this pharmaceutical composition. We also determined that dissolution of the microneedles occurs within minutes upon application of the microneedles onto keloids.

Microneedles embedded with triamcinolone, a steroid currently used as the first-line treatment of keloids.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main results?
Response: The clinical trial demonstrated the efficacy and safety of triamcinolone-embedded dissolving microneedles in reducing the volume of keloids. This was associated with a reduction in pain and itch sensations, which commonly afflict keloid sufferers. Details of the results can be found in: Tan CW, Tan WD, Srivastava R, Yow AP, Wong DWK, Tey HL. Dissolving Triamcinolone-Embedded Microneedles for the Treatment of Keloids: A Single-Blinded Intra-Individual Controlled Clinical Trial. Dermatology and Therapy. In press.
We subsequently performed a randomised intra-individually controlled single-blinded two-phased clinical trial.
MedicalResearch.com: How have you implemented this technique in clinical practice?
Response: We have since implemented this new therapy in our hospital, primarily for patients who cannot receive the standard intra-lesional injection treatment. The microneedle patches (figure 2) are prepared in two sizes, 1cm and 2cm in diameter, to cater to the varying size of keloids.

The microneedle patches are prepared in two sizes, 1cm and 2cm in diameter, to cater to the varying size of keloids.
MedicalResearch.com: What recommendations do you have for future research as a result of this work?
Response: Subsequent to this project, we further developed hyaluronic acid dissolving microneedles embedded with other therapeutic agents, to serve as a platform for drug delivery in the treatment of other medical conditions.
Citation:
Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019 Aug 2. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00316-3. [Epub ahead of print]
Dissolving Triamcinolone-Embedded Microneedles for the Treatment of Keloids: A Single-Blinded Intra-Individual Controlled Clinical Trial.
Tan CWX1, Tan WD1, Srivastava R2, Yow AP3, Wong DWK3, Tey HL4,5,6.
[wysija_form id=”3″]
[last-modified]
The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on August 11, 2019 by Marie Benz MD FAAD
