Author Interviews, Cost of Health Care, JAMA, Kidney Disease, Transplantation / 01.07.2024
Brown University Study Finds No Increase in Home Dialysis or Kidney Transplantation with Government’s Pay-For-Performance Program
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Amal Trivedi, MD, MPH
Professor of Health Services, Policy & Practice
Brown University School of Public Health
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: On January 1st, 2021, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) launched the mandatory End-Stage Renal Disease Treatment Choices (ETC) Model, which randomly assigned approximately 30% of U.S. dialysis facilities and managing clinicians to financial incentives to increase the use of home dialysis and kidney transplantation. The program is set to run through 2027, with financial incentives and penalties increasing as the model progresses.
Our study sought to assess the ETC’s effect on these outcomes of interest in the first two years, as well as to examine outcome changes by race, ethnicity and socioeconomic status.
(more…)


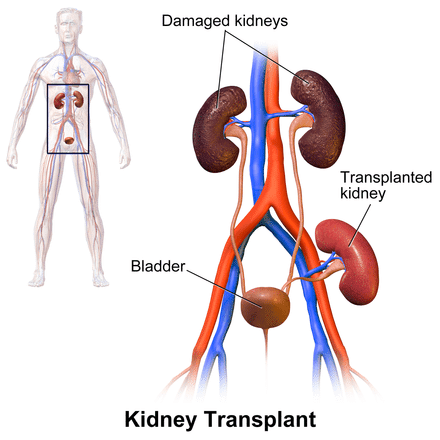






 Jim Gleason, National President of Transplant Recipients International Organization (TRIO), discusses what organ transplant patients are experiencing during the pandemic, and some tips they ought to consider to help ease some of the burden.
Mr. Gleason also discusses his role in the development of the recently released AlloCare app is in the AppStore --
Jim Gleason, National President of Transplant Recipients International Organization (TRIO), discusses what organ transplant patients are experiencing during the pandemic, and some tips they ought to consider to help ease some of the burden.
Mr. Gleason also discusses his role in the development of the recently released AlloCare app is in the AppStore -- 














 Rebecca Ivy Hartman, M.D
Instructor in Dermatology
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Boston MA 02115
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Organ transplant recipients (OTR) are at 100-fold higher risk to develop certain skin cancers compared to the general population due to immunosuppression, and thus preventing skin cancer in this population is critical.
Our study found that in a high-risk Australian OTR population, only half of patients practiced multiple measures of sun protection regularly.
However, after participating in a research study that required dermatology visits, patients were over 4-times more likely to report using multiple measures of sun protection regularly. Patients were more likely to have a positive behavioral change if they did not already undergo annual skin cancer screening prior to study participation.
Rebecca Ivy Hartman, M.D
Instructor in Dermatology
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Boston MA 02115
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Organ transplant recipients (OTR) are at 100-fold higher risk to develop certain skin cancers compared to the general population due to immunosuppression, and thus preventing skin cancer in this population is critical.
Our study found that in a high-risk Australian OTR population, only half of patients practiced multiple measures of sun protection regularly.
However, after participating in a research study that required dermatology visits, patients were over 4-times more likely to report using multiple measures of sun protection regularly. Patients were more likely to have a positive behavioral change if they did not already undergo annual skin cancer screening prior to study participation.