Author Interviews, Dermatology, Gastrointestinal Disease, JAMA / 11.07.2019
Link Between Skin Disease Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Inflammatory Bowel Disease
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Prof Ching-Chi Chi, MD, MMS, DPhil (Oxford)
Department of Dermatology
Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
Guishan Dist, Taoyuan 33305
Taiwan
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
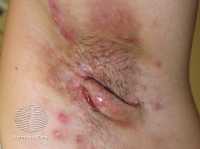
Response: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are inflammatory diseases that share common clinical manifestations, genetic susceptibility, and immunologic features. For example, both diseases have similar clinical manifestations in the skin and gut, characterized by sterile abscesses in perineal and inguinal areas, scarring, and sinus tract formation. Both diseases have been associated with an increased prevalence of spondyloarthropathy, have common risk factors (smoking and obesity), and respond well to tumor necrosis factor-inhibitors. Some studies have suggested a link between HS and IBD, but data on the association of HS and IBD remain inconsistent and unclear. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to investigate the association of hidradenitis suppurativ with IBD.
(more…)