Understanding How Winter Affects Your Sleep Patterns
As the winter season approaches, many people find themselves struggling with changes in their sleep patterns. The shorter days, reduced sunlight, and cooler temperatures can all have a profound effect on how well we sleep. Our internal clocks, which are regulated by sunlight and other environmental cues, are disrupted by these seasonal shifts, leading to various sleep disturbances. Understanding the impact of these changes and learning how to adjust your sleep cycle accordingly can significantly improve the quality of your rest during the colder months. The winter months are often associated with cozy blankets, warm drinks, and earlier bedtimes, but for many people, the lack of daylight can affect their sleep in ways they might not fully understand. As daylight hours shorten, our bodies produce more melatonin, a hormone that signals to our brains that it’s time to sleep. While this can be helpful in aiding sleep, it can also lead to feelings of sluggishness and an overall sense of tiredness throughout the day. For some, this change can result in trouble getting up in the morning or feeling excessively tired in the evening. (more…)
Editor’ note: Cannabis and THCA/HEMP CBD products should have an active ingredient list on the container and have a Certificate of Analysis (COA). As with any supplement, it’s important to research and consult with a professional to find the right fit for you. your use of CBD products with your health care provider. Dosing of CBD is variable, especially since it is not FDA regulated. CBD may interfere with other medications and should not be used in individuals with certain health conditions, including liver issues. CBD skin care products can be absorbed through the skin and have similar effects. Do not use Cannabis products including edibles and CBD if you are pregnant, nursing or may become pregnant. Do not use cannabis products if driving or operating difficult or dangerous machinery.
Children should not be exposed to cannabis or CBD products.
Managing stress and getting a good night’s sleep can feel like a real challenge. Whether it’s work deadlines, family responsibilities, or just life’s endless to-do list, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. And when stress piles up, sleep tends to suffer, creating a frustrating cycle that’s hard to break. "The good news is there are simple, natural ways, like using gummies for sleep, to help take back control and help your body and mind unwind.".
Why Natural Remedies?
While over-the-counter solutions or prescriptions can be helpful, they often come with side effects or the risk of dependency. Natural remedies focus on supporting your body’s ability to relax and reset, rather than masking symptoms. Plus, they’re easy to incorporate into your life and can be a great first step before exploring other options.
(more…)
Obstructive Sleep Apnea / 28.10.2024
Sleep Apnea- ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack: A Comprehensive Overview
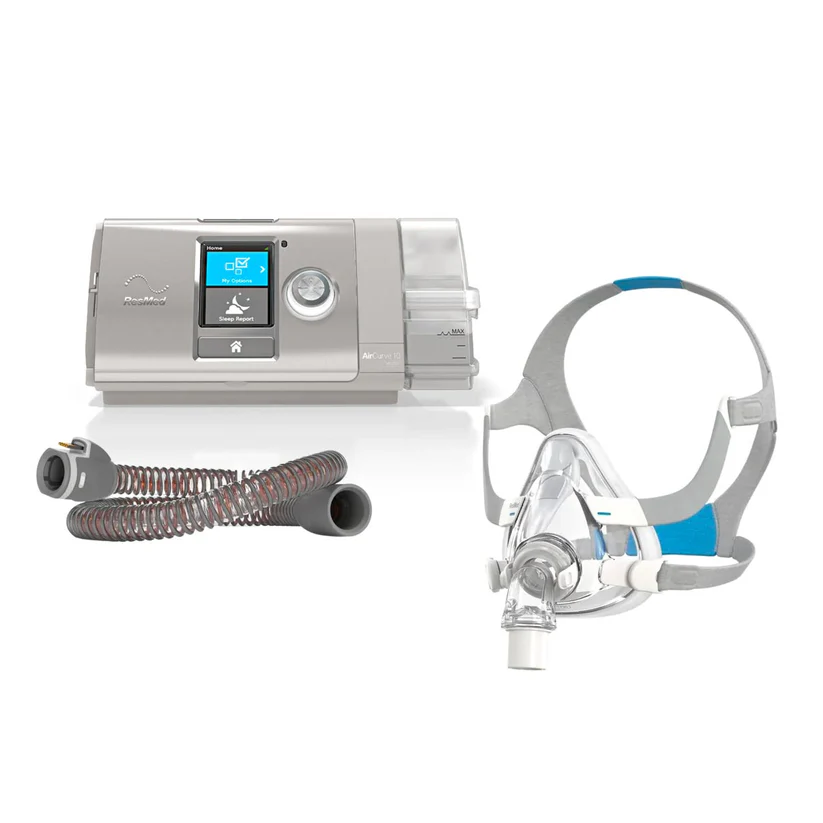
 The ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack is an essential package designed for individuals with sleep apnea who require consistent and effective therapy. This article delves into the key features benefits and frequently asked questions surrounding the ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack offering a guide to help you understand its significance in sleep apnea treatment.
What is the ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack?
The ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack is a bundle that includes three essential items designed to optimize sleep apnea therapy. The package typically consists of the ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ device a humidifier and heated tubing all aimed at improving the comfort and effectiveness of your CPAP therapy. The AutoSet feature ensures that the device automatically adjusts pressure levels based on your needs offering personalized treatment.
(more…)
The ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack is an essential package designed for individuals with sleep apnea who require consistent and effective therapy. This article delves into the key features benefits and frequently asked questions surrounding the ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack offering a guide to help you understand its significance in sleep apnea treatment.
What is the ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack?
The ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ Tri-Pack is a bundle that includes three essential items designed to optimize sleep apnea therapy. The package typically consists of the ResMed AirSense™ 10 AutoSet™ device a humidifier and heated tubing all aimed at improving the comfort and effectiveness of your CPAP therapy. The AutoSet feature ensures that the device automatically adjusts pressure levels based on your needs offering personalized treatment.
(more…)
Obstructive Sleep Apnea / 21.10.2024
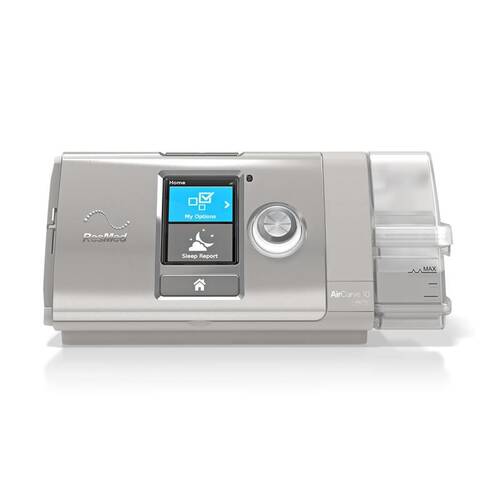
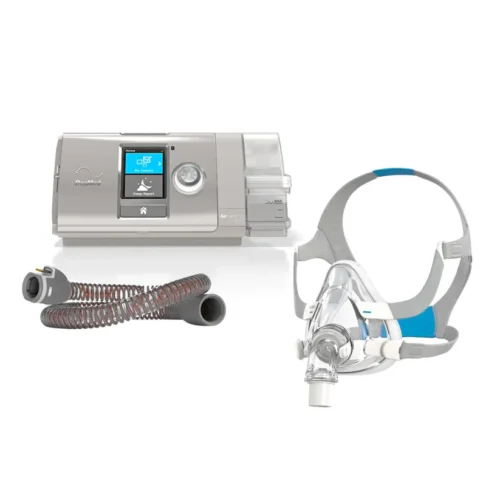
ResMed AirCurve™ 10 VAuto with HumidAir™ For Managing Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Sponsored post:
The ResMed AirCurve™ 10 VAuto with HumidAir™ is a high-performance bilevel PAP Positive Airway Pressure device for individuals with sleep apnea. This device is ideal for patients who require varying pressure support as it automatically adjusts airflow pressure based on the user’s needs. This article explores the features benefits and performance of the ResMed AirCurve™ 10 VAuto with HumidAir™ helping you understand why it stands out in treating obstructive sleep apnea.
Key Features of ResMed AirCurve™ 10 VAuto with HumidAir™
Auto-Adjusting Pressure Support The ResMed AirCurve™ 10 VAuto provides auto-adjusting pressure support to keep the airways open during sleep. This intelligent feature ensures that users receive customized therapy based on their unique respiratory patterns. Unlike fixed-pressure devices, the AirCurve™ 10 VAuto adjusts in real-time optimizing comfort and effectiveness. (more…)
Aging, Sleep Disorders / 14.10.2024
Relaxation Techniques for Better Sleep with a Quilted Blanket: Combating Anxiety in Seniors
 Photo by: RDNE Stock project
Photo by: RDNE Stock project
OBGYNE, Sleep Disorders / 30.09.2024
How to Get Sleep During Pregnancy
 Sleep deprivation is something all new parents go through, but for many women, it starts before the baby is born. As your belly is growing, the baby is kicking, and your hormone levels are fluctuating, you are very likely to experience insomnia, poor sleep quality, or nighttime awakenings. Even though there is no magic solution that can fix your problems entirely, there are some things you can do to get some good night's sleep during pregnancy:
Sleep deprivation is something all new parents go through, but for many women, it starts before the baby is born. As your belly is growing, the baby is kicking, and your hormone levels are fluctuating, you are very likely to experience insomnia, poor sleep quality, or nighttime awakenings. Even though there is no magic solution that can fix your problems entirely, there are some things you can do to get some good night's sleep during pregnancy:
Create a Soothing Bedtime Routine
Try to come up with a bedtime ritual that you can perform every night to signal your brain and your body that it is time to sleep. First, stop using screens because modern devices produce blue light that impedes your body’s production of melatonin. So instead of scrolling through your phone, consider reading a book before bedtime. Additionally, introduce some habits that can support and improve your mental health during pregnancy. For example, you can take a soothing, warm bath, sip on a cup of warm milk or a caffeine-free tea, or listen to a guided meditation. Also, you can introduce aromatherapy to your bedroom. Using a pillow spray or a diffuser can make you feel more relaxed in minutes. Finally, stick with a consistent routine that provides you with at least eight hours of sleep every night. (more…)
Sleep is an essential element of health and so people’s claims that they have more difficulty in falling asleep remain very common. Irrespective of whether this is a passing phase or an established and chronic problem, recognizing the reasons can assist individuals in seeking possible solutions. This article discusses possible sources of sleep hindrances and recommends how to fall asleep faster.
What is Difficulty in Falling Asleep?
‘Difficulty in falling asleep’ as it sounds, by definition falls under the category of sleep disturbances that can best be referred to as sleep-onset insomnia. It is the failure to fall asleep after lying down over a period that is reasonable after bed. A person's parents who have this disorder are also more likely to have this disorder. This condition can have a detrimental influence on multiple aspects of health, resulting in low energy levels, high levels of mood swings, and poor concentration during working hours.
(more…)
In our fast-paced, always-on world, sleep often takes a backseat to work, social activities, and screen time. Many people view sleep as a luxury or an inconvenience, failing to recognize its fundamental role in our overall health and success. However, the truth is that quality sleep is not just beneficial—it's essential for our physical health, mental well-being, and cognitive performance. Understanding the hidden power of sleep can be the key to unlocking your full potential and achieving lasting success in all areas of life.
The Vital Functions of Sleep
Sleep is far more than just a period of inactivity or rest. During those precious hours of slumber, our bodies and minds engage in critical processes that are essential for our survival and optimal functioning. Let's delve deeper into some of the vital functions of sleep: (more…)
Author Interviews, Science, Sleep Disorders / 18.08.2024
Deep Sleep Required to Reset Memory Neurons
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Azahara Oliva PhD
Assistant Professor
Department of Neurobiology and Behavior
Cornell University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The background is that we knew for a while now that neurons work hard to consolidate into memories each experience that we have during the day. But at the same time, it is known that sleep restore activity of our body and physiology. How was that possible? How can the neurons in our brain "work hard" during the time that we are supposed to be restoring our vitals? We found that in between their hard work, during sleep, our neurons take "breaks of activity" so our brain can build memories with precision.
(more…)
In an era where technology is rapidly transforming healthcare, Dr. Avinesh Bhar has emerged as a leading figure in the field of sleep medicine. Through his innovative platform, Sliiip.com, Dr. Bhar is revolutionizing how people with sleep issues access care. His accomplishments in telemedicine are not only groundbreaking but also essential for addressing the growing prevalence of sleep disorders.
Who is Dr. Avinesh Bhar?
Dr. Avinesh Bhar is a renowned sleep doctor dedicated to advancing the treatment and understanding of sleep disorders. With a background in sleep medicine and a passion for leveraging technology to improve patient outcomes, Dr. Bhar has made significant strides in making sleep health services more accessible and effective. (more…)
Author Interviews, Pulmonary Disease, Sleep Disorders / 21.05.2024
ATS24: Mount Sinai Study Develops Algorithm to Distinguish Central vs Obstructive Sleep Apnea
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ankit Parekh, PhD
Director of the Sleep And Circadian Analysis (SCAN) Group
Assistant Professor of Medicine
(Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine)
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Sleep apnea is associated with incident cardiovascular disease, and is a common chronic condition affecting over a billion people worldwide. In diagnosing and treating sleep apnea, it is imperative to establish the type of sleep apnea—whether it is obstructive or central sleep apnea. The differential contribution of central vs. obstructive sleep apnea toward incidental cardiovascular disease in those with significant sleep apnea has not been well studied.
Our group has developed an automated algorithm that deduces on a breath-by-breath level whether reductions in airflow are predominantly due to obstructive or central phenomena. Our algorithm uses several features that are known to be key in distinguishing the type of events and derives a probability of obstruction across each “small” (reduced amplitude) breath. The breath-by-breath probability is then used to determine whether a patient’s burden of sleep apnea is predominantly obstructive or central.
In this work, we analyzed sleep study data from The Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) cohort (N=2793) consisting of elderly men, across two visits separated on average by 6.5 years, and derived the probability of obstruction on a breath-by-breath level. The median probability of obstruction for each subject was computed and analyzed against outcomes of cardiovascular disease. We also assessed the stability of the metric in those without any prevalent cardiovascular disease. We find that median probability of obstruction was stable across the two visits, and those with any incident cardiovascular disease had a lower median probability of obstruction: patients with incident cardiovascular outcomes had a significant burden of sleep apnea that was predominantly “central” in nature.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Sleep Disorders / 12.03.2024
Insomnia Linked to Increased Risk of Multiple Chronic Conditions
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Soomi Lee, PhD
Associate Professor | Department of Human Development and Family Studies | Center for Healthy Aging
Director of STEALTH Lab: https://sites.psu.edu/stealth/
The Pennsylvania State University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Sleep quantity and quality decline with advancing age; a risk of chronic conditions also increases with age.
While previous studies report that poor sleep is a significant risk for chronic conditions, many have focused solely on a single dimension of sleep, such as duration, thereby limiting the ability to assess multiple co-occurring dimensions and their associations with chronic conditions.
This study aimed to evaluate multiple dimensions of sleep health, including regularity, satisfaction, alertness, efficiency, and duration. By analyzing data from a national sample of adults (n=3,683) collected over two time points spanning a decade, the study identified four distinct sleep health phenotypes: good sleepers, insomnia sleepers, weekend catch-up sleepers, and nappers. (more…)
Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Gastrointestinal Disease, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Technology / 18.11.2023
Brigham/MIT/WVU Scientists Develop Pill to Measure Vital Signs Without Blood Tests or Wires
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Giovanni Traverso MD PhD
Karl Van Tassel (1925) Career Development Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Koch Institute of Integrative Cancer Research
Division of Gastroenterology
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: I think its always important to acknowledge that this is a big team effort. We have the teams from MIT, Celero Systems, West Virgnia University (WVU) and Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) all working together on this. For this study, Celero prototyped the devices that we tested in pre-clinical (Swine) models and in a first-in-human study with the team at WVU.
Our lab focuses on the development of ingestible devices for drug delivery and sensing and these have informed the development of these efforts as you can see.
MedicalResearch.com: What types of vital signs are measurable in this fashion?
Response: Heart rate and respiratory rate.
(more…)
AHA Journals, Author Interviews, Heart Disease, Kidney Disease, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Sleep Disorders / 15.11.2023
AHA23: Unexpected Link Between Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Events in Kidney Disease Patients
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lead Author: Rupak Desai, MBBS
Atlanta Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Independent Researcher, Atlanta, GA,
Presenter: Vamsikalyan Borra, MD
Resident Physician, Internal Medicine
University of Texas Rio Grande Valley, Weslaco, TX
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The relationship between sleep apnea (OSA) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) is quite complex. OSA can cause hypoxia, activation of the sympathetic nervous system, and hypertension, all of which can have negative effects on kidney function. On the other hand, in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), intensifying renal replacement therapy has shown some improvement in sleep apnea severity, suggesting a bi-directional relationship between the two conditions. While there are still uncertainties, recent studies have focused on understanding the interplay between OSA and CKD.
The role of CPAP therapy, a common treatment for OSA, in relation to CKD is not yet clear. Observational studies present findings regarding the impact of CPAPs on kidney function. However, researchers are actively investigating its cardiovascular benefits and its influence on the progression of CKD.
The objective of this study is to analyze the trends in composite cardiovascular events in hospital encounters among geriatric patients with CKD, comparing those with and without obstructive sleep apnea. Additionally, we are also investigating sex and racial disparities in trends of major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) among geriatric patients with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Furthermore, we are assessing the impact of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) treatment and dependence on MACCE outcomes in OSA patients
(more…)
Aging, Author Interviews, Mental Health Research, Sleep Disorders / 02.07.2023
Regular Napping Might Protect Against Some Aging Brain Shrinkage
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Valentina Paz, M.Sc Ph.D. Student
Research and teaching assistant
Universidad de la República, UruguayHon. Research Assistant
MRC Unit for Lifelong Health & Ageing
Department of Population Science & Experimental Medicine
Institute of Cardiovascular Science
University College London MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: Prior research indicates that napping can enhance performance on specific cognitive tasks. However, some authors argue that the advantages derived from napping may vary between individuals who frequently have a nap and those who never naps. Furthermore, it remains to be seen whether habitual daytime napping has a positive or negative impact on cognition and the association between napping and brain volume is not well characterized. Therefore, our study aimed to examine whether the association between genetic liability to daytime napping, cognitive function, and brain volumes might be causal using a technic called Mendelian randomization and the UK Biobank.
(more…)
MRC Unit for Lifelong Health & Ageing
Department of Population Science & Experimental Medicine
Institute of Cardiovascular Science
University College London MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: Prior research indicates that napping can enhance performance on specific cognitive tasks. However, some authors argue that the advantages derived from napping may vary between individuals who frequently have a nap and those who never naps. Furthermore, it remains to be seen whether habitual daytime napping has a positive or negative impact on cognition and the association between napping and brain volume is not well characterized. Therefore, our study aimed to examine whether the association between genetic liability to daytime napping, cognitive function, and brain volumes might be causal using a technic called Mendelian randomization and the UK Biobank.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Lifestyle & Health, Mental Health Research, Sleep Disorders / 30.05.2023
Early Birds More Likely to Be Conscientious, Religious and Satisfied with Life
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Joanna Gorgol
PhD Student
University of Warsaw
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: People differ in the time when they prefer to wake up and fall asleep: some people prefer going to bed and waking up early, while others prefer later hours. Most of the population is somewhere between them. Research indicates that being a morning person is related to reporting higher satisfaction with life and conscientiousness. Studies also show the associations between being religious and having higher life satisfaction and conscientiousness. It seems that religiosity might mediate the relationship between morningness and higher life satisfaction. To better understand these associations we conducted two questionnaire-based studies of Polish adults, one with 500 participants and the other with 728 participants. All participants completed questionnaires measuring their chronotype, satisfaction with life, personality traits, and religiosity
(more…)
Author Interviews, Health Care Systems, Sleep Disorders / 16.02.2023
McMaster Study Finds Musical Alarms Can Decrease Stress For Hospital Workers
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Michael R. Schutz, Ph.D.
Professor of Music Cognition/Percussion at McMaster University
Founding director of the MAPLE Lab and
Core member of the McMaster Institute for Music and the Mind.
Prof. Schutz is also a professional musician and directs McMaster’s percussion ensemble.
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospitals around the world are filled with devices generating a
constant stream of tones conveying information to medical staff.
overburdened healthcare professionals, and contributes to burnout in
medical staff. The Emergency Care Research Institute (ECRI) regularly
includes problems with auditory alarms in their list of "Top 10 Health
Technology Hazards" and they are so problematic an FDA survey
implicated them in hundreds of patient deaths.
While there is currently a lot of interest in how to improve alarm
management protocols, this study is different in that it looks at
improving the quality of the alarm sounds themselves. For historical
reasons many default to simplistic "beeps" which are generally
annoying. While annoying is useful for critical alarms requiring
immediate action, the vast majority of these messages are merely
intended to update medical staff of changes (i.e. blood pressure is
rising) or indicate other situations that do not require immediate
action. Unfortunately, many machines use the same simplistic and
annoying "beeps" regardless of whether the messages are urgent or
non-urgent. This constant flood of annoying beeps negatively affects
both patients (extending recovery time due to interrupted rest) and
staff (who can develop "alarm fatigue" from the constant cacophony).
(more…)
constant stream of tones conveying information to medical staff.
overburdened healthcare professionals, and contributes to burnout in
medical staff. The Emergency Care Research Institute (ECRI) regularly
includes problems with auditory alarms in their list of "Top 10 Health
Technology Hazards" and they are so problematic an FDA survey
implicated them in hundreds of patient deaths.
While there is currently a lot of interest in how to improve alarm
management protocols, this study is different in that it looks at
improving the quality of the alarm sounds themselves. For historical
reasons many default to simplistic "beeps" which are generally
annoying. While annoying is useful for critical alarms requiring
immediate action, the vast majority of these messages are merely
intended to update medical staff of changes (i.e. blood pressure is
rising) or indicate other situations that do not require immediate
action. Unfortunately, many machines use the same simplistic and
annoying "beeps" regardless of whether the messages are urgent or
non-urgent. This constant flood of annoying beeps negatively affects
both patients (extending recovery time due to interrupted rest) and
staff (who can develop "alarm fatigue" from the constant cacophony).
(more…)
Author Interviews, Health Care Systems, JAMA, Sleep Disorders, Yale / 18.01.2023
Early Morning Blood Draws in Hospitalized Patients Come with Benefits and Drawbacks
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
César Caraballo-Cordovez, MD
Postdoctoral Associate
Yale/YNHH Center for Outcomes Research and Evaluation (CORE)
New Haven, CT 06511
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Our group has been interested in how patients’ experience during hospitalization impacts their recovery and their health for a while. In 2013, Dr. Harlan Krumholz (senior author of the current study) identified that patients who were recently hospitalized experienced a period of generalized risk for myriad adverse health events, a condition that he named ‘post-hospital syndrome’. One of the possible explanations for this observation is that the stress from being hospitalized negatively impacts patients’ health during their stay in the hospital and after being discharged. The stress in a hospital may come from different sources–including sleep deprivation.
Sleep is fundamental for recovery, and there are many challenges for patients to have adequate sleep while being hospitalized. Among the many sources of sleep interruption are early morning blood draws. Blood draws are often performed in the early morning in order to have recent lab tests results available during morning medical rounds. However, this common practice may disrupt patients’ recovery by interrupting their sleep. We were interested in determining to what extent blood draws contribute to early morning sleep disruptions and whether there has been recent progress in reducing them.
We used data from Yale New Haven Hospital from 2016 to 2019 and found that nearly 4 in 10 of total daily blood draws were collected between 4:00am and 7:00am–a proportion that was persistently high over the 3 years we studied. Importantly, we found that this occurred across patients with different sociodemographic characteristics, including older individuals who are at highest risk of adverse health events from sleep deprivation.
(more…)
Author Interviews, CHEST, Pulmonary Disease, Sleep Disorders / 12.12.2022
Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Associated with Increased Risk of Hospitalization with Pneumonia
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Pamela L. Lutsey, PhD, MPH
Minneapolis, Minnesota
Professor, Division of Epidemiology and Community Health
School of Public Health
University of Minnesota
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Emerging evidence suggests that patients with OSA may be more susceptible to developing pneumonia. Mechanistically, OSA causes upper airway sensory dysfunction and excessive microaspirations, which can result in significant increases in bacterial organisms in the airway leading to upper airway and laryngeal inflammation. Systemically, healthy sleep is believed to play an important role in the body’s inflammation control and immune system regulation. Despite this evidence, few studies have prospectively evaluated whether individuals with OSA are at elevated risk of being hospitalized with pneumonia, respiratory infection, or any infection
(more…)
Author Interviews, JAMA, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Sleep Disorders, USPSTF / 23.11.2022
USPSTF: More Evidence Needed Before Routine Screening of Adults Can Be Recommended
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Martha Kubik, Ph.D., R.N.
Professor, School of Nursing
College of Health and Human Services
George Mason University
Member, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Obstructive sleep apnea is a health condition in which part or all of a person’s airway gets blocked during sleep, causing their breathing to stop and restart many times. Untreated sleep apnea is associated with heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. However, there is currently very limited evidence on screening people who don’t have signs or symptoms like snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, JAMA, Nutrition, Occupational Health, Sleep Disorders / 09.11.2022
Americans’ Sleep Patterns Differ on Work and Free Days
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Zhilei Shan, MD, PhD
Postdoctoral fellow on Nutritional Epidemiology
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Unhealthy sleep behaviors and sleep disturbances are associated with higher risk of multiple diseases and mortality. The current profiles of sleep habits and disturbances, particularly the differences between workdays and free days, are unknown in the contemporary US.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: In this nationally representative cross-sectional analysis with 9004 adults aged 20 years or older, differences in sleep patterns between workdays and free days were observed. The mean sleep duration was 7.59 hours on workdays and 8.24 hours on free days (difference, 0.65 hour). The mean sleep and wake times were at 11:02 PM and 6:41 AM, respectively, on workdays and 11:25 PM and 7:41 AM, respectively, on free days (differences, 0.23 hour for sleep time and 1.00 hour for wake time). With regard to sleep disturbances, 30.5% of adults experienced 1 hour or more of sleep debt,46.5% experienced 1 hour or more of social jet lag, 29.8% had trouble sleeping, and 27.2% experienced daytime sleepiness.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Schizophrenia, Sleep Disorders / 18.10.2022
Brain Waves Form Unique “Fingerprint” For Each Person
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Michael J. Prerau, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor of Medicine,
Faculty, Division of Sleep Medicine
Harvard Medical School
Associate Neuroscientist and
Director of the Neurophysiological Signal Processing Core
Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders
Department of Medicine Brigham and Women's Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The brain is highly active during sleep, which makes it an important, natural way to study neurological health and disease. Scientists typically study brain activity during sleep using the electroencephalogram, or EEG, which measures brainwaves at the scalp. Starting in the mid 1930s, the sleep EEG was first studied by looking at the traces of brainwaves drawn on a paper tape by a machine. Many important features of sleep are still based on what people almost a century ago could most easily observe in the complex waveform traces. Even the latest machine learning and signal processing algorithms for detecting sleep waveforms are judged against their ability to recreate human observation.
In this study, the researchers asked: What can we learn if we expand our notion of sleep brainwaves beyond what was historically easy to identify by eye?
(more…)
Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Melatonin, Pediatrics, Sleep Disorders / 28.09.2022
Myths About Teenager Sleep Needs Are Common
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Rebecca Robbins, Ph.D.
Instructor in Medicine
Associate Scientist, Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders
Investigator, Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders
Departments of Medicine and Neurology
Brigham and Women's Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Teens face myriad challenges to sleep, ranging from biological factors, including a preference for later bedtimes and increased need for sleep, to social factors, including social pressures and increased academic workloads, all limiting teenagers in their ability to keep a healthy sleep schedule.
In a nationally representative sample, we explored the prevalence of another potential barrier to sleep among teens, which are a set of beliefs that are held in the population, yet are actual counter to scientific principles regarding sleep and circadian rhythms.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Diabetes, Sleep Disorders, Weight Research / 26.09.2022
Night Owls May Have Increased Risk of Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Steven K. Malin, PhD, FACSM (he/him)
Associate Professor
Department of Kinesiology and Health | School of Arts and Sciences
Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Nutrition | Robert Wood Johnson Medical School
Institute of Translational Medicine and Science
New Brunswick, NJ 08901
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Type 2 diabetes is a condition where blood glucose (sugar) is elevated in the blood. This can be problematic as it leads to blood vessel damage and the promotion of cardiovascular disease. Nearly 30 million people in the U.S. have type 2 diabetes, making it a major public health issue. The cause is not entirely clear, but many, including our team view insulin resistance as a central culprit.
Insulin resistance is when the body does not respond well to the hormone insulin. Insulin is vital because it promotes glucose uptake into tissues, like skeletal muscle. Two reasons that are often used to explain the development of insulin resistance include: poor diet (e.g. high sugar and/or high fat coupled with excess calories) and a lack of physical activity. However, more recently, a lack of sleep has been raised as another critical behavioral factor contributing to insulin resistance. Thus, targeting a healthy diet, activity and sleep pattern is thought to prevent the transition from health to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
(more…)
Abuse and Neglect, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Melatonin, Sleep Disorders / 24.05.2022
Harvard Study Finds Melatonin May Improve Daytime Sleep in Shift Workers and Travelers
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Jeanne Duffy, MBA, PhD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders
Harvard Medical School
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Aging is associated with changes in sleep timing, quality and duration, and even older adults without chronic medical problems have shorter and more disrupted sleep than young adults. Many prescription sleep aids increase the risk of nighttime falls, have
adverse effects on next‐day cognition, and are associated with increased mortality, and so are not recommended for long-term use in older adults. In previous studies, we and others have shown that melatonin, a hormone secreted at night, increases sleep duration in young adults but only when administered during the day when endogenous melatonin levels are low. We wanted to explore whether melatonin could improve the sleep of healthy adults and whether, like young adults, its impact depends on when during the day the person is trying to sleep.
(more…)
Author Interviews, BMJ, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Education, Health Care Systems, Sleep Disorders / 20.05.2022
Medical Residents: Extended Work Hours Linked to Medical Errors and Patient Harm
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr Matthew D Weaver M.P.H., Ph.D.
Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders
Departments of Medicine and Neurology
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Boston, Massachusetts
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The name “resident” stems from the historical practice of resident-physicians residing in hospitals as part of their training. Even after that practice abated, it was common for resident physicians to work 36 consecutive hours followed by 12 or fewer hours of rest. In 1989, the state of New York restricted resident physicians to work no more than 24 consecutive hours and no more than 80 hours per week as part of collective intervention to improve patient safety. The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) then followed in 2003 by limiting work hours to an average of 80 per week over a month and no more than 30 consecutive hours of work.
Evidence accumulated demonstrating an association between shifts lasting ≥24 hours and adverse resident and patient safety. As a result, the Institute of Medicine convened a review and report on the issue, ultimately concluding that no resident should work more than 16 consecutive hours without sleep. This recommendation, combined with evidence following the 2003 rules, led the ACGME to issue new rules in 2011 that limited first-year resident physicians to work no more than 16 consecutive hours.
Our study compares resident-reported patient safety outcomes before and after this 2011 policy change.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Genetic Research, Sleep Disorders, UCSF / 20.03.2022
Quality, Not Length, is What Matters When It Comes to Sleep
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ying-Hui Fu, PhD
Professor, Neurology
Weill Institute for Neurosciences
UCSF
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Most people are aware that a lack of sleep is associated with all sorts of health issues. However, familial natural short sleeper (FNSS) individuals sleep 4-6.5 hours a night most of their live and stay healthy. We set out to determine whether natural short sleep mutations can offer protection from various diseases. We chose Alzheimer as an example to start.
(more…)
Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Sleep Disorders / 18.03.2022
Excessive Daytime Naps May Be a Sign of Early Cognitive Decline
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Peng Li, Ph.D.
Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School
Research Director, Medical Biodynamics Program (MBP)
Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders
Associate Physiologist, Brigham and Women's Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: People commonly see increased sleep during daytime in older adults. In people with Alzheimer’s disease or dementia, daytime drowsiness or sleepiness are even more common. Prior studies have showed protective effects of short naps on cognitive performance and alertness acutely, while also there are studies that have demonstrated more daytime naps are associated with faster cognitive decline in the long-term. We sought to investigate whether daytime napping behavior predicts future development of Alzheimer’s dementia. And we noted that there had been no studies to date that have documented the longitudinal profile of daytime napping during late life objectively.
(more…)
Aging, Author Interviews, Sleep Disorders / 15.03.2022
Sleep Apnea Accelerates Aging – CPAP Therapy May Help Slow it Down
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Rene Cortese, PhD
Assistant Professor
Department of Child Health – Child Health Research Institute
Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Women’s Health
School of Medicine
Core Faculty - MU Institute for Data Science and Informatics
University of Missouri
Columbia, MO 65212
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) affects 22 million people in the U.S. and is linked to a higher risk of hypertension, heart attacks, stroke, diabetes, and many other chronic conditions.
We have found that untreated OSA also accelerates the biological aging process, and that appropriate treatment can slow or possibly reverse the trend. Age acceleration testing involves a blood test that analyzes DNA and uses an algorithm to measure a person’s biological age. The phenomenon of a person’s biological age surpassing their chronological age is called “epigenetic age acceleration” and is linked to overall mortality and to chronic diseases.
(more…)