Annals Internal Medicine, Author Interviews, Heart Disease, Infections, Opiods / 04.12.2018
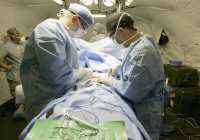
Marked Increase in Infected Heart Valves Due to Injected Opioids
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Asher Schranz, MD
Division of Infectious Disease
Department of Medicine
UNC School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The opioid crisis has led to several major infectious diseases concerns, including HIV and Hepatitis C.
Drug use-associated infective endocarditis (DUA-IE) is a less commonly discussed consequence of the opioid epidemic. DUA-IE is an infection of one or more heart valves that occurs from injecting drugs. It can be a severe, life-threatening infection and requires a long course of intravenous antibiotics as well as, in some cases, open heart surgery to replace an infected heart valve. Several studies over the past few years have shown that DUA-IE has been increasing.
Our study examined hospital discharges in North Carolina statewide from 2007 to 2017. We sought to update trends in DUA-IE and describe how much heart valve surgery was being performed for DUA-IE. We also aimed to report the demographics of persons who are undergoing heart valve surgery for DUA-IE and the charges, lengths of stay and outcomes of these hospitalizations. (more…)






 Yingxi (Cimo) Chen, MD, MPH, PhD
Postdoctoral Fellow
Radiation Epidemiology Branch, DCEG, NCI, NIH
Rockville MD 20850
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Death rates from drug overdose have more than doubled in the US in the 21st century. Similar increases in drug overdose deaths have been reported in other high-income countries but few studies have compared rates across countries.
Yingxi (Cimo) Chen, MD, MPH, PhD
Postdoctoral Fellow
Radiation Epidemiology Branch, DCEG, NCI, NIH
Rockville MD 20850
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Death rates from drug overdose have more than doubled in the US in the 21st century. Similar increases in drug overdose deaths have been reported in other high-income countries but few studies have compared rates across countries.