Abbvie, Author Interviews, Dermatology, Immunotherapy / 11.03.2019
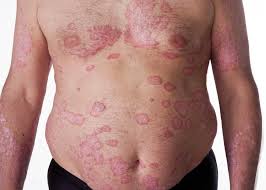
Risankizumab for Moderate to Severe Psoriasis: High Rates of Durable Clearance Through One Year
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Anne Robinson, Pharm D
Executive Scientific Director
AbbVie
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for the risankizumab data presented at the American Academy of Dermatology 2019 Annual Meeting?
Response: Abstracts presented by AbbVie at the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) 2019 Annual Meeting highlight additional data from the Phase 3 clinical trial program evaluating the safety and efficacy of risankizumab, an investigational interleukin-23 (IL-23) inhibitor. The registrational program for risankizumab evaluated more than 2,000 adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis across four pivotal studies. (more…)