Author Interviews, COVID -19 Coronavirus, Dermatology, Respiratory / 06.10.2021
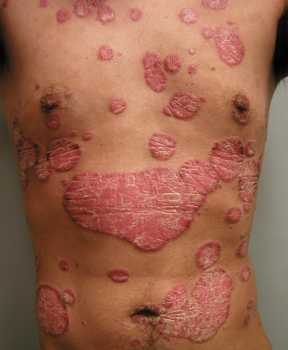
Study Evaluates Risk of Respiratory Infections, Including COVID-19, In Psoriasis Patients on Biologics
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lara van der Schoot
MD, PhD candidate
Department of Dermatology
Radboud University Medical Center
Nijmegen, The Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Psoriasis is a chronic, immune mediated skin disease for which effective targeted biological agents have become available the past years. Inherent to their immunomodulatory mechanism of action, biologics might increase infections risk. We know from clinical trial data that respiratory tract infections are among the most common adverse events during biologic treatment, but real-world data is sparse. Regarding the risk of serious infections among biologic users, mostly defined as infections requiring hospitalization, previous studies provided different results and there is limited comparative data for the newer biologics available.
The COVID-19 pandemic turned attention to the risk of infections among biologic users, especially for respiratory tract infections, as they might relate to susceptibility for viral respiratory tract infections such as COVID-19.
In our study, the primary aim was to determine the risk of respiratory tract infections among real-world psoriasis patients treated with biologics, including the newer IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors. The secondary aim was to assess risk of serious infections in this cohort. Additionally, rates of SARS-CoV-2 infections were assessed.
(more…)

 Professor Marie-Aleth Richard
EADV Communications Committee Chair
Professor, University Hospital of La Timone
Marseille, France
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this Roundtable event? Would you describe the mission of the European Commission’s Beating Cancer Plan?
Response: Europe’s Beating Cancer Plan is the first, comprehensive EU strategy on cancer, aimed at tackling the disease through all key stages: prevention; early detection; diagnosis and treatment; and quality of life of cancer patients and survivors. The Plan also aims to create opportunities to improve cancer care through research and innovative projects, such as artificial intelligence, and to promote equal access to knowledge and treatments in cancer care across Europe.
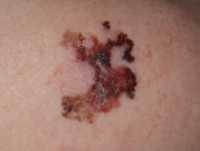
The EADV seeks to create a bridge between the EU health policy agenda and scientific research, by engaging with policymakers, patient organisations and other stakeholders to support a patient centric-approach; tackling melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC) at all stages of the pathway, from prevention to follow-up care.
Through our Roundtable event, the EADV brought together these key stakeholders to evaluate the effectiveness of the EBCP on preventing both melanoma and NMSC, as well as identify joint recommendations that step-up measures towards this goal.
Professor Marie-Aleth Richard
EADV Communications Committee Chair
Professor, University Hospital of La Timone
Marseille, France
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this Roundtable event? Would you describe the mission of the European Commission’s Beating Cancer Plan?
Response: Europe’s Beating Cancer Plan is the first, comprehensive EU strategy on cancer, aimed at tackling the disease through all key stages: prevention; early detection; diagnosis and treatment; and quality of life of cancer patients and survivors. The Plan also aims to create opportunities to improve cancer care through research and innovative projects, such as artificial intelligence, and to promote equal access to knowledge and treatments in cancer care across Europe.
The EADV seeks to create a bridge between the EU health policy agenda and scientific research, by engaging with policymakers, patient organisations and other stakeholders to support a patient centric-approach; tackling melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers (NMSC) at all stages of the pathway, from prevention to follow-up care.
Through our Roundtable event, the EADV brought together these key stakeholders to evaluate the effectiveness of the EBCP on preventing both melanoma and NMSC, as well as identify joint recommendations that step-up measures towards this goal. 


