Endocrinology, Hormone Therapy / 20.01.2025
The Hormonal Connection: Unraveling Cardiovascular Health Beyond the Basics
Editor’s note: There are short and long term risks of hormone therapy, including oxytocin.
Hormone and supplements products may not be FDA tested or approved.
All hormone therapy should be taken only under the direction of an experienced endocrinologist or medical provider.
Please also remember that photos, text and illustrations on websites do not guarantee results.
Cardiovascular health is often viewed through a lens dominated by risk factors like cholesterol, blood pressure, and lifestyle choices. While these are crucial, emerging research highlights a deeper interplay between hormones and heart health. Among these, the role of oxytocin, often called the "love hormone," provides intriguing insights. However, the scope extends far beyond oxytocin, encompassing a web of hormonal influences that shape cardiovascular resilience and risk. This article explores these connections, emphasizing a more holistic understanding of heart health.
The Hormonal Web and the Heart
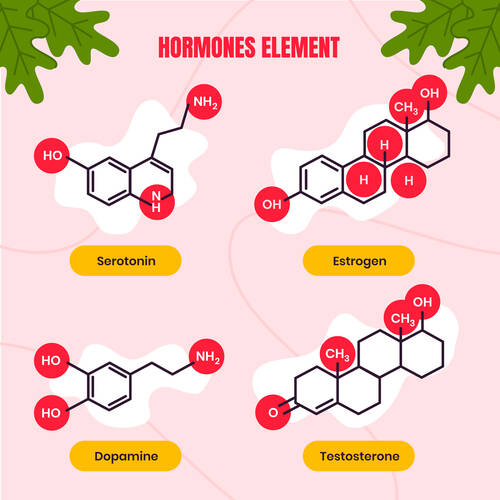
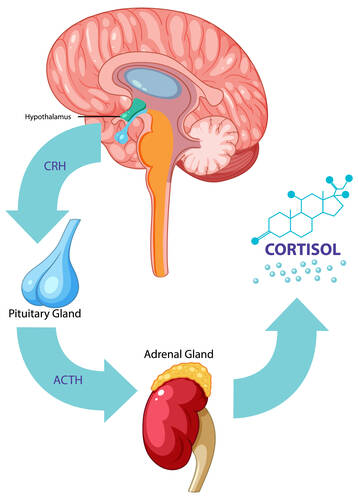
The cardiovascular system is heavily influenced by hormones, which act as chemical messengers coordinating various bodily functions. Key players include adrenaline, cortisol, estrogen, testosterone, and oxytocin. These hormones regulate heart rate, blood vessel dilation, inflammation, and cholesterol metabolism. While acute hormonal changes prepare the body for immediate challenges, chronic imbalances can wreak havoc on cardiovascular health. For instance, prolonged exposure to elevated cortisol levels from stress contributes to hypertension, arterial damage, and increased risk of heart attack. Understanding these hormonal dynamics is essential for developing targeted interventions that not only treat symptoms but also address the root causes of cardiovascular issues.Cortisol: The Stress-Induced Culprit
Cortisol, often dubbed the "stress hormone," is a double-edged sword. In short bursts, it helps manage acute stress by increasing heart rate and energy availability. However, chronic stress leads to consistently elevated cortisol levels, which can:- Increase blood pressure by promoting sodium retention.
- Elevate blood sugar levels, contributing to insulin resistance and diabetes—both risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
- Encourage visceral fat accumulation, which exacerbates inflammation and atherosclerosis.