15 Sep RANK signaling-blockade reduces breast cancer recurrence by inducing tumor cell differentiation
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Eva Gonzalez Suarez, PhD
Group Leader Transformation and Metastasis lab.
Cancer Epigenetics and Biology Program-PEBC
Institut d’Investigació Biomédica de Bellvitge-IDIBELL
Hospital Duran i Reynals Avinguda Gran Via de l’Hospitalet,
L’Hospitalet de Llobregat-Barcelona-Spain
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
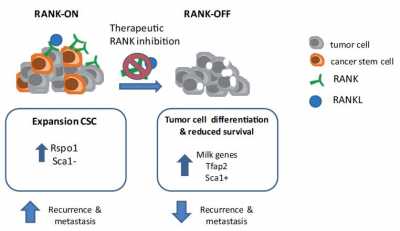
Response: Thousands of cancer patients worldwide are taking RANKL inhibitors for the management of bone metastasis, based on the key role of RANKL and its receptor, RANK, driving osteoclastogenesis. RANK signaling pathway acts as a paracrine mediator of progesterone in mouse and human mammary epithelium. RANK expression is associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer even though its therapeutic potential remained unknown.
Complementary genetic and pharmacological approaches demonstrate that therapeutic inhibition of RANK signaling drastically reduces the cancer stem cell pool, decreases tumor and metastasis initiation and enhances sensitivity to chemotherapy in mouse models that closely resemble the clinical disease. Mechanistically, genome wide expression analyses showed that anti-RANKL therapy promotes differentiation of tumor cells into milk-producing cells, as observed during pregnancy.
MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report?
Response: Findings show how neoadjuvant therapy with inhibitors of RANK signaling can provide a differentiation therapy in breast cancer, through the depletion of cancer stem -like cells, extending the use of these inhibitors beyond simply the management of skeletal-related events.
MedicalResearch.com: What recommendations do you have for future research as a result of this study?
Response: RANK enhances hallmark capabilities of tumor cells, mostly described in the mouse mammary epithelia, increasing proliferation and stemness in early steps of mammary tumorigenesis and enhancing survival and migration in neoplasic cells. Before translating these results to the clinic, they need to be validated in additional mouse and human breast cancer cells and models, and in clinical trials.
MedicalResearch.com: Is there anything else you would like to add?
Response: Considering that inhibitors or RANK pathway are already in the clinic it is essential to demonstrate whether anti-RANKL treatment in human breast cancer and other tumors has benefits beyond the management of bone metastasis.
MedicalResearch.com: Thank you for your contribution to the MedicalResearch.com community.
Citation:
Note: Content is Not intended as medical advice. Please consult your health care provider regarding your specific medical condition and questions.
More Medical Research Interviews on MedicalResearch.com
[wysija_form id=”5″]
Last Updated on September 15, 2016 by Marie Benz MD FAAD