15 Jul Dermatology Researchers Test First Topical Gel for Treatment of Molluscum Contagiosum
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr Dilip Kachhawa, MD
Department of Skin & Venereal Disease
Dr Sampurnanand Medical College
Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?

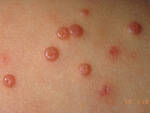
Molluscum DermNet image
Response: Molluscum Contagiosum (MC) is an infection caused by molluscipoxvirus. It is difficult to study since the virus only survives in human skin, and therefore there isn’t an animal or cell model to study potential treatments. Molluscum lesions appear as raised, domed shaped skin-colored lesions and can occur anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, neck, arms, legs, and abdomen. Sometimes there are few lesions, but clusters of several lesions can appear. Children are the most likely to get molluscum, and the virus is highly contagious, transmitted by direct contact with infected skin or contaminated objects, like towels, linens and toys. Scratching can cause autoinoculation which is when a person reinfects themself.
MC is very common, impacting an estimated 6 million adults and mostly children in the US each year. In 2010, there was an estimated 122 million cases worldwide. It occurs primarily in humid and warm climates, and transmission via swimming pools and bathtubs may be possible. Therefore, molluscum is often called “water warts.”
Many physicians may take a “watch and wait” approach since the virus may clear on its own. However, it can take months to up to 5 years for some to experience complete clearance, In the meantime, the person is still highly contagious and may spread the virus to others, particularly children. Lesions can be bothersome, causing itching and sometimes a secondary infection. There is also a psychosocial component. In a recent study, 1 in 10 children with molluscum experienced a major quality of life issue.
Berdazimer Gel, 10.3% is a potential first-in-class topical controlled-nitric oxide releasing medication containing Berdazimer (sodium), a new chemical entity, and the active ingredient in berdazimer gel 10.3%. The mechanism of action of berdazimer in the treatment of molluscum is unknown, but in vitro lab studies show that the nitric oxide, released when berdazimer is combined with a hydrogel, may impede viral replication and perhaps help body’s natural immune response against molluscum.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: Berdazimer Sodium in Molluscum Patients with Lesions (B-SIMPLE) 4 was a multi-center, vehicle controlled double blind phase 3 randomized clinical trial conducted in 55 clinics in the United States to understand if berdazimer, 10.3% had a statistically positive impact on clearance of MC. The primary efficacy endpoint was complete clearance of all MC lesions at week 12. Safety and tolerability measures included adverse event frequency and severity and assessment of local skin reactions and scarring.
B-SIMPLE 4 enrolled the largest number of molluscum patients ever studied in a Phase 3 interventional trial, 891 with 444 receiving berdazimer and 447 receiving vehicle. The data showed that Novan’s potential first-in-class topical controlled-nitric oxide releasing medication was significantly more effective than vehicle in completely clearing lesions associated with the highly contagious viral skin disease at 12 weeks. No treatment-related serious adverse events were reported.
The multicenter, vehicle-controlled, double blind study included patients 6 months or older with 3 to 70 raised MC lesions. Patients were randomized to treatment with berdazimer gel, 10.3% or vehicle gel, applied as a thin layer to all lesions once daily for 12 weeks. At the end of 12 weeks, 32.4% of patients in the berdazimer group achieved complete clearance of lesions as compared to 19.7% in the vehicle group.
MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report?
Response: Molluscum Contagiosum is highly contagious and can be transmitted via skin-to-skin contact with someone who has molluscum bumps on their skin or contaminated objects. For this reason, children with molluscum may be unable to participate in sports (wrestling), sleepovers, swimming and other social activities for fear of spreading the virus to others. The lesions may become irritated and red and be unsightly, creating anxiety. In addition, if the MC lesions are scratched or rubbed, they can spread to other parts of the body and even become infected with bacteria. Healing the lesions more quickly reduces both the risk of infection and further spread of MC to others.
MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report? Is it necessary to treat them?
Response: These results demonstrate the promise of berdazimer gel, 10.3% as a potential first and only prescription medication for molluscum. If approved, berdazimer gel 10.3% could offer molluscum patients and their caregivers the ease of at-home self-application. Since so many patients go untreated due to limited options, this will be a breakthrough in molluscum treatment.
MedicalResearch.com: Is there anything else you would like to add?
Response: These results demonstrate the promise of berdazimer gel, 10.3% as a potential first and only prescription medication for molluscum. If approved, berdazimer gel 10.3% could offer molluscum patients and their caregivers the ease of at-home self-application. Since so many patients go untreated due to limited options, this will be a breakthrough in molluscum treatment.
Citation:
A randomized controlled pilot study of autoinoculation versus 35% trichloroacetic acid for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum
Kachhawa, Dilip et al.
Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Volume 0, Issue 0
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2022.02.066
[wysija_form id=”3″]
[last-modified]
The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on July 15, 2022 by Marie Benz MD FAAD
