Author Interviews, Colon Cancer, Heart Disease, JAMA, Nutrition / 18.02.2021
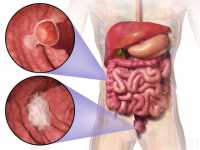
Diet Plays a Role in Colon Cancer Incidence
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Nathorn (Nui) Chaiyakunapruk PharmD, PhD
Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy
University of Utah College of Pharmacy
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Colorectal cancer is one of the cancers for which we found that the risk can be significantly reduced by modifying diet. Individual components of your diet can contribute to an overall healthy diet pattern to lower the risk of colorectal cancer or increase it. Strong scientific evidence shows that limiting red meat and alcohol consumption, eating foods containing fiber and calcium, consumption of dairy products especially yogurt can help prevent colorectal cancer. (more…)