Struggling with Addiction? Here’s Why Minority Groups Need a Special Kind of Care
Culturally Competent Nursing Care: Meeting the Needs of Diverse Patient Populations
1. Understanding Cultural Competence in Nursing
Cultural competence refers to the ability of healthcare providers to recognize and respect the cultural differences that influence how patients experience illness, access care, and respond to treatment. For nurses, cultural competence involves a combination of knowledge, attitudes, and skills that enable them to deliver care that is sensitive to the cultural preferences, beliefs, and values of their patients. To be culturally competent, nurses must be aware of their own biases and assumptions and continuously educate themselves about the diverse cultural backgrounds of the patients they serve. This awareness helps nurses avoid making assumptions based on stereotypes, allowing them to deliver individualized care that meets the specific needs of each patient. (more…)Texas A&M Studies Effect of Affordable Care Act on Uninsured Hospitalizations
ASCO24: Icahn Mt Sinai Researchers Develop Streamlined Cancer Trial Recruitment to Broaden Access to Diverse Groups
Weill Cornell Dermatologist Discusses Skin Cancer Prevention and Detection
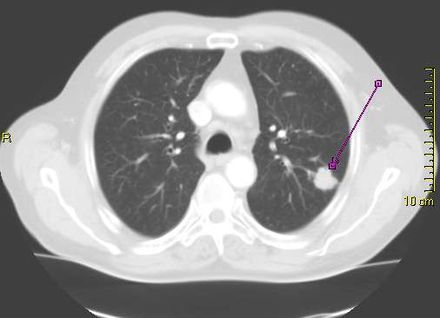
Lung Cancer: Stanford Risk-Based Model Reduces Screening Disparities
- Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States, killing about 127,000 people annually, but it can be treatable if detected early.
- Low-dose computed tomography, or CT scan, has been shown to significantly reduce the number of lung cancer deaths. But because the radiation delivered by the scans can be harmful (they use on average about 10 times the radiation of standard X-rays), only those people at relatively high risk for lung cancer should be screened. The two biggest risk factors for lung cancer are exposure to tobacco smoke and age. Current national guidelines that rely on age and smoking exposure to recommend people for lung cancer screening are disproportionally failing minority populations including African Americans, according to a new study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine.
- In 2021, the national guidelines by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued revised recommendation guidelines on lung cancer screening, lowering the start age from 55-year to 50-year and the smoking pack-year criterion from 30 to 20, compared to the 2013 USPSTF criteria. In comparison to the 2013 criteria, the new modifications have been shown to lessen racial disparities in screening eligibility between African Americans and Whites. However, potential disparities across other major racial groups in the U.S., such as Latinos, remains poorly examined.
- Meanwhile, risk prediction model assesses a person’s risk score of developing an illness, such as lung cancer.
Low Income and Minority Children Risk Impaired Cognitive Function from Environmental Hazards
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Devon Payne-Sturges, DrPH, MPH, MEngr
Associate Professor
Maryland Institute for Applied Environmental Health
School of Public Health
University of Maryland, College Park
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: My co-authors and I conducted this study to fill a knowledge gap and to inform the work of Project TENDR. No systematic or scoping review had examined both exposure disparities and the joint effects of combined exposures of environmental neurotoxicants and social disadvantage as they relate to disparities in neurodevelopmental outcomes specifically among children living in the U.S.
Our study is the first to summarize the evidence on 7 neurotoxicants that children in the U.S. are routinely exposed to and we examined both disparities in these exposures and disparities in the effects of those exposures on children’s brain development, cognition, and behavior by race, ethnicity, and economic status.
We reviewed over 200 independent studies spanning five decades from 1974 to 2022 on social disparities in exposure to 7 exemplar neurotoxic chemicals and pollutants, including chemical mixtures, and their relationship with disparities with neurodevelopmental outcomes among children in the U.S.
Alarming Rate of Attrition Among Black MD-PhD Students
Potentially Lifesaving Genetic Testing After Cancer Diagnosis Underutilized
Disparity and Diversity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Imaging and Genomics
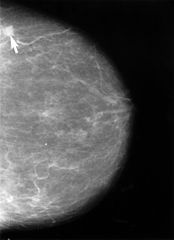
Breast Cancer Screening: One-Size-Fits-All Approach May Not be Optimal, Equitable or Fair
Fentanyl Death Rates Shoot Upwards Especially Among Black Men
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Racial and Ethnic Disparities Vary Between US States
 Hyuna Sung, PHD
Senior Principal Scientist, Cancer Surveillance Research
American Cancer Society
Kennesaw, GA 30144
Hyuna Sung, PHD
Senior Principal Scientist, Cancer Surveillance Research
American Cancer Society
Kennesaw, GA 30144
Weill Cornell Medicine Studies Racial Differences in Long COVID
ACC23: Encouraging Findings on Mortality After Acute Heart Attack
(more…)
Stanford Study Identifies Genetic Variant Linked to Alzheimer’s in African Americans
Factors Influencing COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy in Eastern Pennsylvania
New Kidney Function Equation Works Independent of Sex and Race
Overdose Deaths Among Black Women: High and Rising
Spike in Firearm Fatalities Differ Among Ethnic and Age Groups
Hair Straightening Chemicals May Increase Uterine Cancer Risk
Medical School Drop-Out Rates Highest Among Low Income Students from Marginalized Neighborhoods
Lupus Awareness Month: Award Winners Will Improve Diversity in Clinical Trial Landscape
Lupus is a rare chronic, hard-to-diagnosis autoimmune disease which disproportionately impacts women of color, particularly Black women, and the implicit...
Rural Cancer Survival Trails Urban Patients, Especially for Minorities
African American Women Face Increased Odds of Dying from Metastatic Breast Cancer
Mistreatment of Physicians in the Health Care Workplace
Racial Disparities in Rising Incidence and Mortality from Uterine Cancer
- Through our prior work, we have demonstrated that uterine cancer incidence rates have been significantly increasing in the U.S. from 2003 to 2015 and that these increases were primarily driven by rising rates of aggressive (non-endometrioid) subtypes of this cancer. We observed that rates of these aggressive cancers increased among all women and were more than twice as high among Non-Hispanic Black women compared to other racial and ethnic groups. Factors explaining these trends, as well as the disproportionately higher rates of these aggressive subtypes among non-Hispanic Black women, remain unclear, in part because risk factors are poorly understood.
- In addition to differences in incidence rates by race and ethnicity, we have also observed strong disparities in our prior studies, with Non-Hispanic Black women having substantially lower 5-year survival, regardless of subtype or stage at diagnosis, compared to other racial and ethnic populations.
- The next logical step, and the focus of the current study, was to evaluate how increases in the incidence of aggressive, non-endometrioid uterine cancer affects racial disparities and rates of death from uterine cancer.