Author Interviews, Dermatology, NEJM / 28.04.2021
Psoriasis: Monoclonal Antibody Bimekizumab vs Secukinumab: Faster, More Complete Clearing
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Prof. Kristian Reich, MD, PhD
Professor for Translational Research in Inflammatory Skin Diseases
Institute for Health Services Research in Dermatology and Nursing
University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
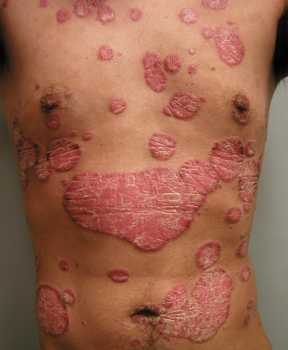
Response: Complete skin clearance is an important treatment goal for patients with psoriasis and is closely associated with treatment satisfaction and improved quality of life. However, it remains an unmet need for many patients.
The interleukin (IL)-17 isoforms IL-17A and IL-17F play central roles in psoriasis pathophysiology and are overexpressed in psoriatic tissues. Existing biologic therapies, such as secukinumab, inhibit IL-17A only. However, increasing evidence indicates that IL-17F contributes independently to the pathobiology of plaque psoriasis, and that blocking both IL-17A and IL-17F may lead to more complete suppression of inflammation and superior clinical outcomes, compared with blocking IL‑17A alone.
Bimekizumab is a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody that has been designed to selectively inhibit IL-17F in addition to IL-17A.
(more…)