Author Interviews, COVID -19 Coronavirus, Dermatology, Respiratory / 06.10.2021
Study Evaluates Risk of Respiratory Infections, Including COVID-19, In Psoriasis Patients on Biologics
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lara van der Schoot
MD, PhD candidate
Department of Dermatology
Radboud University Medical Center
Nijmegen, The Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
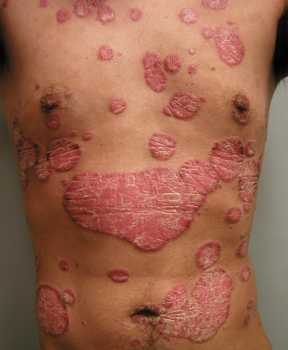
Response: Psoriasis is a chronic, immune mediated skin disease for which effective targeted biological agents have become available the past years. Inherent to their immunomodulatory mechanism of action, biologics might increase infections risk. We know from clinical trial data that respiratory tract infections are among the most common adverse events during biologic treatment, but real-world data is sparse. Regarding the risk of serious infections among biologic users, mostly defined as infections requiring hospitalization, previous studies provided different results and there is limited comparative data for the newer biologics available.
The COVID-19 pandemic turned attention to the risk of infections among biologic users, especially for respiratory tract infections, as they might relate to susceptibility for viral respiratory tract infections such as COVID-19.
In our study, the primary aim was to determine the risk of respiratory tract infections among real-world psoriasis patients treated with biologics, including the newer IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors. The secondary aim was to assess risk of serious infections in this cohort. Additionally, rates of SARS-CoV-2 infections were assessed.
(more…)






![Prof. Dr. Kristian Reich, Dermatologikum Hamburg, Hamburg 07.04.2009 | Prof. Dr. Kristian Reich, Dermatologikum Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany, 07.04.2009 | [© (c) Martin Zitzlaff, Emilienstr.78, 20259 Hamburg, Germany, Tel. +491711940261, http://www.zitzlaff.com, martin@zitzlaff.com, Postbank Hamburg BLZ 20010020 Kto.-Nr. 10204204, MwSt. 7%, Veroeffentlichung nur gegen Honorar (MFM) und Belegexemplar, mit Namensnennung]](https://medicalresearch.com/wp-content/uploads/Professor-Reich.jpg)


