MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Robert Ritch, MD, FACS, FARVO
Shelley and Steven Einhorn Distinguished Chair
Professor of Ophthalmology, Surgeon Director Emeritus
Chief, Glaucoma Services Emeritus
The New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai
New York, NY 10003
Founder, Medical Director and
Chairman, Scientific Advisory Board
The Glaucoma Foundation
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
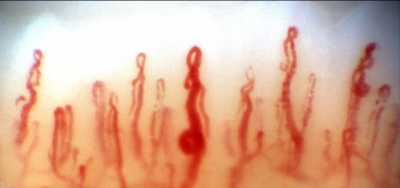
Response: Nailfold capillaroscopy (NFC), long used in rheumatology is a new approach to investigation of glaucoma.
Posterior to the nailbed and just anterior to the proximal nailfold is the cuticle, which has no structural elements visible to the naked eye. NFC is a non-invasive imaging modality that provides a highly magnified view of the capillaries at the nailfold of digits. It has also been used in ophthalmology to show morphological changes at the nailfold capillaries of POAG and XFG/XFS patients, helping to confirm the systemic nature of these diseases.
With nailfold capillaroscopy, an extensive array of capillaries can be seen greatly enlarged on a monitor screen. Capillary loops can be imaged, stored, recorded with videoscopy, and blood flow actively imaged and measured..
The first series of papers on glaucoma were written by Prof Josef Flammer’s group at the turn of the 21
st century, looking at vasospasm, blood flow in normal-tension and high-tension glaucoma, and relating ocular blood flow alterations to systemic vascular regulation and relating laser Doppler flowmetry to NFC.
Studies from Korea later associated nailbed hemorrhages and loss of nailbed capillaries to the presence of optic disc hemorrhages and investigated correlation of of heart rate variability with visual field defects and nailfold capillaroscopy.
Studies by our group began with the publication in 2015 of a paper by Pasquale et al (Nailfold Capillary Abnormalities in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma: A Multisite Study. IOVS;56:7021) using NFC video microscopy, associating dilated capillaries, avascular zones, and hemorrhages with primary open-angle glaucoma. Successive manuscripts and presentations at conferences have indicated differences between capillary loop patterns in high-tension and normal-tension POAG and exfoliation syndrome/exfoliation glaucoma.
Our goal in this paper was to compare nailfold peripheral blood flow in XFG, which had not previously been compared to control subjects using NFC. We explored the peripheral blood flow at the nailfold of patients with high-tension glaucoma, normal-tension glaucoma, exfoliation glaucoma (XFG) and compared it to control subjects further evaluate the possible difference
s between these glaucoma entities. We examined the morphology and extent of nailfold capillary loops, vascular tortuosity, blood flow, and nailfold hemorrhages.
(more…)
 Glaucoma is often called the "sneak thief of sight," and that name fits. Many folks don't know they have it until it's too late. Spotting the earliest sign of glaucoma can help save your vision and get you the care you need.
Let's explore four important symptoms to keep an eye out for and discuss why catching glaucoma early is so crucial for keeping your eyes healthy.
Please note everyone should be screened for glaucoma as well as other eye diseases including macular degeneration. Make a regularly scheduled visit to an opthamologist part of your health care routine.
Four Key Symptoms
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can lead to vision loss and are often associated with increased pressure in the eye. Here are four key symptoms to look out for as earliest sign of glaucoma:
Glaucoma is often called the "sneak thief of sight," and that name fits. Many folks don't know they have it until it's too late. Spotting the earliest sign of glaucoma can help save your vision and get you the care you need.
Let's explore four important symptoms to keep an eye out for and discuss why catching glaucoma early is so crucial for keeping your eyes healthy.
Please note everyone should be screened for glaucoma as well as other eye diseases including macular degeneration. Make a regularly scheduled visit to an opthamologist part of your health care routine.
Four Key Symptoms
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can lead to vision loss and are often associated with increased pressure in the eye. Here are four key symptoms to look out for as earliest sign of glaucoma: