09 Dec Understanding the Impact of Endocrine Health on Longevity
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones. These hormones control many vital body functions, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. As we age, the efficiency of this system declines, leading to various age-related diseases and conditions. Understanding how the endocrine system impacts longevity can help us develop strategies to live longer and healthier lives.
The Role of Endocrine Health in Aging
Endocrine health is integral to aging because hormones regulate processes like cell regeneration, immune function, and energy metabolism. For example, a decline in growth hormone levels is associated with decreased muscle mass and bone density, while imbalances in insulin can lead to type 2 diabetes, a condition that significantly shortens lifespan.
The Endocrine Theory of Aging
The endocrine theory of aging posits that the aging process is largely regulated by hormones, which act as messengers coordinating various physiological processes. According to this theory, as we age, the production and regulation of hormones change, leading to the deterioration of bodily functions. For instance, the decline in growth hormone and sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone are associated with muscle wasting, reduced bone density, and increased fat accumulation—all hallmarks of aging. By understanding and potentially manipulating these hormonal changes, it might be possible to slow down or mitigate some aspects of aging.
Key Hormones Responsible for Longevity
While many hormones influence health, certain ones are particularly important for longevity. Understanding their roles can help us maintain hormonal balance as we age.
Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
Human Growth Hormone (HGH) is crucial for growth, cell repair, and metabolism. It helps maintain, build, and repair healthy tissue in the brain and other organs, boosting overall vitality. However, HGH levels decline significantly after the age of 30, contributing to signs of aging like muscle loss, increased body fat, and decreased energy levels. For those considering HGH therapy, it’s important to buy HGH only with a prescription and under strict medical supervision, as there are risks such as joint pain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Insulin
Insulin regulates blood glucose levels, ensuring cells receive the energy they need to function. However, insulin resistance, where cells don’t respond properly to insulin, becomes more common with age and is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Chronic hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can damage tissues and organs, accelerating aging and increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Managing insulin levels through diet, exercise, and, if necessary, medication, is essential for maintaining health and longevity.
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are vital for regulating metabolism. These hormones influence how the body uses energy, produces heat, and consumes oxygen. Hypothyroidism, or low thyroid function, becomes more prevalent with age and is associated with symptoms like weight gain, fatigue, and depression. Proper thyroid function is essential for keeping the body’s metabolic processes running smoothly, thereby supporting longevity.
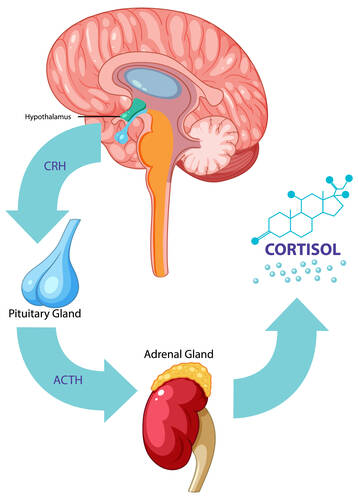
Cortisol
Cortisol, produced by the adrenal glands, helps the body respond to stress. While acute cortisol release is necessary for survival, chronic high levels of cortisol due to prolonged stress can lead to harmful effects, including impaired cognitive performance, suppressed thyroid function, and increased abdominal fat, which is linked to a higher risk of heart disease. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep can help keep cortisol levels in check, promoting better health and longevity.
New Discoveries in Endocrine Health and Aging
The relationship between endocrine health and longevity is an area of active research. Recent discoveries are shedding light on how we might manipulate the endocrine system to extend lifespan and improve quality of life.
Advances in Hormonal Regulation
Recent studies have revealed the complex interplay between hormones and aging. For instance, research on calorie restriction, which has been shown to extend lifespan in various species, suggests that it works in part by reducing insulin and IGF-1 (Insulin-like Growth Factor 1) levels, thereby slowing down cellular aging processes. This discovery highlights the potential of dietary interventions in managing hormone levels to promote longevity.
The Potential of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) for aging-related hormonal decline is another area of significant interest. For example, estrogen replacement therapy in postmenopausal women has been shown to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and potentially improve cognitive function. However, the long-term use of HRT carries risks, including an increased chance of breast cancer and cardiovascular issues. The decision to use HRT should be based on a careful assessment of benefits versus risks, tailored to the individual’s health profile.
Emerging Therapies Targeting Hormonal Pathways
Innovative treatments are being developed to target specific hormonal pathways associated with aging. One promising area is the use of senolytics drugs that selectively eliminate senescent cells, which are cells that no longer divide and contribute to aging. Senescent cells secrete harmful substances that can disrupt normal tissue function, and their removal has been shown to improve health and extend lifespan in animal models. Additionally, researchers are exploring the role of the gut microbiome in regulating hormones and aging, with potential implications for new therapies that could optimize endocrine health and promote longevity.
Conclusion
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in determining longevity by regulating key bodily functions. Maintaining hormonal balance through lifestyle choices and, where appropriate, medical interventions, can help mitigate the effects of aging and enhance both lifespan and healthspan. As scientific research continues to advance our understanding of the endocrine system’s role in aging, new therapies and strategies may emerge that could significantly impact how we age and how long we live.
—————————————
The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition.
Do not take growth hormones, endocrine products, peptides or any supplements unless under your health care provider’s supervision
Some links are sponsored. Products above are not warranted or endorsed.
Do not purchase or take growth hormones, endocrine products, peptides or any supplements unless under your health care provider’s supervision.
Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.
Last Updated on December 9, 2024 by Marie Benz MD FAAD
