Author Interviews, Ophthalmology / 30.07.2020
Wet AMD: Genentech’s Port Delivery System Can Allow Longer Intervals Between Ranibizumab Treatments
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Carl D. Regillo, MD, FACS
Chief, Retina Service
Wills Eye Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for the Phase III Archway study? Would you briefly explain what Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration means?
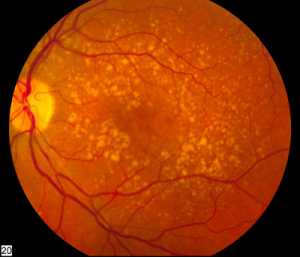
Genentech announced in late July the results from the Phase III Archway study evaluating Port Delivery System (PDS) with ranibizumab (PDS) in people living with neovascular or “wet” age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) which showed PDS enabled 98.4% of people to go six months between treatments, while achieving vision outcomes equivalent to those receiving monthly ranibizumab eye injections, a current standard of care.
AMD is a condition that affects the part of the eye that provides sharp, central vision needed for activities like reading and is a leading cause of blindness for people age 60 and over in the U.S. Neovascular AMD is an advanced form of AMD that can cause rapid and severe vision loss. Approximately 11 million people in the United States have some form of AMD and of those, about 1.1 million have nAMD.
(more…)
Carl D. Regillo, MD, FACS
Chief, Retina Service
Wills Eye Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for the Phase III Archway study? Would you briefly explain what Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration means?
Genentech announced in late July the results from the Phase III Archway study evaluating Port Delivery System (PDS) with ranibizumab (PDS) in people living with neovascular or “wet” age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) which showed PDS enabled 98.4% of people to go six months between treatments, while achieving vision outcomes equivalent to those receiving monthly ranibizumab eye injections, a current standard of care.
AMD is a condition that affects the part of the eye that provides sharp, central vision needed for activities like reading and is a leading cause of blindness for people age 60 and over in the U.S. Neovascular AMD is an advanced form of AMD that can cause rapid and severe vision loss. Approximately 11 million people in the United States have some form of AMD and of those, about 1.1 million have nAMD.
(more…)
 Carl D. Regillo, MD, FACS
Chief, Retina Service
Wills Eye Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for the Phase III Archway study? Would you briefly explain what Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration means?
Genentech announced in late July the results from the Phase III Archway study evaluating Port Delivery System (PDS) with ranibizumab (PDS) in people living with neovascular or “wet” age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) which showed PDS enabled 98.4% of people to go six months between treatments, while achieving vision outcomes equivalent to those receiving monthly ranibizumab eye injections, a current standard of care.
AMD is a condition that affects the part of the eye that provides sharp, central vision needed for activities like reading and is a leading cause of blindness for people age 60 and over in the U.S. Neovascular AMD is an advanced form of AMD that can cause rapid and severe vision loss. Approximately 11 million people in the United States have some form of AMD and of those, about 1.1 million have nAMD.
(more…)
Carl D. Regillo, MD, FACS
Chief, Retina Service
Wills Eye Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for the Phase III Archway study? Would you briefly explain what Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration means?
Genentech announced in late July the results from the Phase III Archway study evaluating Port Delivery System (PDS) with ranibizumab (PDS) in people living with neovascular or “wet” age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) which showed PDS enabled 98.4% of people to go six months between treatments, while achieving vision outcomes equivalent to those receiving monthly ranibizumab eye injections, a current standard of care.
AMD is a condition that affects the part of the eye that provides sharp, central vision needed for activities like reading and is a leading cause of blindness for people age 60 and over in the U.S. Neovascular AMD is an advanced form of AMD that can cause rapid and severe vision loss. Approximately 11 million people in the United States have some form of AMD and of those, about 1.1 million have nAMD.
(more…)