Author Interviews, Dermatology, Pediatrics / 25.07.2020
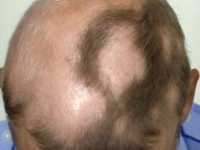
Seasonal Patterns in Pediatric Alopecia Areata
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Eunyoung Cho, Sc.D.
Associate Professor and Director of Research
Department of Dermatology
The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University.
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We are interested in whether flares of alopecia area (AA), one of the most common autoimmune diseases resulting in sudden loss of scalp and facial hair, follow seasonal patterns and whether these potential patterns are related to climate factors. We recently analyzed a set of data on pediatric AA flares, which demonstrated seasonal patterns, with the largest number of flares in the fall, finding that climate factors such as UV index were correlated with the AA flare frequency of patients in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, a geographical region with four distinct seasons. Here, we explored the seasonal patterns and contribution of climate factors in pediatric AA patients in Providence, Rhode Island, another geographical region with four distinct seasons, to test whether we can replicate our previous findings.
(more…)