
05 Mar AI-Deep Learning Interpreted Lung Cancer Biopsies As Well As Pathologists
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:

Dr. Hassanpour
Saeed Hassanpour, PhD
Assistant Professor
Departments of Biomedical Data Science,
Computer Science, and Epidemiology
Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth
Lebanon, NH 03756
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Lung cancer is the deadliest cancer for both men and women in the western world. The most common form, lung adenocarcinoma, requires pathologist’s visual examination of resection slides to determine grade and treatment. However, this is a hard and tedious task. Using new technologies in artificial intelligence and deep learning, we trained a deep neural network to classify lung adenocarcinoma subtypes on histopathology slides and found that it performed on par with three practicing pathologists.
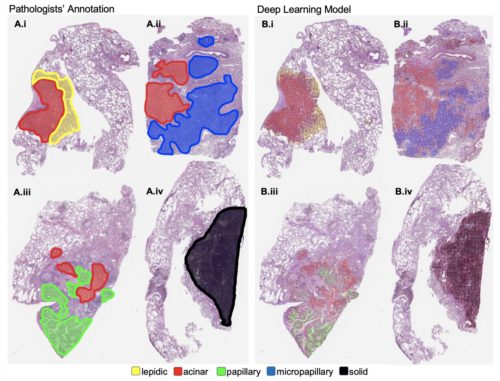
Visualization on sample whole-slide images of the lung cancer histologic patterns identified by pathologists compared to those detected by a new machine learning model developed by researchers at Dartmouth’s Norris Cotton Cancer Center. The team rendered the image by overlaying color-coded dots on patches based on decisions generated by their computer model. A subjective qualitative assessment by pathologist annotators confirmed that the patterns detected on each slide are on target.
CREDIT
Hassanpour Lab, Dartmouth’s Norris Cotton Cancer Center
MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report?
Response: Artificial intelligence (AI) has improved dramatically in recent years and shown great promise in the field of medical image analysis. Our study demonstrates that AI can achieve high performance on a challenging image classification task and has the potential to greatly assist clinicians in lung cancer diagnosis. Our approach can be applied to any histopathology image analysis task and we have released our code publicly at https://github.com/BMIRDS/deepslide.
MedicalResearch.com: What recommendations do you have for future research as a result of this work?
Response: We are planning to test our deep learning model in a clinical setting to validate its ability to improve the diagnoses of pathologists. In addition, we are currently applying our method to other histopathology image analysis tasks such as esophageal and colorectal cancer classification.
No disclosures
Citation:
Jason W. Wei, Laura J. Tafe, Yevgeniy A. Linnik, Louis J. Vaickus, Naofumi Tomita, Saeed Hassanpour. Pathologist-level classification of histologic patterns on resected lung adenocarcinoma slides with deep neural networks. Scientific Reports, 2019; 9 (1) DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40041-7
[wysija_form id=”3″]
[last-modified]
The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on March 5, 2019 by Marie Benz MD FAAD
