Risks and Complications Associated With Anterior Cervical Discectomy
 While anterior cervical discectomy surgery has become a widely accepted and frequently performed procedure to relieve spinal cord or nerve root compression, it is not without potential risks and complications. These can range from common surgical risks, such as infection, to more procedure-specific complications like nerve damage, dural tears, and the possibility of recurrent disc herniation. As there is a critical need for increased awareness and understanding of these challenges, it is essential to engage in a thorough exploration of the potential outcomes and their management tactics.
While anterior cervical discectomy surgery has become a widely accepted and frequently performed procedure to relieve spinal cord or nerve root compression, it is not without potential risks and complications. These can range from common surgical risks, such as infection, to more procedure-specific complications like nerve damage, dural tears, and the possibility of recurrent disc herniation. As there is a critical need for increased awareness and understanding of these challenges, it is essential to engage in a thorough exploration of the potential outcomes and their management tactics.
Understanding Anterior Cervical Discectomy
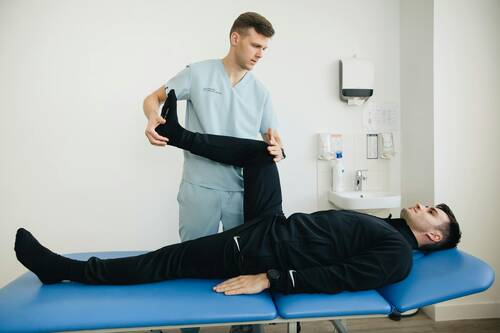
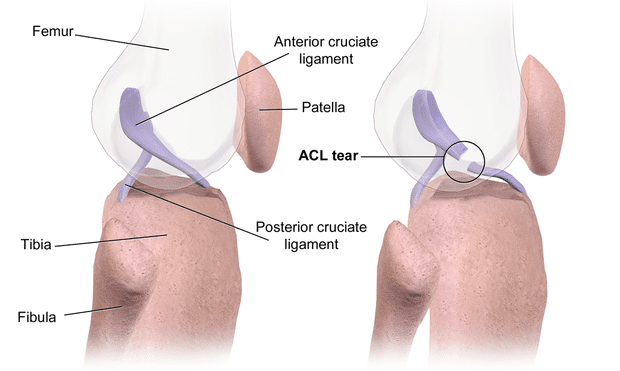
The anterior cervical discectomy is a surgical procedure that warrants comprehension due to its complex nature. This surgical technique involves the removal of an intervertebral disc or a portion of this disc from the neck area, specifically in the anterior cervical spine. It is typically performed to alleviate spinal cord or nerve root pressure, leading to considerable pain relief and functional improvement. The procedure is often paired with a fusion to stabilize the spine. The recovery timeline varies for each individual depending upon factors like age, overall health status, and the severity of the disc problem. However, the immediate postoperative recovery period typically lasts for a few hours to a few days, during which time patients are closely monitored. Subsequent recovery, involving physical therapy and gradual return to normal activities, can stretch from several weeks to a few months. Though the anterior cervical discectomy is generally regarded as a safe and effective procedure, it is not devoid of risks. Potential complications include infection, nerve damage, difficulties swallowing or speaking, and issues related to the graft or hardware used in fusion. The understanding of these risks is paramount for patients undergoing this procedure. (more…)The Role of Minimally Invasive Techniques in Modern Spine Surgery
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) has become a game changer in orthopedic surgery, offering patients safer and less painful options for treating spinal issues. Dr. Brent Felix, a leading orthopedic spine surgeon, is at the forefront of this movement, advocating for these innovative techniques that provide multiple benefits over traditional methods.
What Is Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery?
Minimally invasive spine surgery, or MISS, is a technique that allows surgeons to address spine conditions with much smaller incisions compared to traditional surgery. Rather than making large cuts to access the spine, Dr. Felix and his team use special instruments and imaging tools to perform surgery through small incisions. These tools include tiny cameras or endoscopes, which provide a clear view of the spine without the need for large openings.
(more…)The moon boot's purpose is to relieve the pressure on the injured foot, which means your other foot and leg...
Long-Term Outcomes For Patients With Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis affects millions of people and its symptoms can range in severity, with some people not even knowing they...
- Neck Pain and Stiffness
Advancements in Scoliosis Surgery: Minimally Invasive Techniques and Patient Outcomes
Understanding Minimally Invasive Scoliosis Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) for scoliosis marks a shift from traditional open surgery to methods that involve smaller incisions and less disruption to the body’s tissue. Surgeons use specialized tools and technology to perform precision surgery with less physical impact, leading to faster recovery and less post-surgery discomfort. (more…)When to Consider Joint Replacement: Key Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
1. Persistent Pain That Won’t Quit
Pain is your body's way of sending you a message. But what happens when the message never seems to stop? If you’re dealing with joint pain that’s constant or regularly interrupts your daily activities, it might be time to think about looking into self pay joint replacement so you can get the expert help you need as soon as possible. Pain that keeps you awake at night, doesn’t respond well to medication, or is present even when resting are all red flags. The purpose of joint replacement isn’t just to eliminate pain; it’s about reclaiming your everyday life. When over-the-counter pain relievers, physical therapy, or other treatments aren’t cutting it anymore, it could be time to consult with a specialist. (more…)Orthopedic Treatment
Modern orthopedic care encompasses a wide range of surgical and non-surgical interventions tailored to specific conditions. From minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures to complex joint replacements, orthopedic surgeons employ advanced techniques to address musculoskeletal problems. For less severe cases, non-surgical options such as medications, injections, and physical therapy may be sufficient. Facilities like Modern Orthopaedics offer comprehensive orthopedic care, combining surgical expertise with rehabilitation services to provide patients with a seamless treatment journey. (more…)Effective Treatments for Spine Problems
Don't hesitate to schedule a consultation with a qualified healthcare professional like an orthopedist specializing in spine care to discuss...
8 Ways to Keep Your Spine Healthy and Happy
1. Practice Good Posture
Good posture is the foundation of a healthy spine. When you maintain proper alignment, you reduce strain on your back muscles and spine. Whether you are sitting, standing, or sleeping, being mindful of your posture can make a significant difference. When sitting, keep your feet flat on the floor, your knees at a right angle, and your back straight. Use a chair that supports the natural curve of your spine. If you spend long hours at a desk, consider using an ergonomic chair that offers proper lumbar support. Standing with good posture involves keeping your shoulders back, your head level, and your weight evenly distributed on both feet. Avoid slouching or leaning to one side. When sleeping, choose a mattress and pillows that keep your spine aligned, whether you sleep on your back, side, or stomach. Maintaining good posture not only helps your spine but also improves your overall appearance and confidence.Knee Strengthening And Rehabilitation Exercises for MMA Fighters
What Knee Health Means for MMA Fighters
 The knees are equally essential for us all — athlete or not. It’s the single most important joint for basic mobility. But, for MMA practitioners, it means much more than that. Due to the dynamic nature of the sport, the knees go through immense strain during training and fights. From kicking, takedowns, and submission defense, the knees do the heavy lifting for it all. To make matters worse, a “leg kick” to the knee can sometimes be enough to cause a fracture then and there.
With all that in mind, it makes sense that ligament tears, strains, and knee sprains aren’t uncommon in this sport. Problems usually stem from insufficient rest or overuse, conditioning, poor technique, or just bad luck (for example if you’re fighting Justin Gaethje, the meanest leg-kicker).
Your best bet against these risk factors is to build and maintain optimal knee health all year round. Have a proactive approach by incorporating knee rehab and strengthening exercises. Even if your knees aren’t injured, they can still be inflamed or overworked, so some rehabilitation movements could go a long way.
(more…)
The knees are equally essential for us all — athlete or not. It’s the single most important joint for basic mobility. But, for MMA practitioners, it means much more than that. Due to the dynamic nature of the sport, the knees go through immense strain during training and fights. From kicking, takedowns, and submission defense, the knees do the heavy lifting for it all. To make matters worse, a “leg kick” to the knee can sometimes be enough to cause a fracture then and there.
With all that in mind, it makes sense that ligament tears, strains, and knee sprains aren’t uncommon in this sport. Problems usually stem from insufficient rest or overuse, conditioning, poor technique, or just bad luck (for example if you’re fighting Justin Gaethje, the meanest leg-kicker).
Your best bet against these risk factors is to build and maintain optimal knee health all year round. Have a proactive approach by incorporating knee rehab and strengthening exercises. Even if your knees aren’t injured, they can still be inflamed or overworked, so some rehabilitation movements could go a long way.
(more…)Rutgers Study Finds Marked Increase in Fractures in Nursing Home Patients Started on Blood Pressure Meds
 Imagine life without the freedom of movement. A simple task like climbing stairs or walking could become a daunting challenge. Unfortunately, this reality faces millions of Americans due to knee pain.
Classic Rehabilitation reports that approximately 100 million Americans endure chronic pain, with knee pain emerging as the second most prevalent source. This statistic indicates that one-third of the American population encounters knee discomfort at some stage in their lives. But fear not. Here's where the power of staying agile comes in.
In this article, we'll discuss the key techniques that can significantly enhance knee health and mobility. By incorporating these techniques, you can prevent future issues and keep your knees feeling strong and supported for years.
(more…)
Imagine life without the freedom of movement. A simple task like climbing stairs or walking could become a daunting challenge. Unfortunately, this reality faces millions of Americans due to knee pain.
Classic Rehabilitation reports that approximately 100 million Americans endure chronic pain, with knee pain emerging as the second most prevalent source. This statistic indicates that one-third of the American population encounters knee discomfort at some stage in their lives. But fear not. Here's where the power of staying agile comes in.
In this article, we'll discuss the key techniques that can significantly enhance knee health and mobility. By incorporating these techniques, you can prevent future issues and keep your knees feeling strong and supported for years.
(more…)AAOS: Patients on Semaglutide Did Better After Total Hip Replacement Surgery
Dog Walking Sends Thousands to Emergency Rooms Each Year
Higher HDL-C levels Associated With Increased Fracture Risk
Risk of Hip Fractures Greater in Vegetarians
Study Finds Promising Effects of Jarlsberg® Cheese on Bone and Metabolic Markers
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Stig Larsen PhD Professor Emeritus Controlled Clinical Research Methodology and Statistics Norwegian University of Life Sciences Oslo, Norway
MedicalResearch.com:? What are the main findings?
Response: Osteoporosis is a major problem among elderly and malnourished people. Calcium, Vitamin D and Vitamin K are beneficial for bone health. Vitamin D stimulates calcium absorption and studies have shown that poor Vitamin K status intake is linked to low bone mass. Osteocalcin (OC) is a protein hormone found in the blood in activated and inactivated form. The activated form of Osteocalcin (cOC) binds calcium to bone tissue and plays an important role in regulating the metabolism. In addition, low levels of cOC are associated with insulin resistance, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. It is desirable to have largest possible uOC, and vitamin K2 central in this process. The most important vitamin K2 variants in Jarlsberg® are the long-chain MK-7, -8, -9 and -9(4H), where lactic acid bacteria produce the first three, while MK-9(4H) is produced by Propionibacterium freudenreichii. The latter bacterium also produces the substance "1,4-dihydroxy-2- naphthoic acid" (DHNA), which has previously been shown to increase bone density in experimental mice. Two previous studies related to Jarlsberg® intake have been published:
- The first study showed that cOC in the blood increased with increasing Jarlsberg® dose up to a daily intake of 57 grams of Jarlsberg®. Even more startling was that the total OC (tOC) level increased significantly, and that triglycerides and cholesterol were significantly reduced.1
- The second study reproduced the findings from the first study and demonstrated additionally that the Jarlsberg dose of 57g/day could be reduced to 45 grams after 6 weeks without reducing the achieved level of tOC and vitamin K2.2
The BMJ-study3: The central variables measured in this study were the serum bone turnover markers (BTM); tOC and cOC, procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (PINP) and serum cross-linked C- telopeptide type I collagen (CTX). Additionally, Vitamin K2 and Vitamin K status, serum calcium and serum magnesium were recorded together with the development in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipids and protein turnover. The participants in the study were randomly divided into two groups. One group of 41 healthy volunteer women of childbearing age ate 57 grams of Jarlsberg® per day and the other group of 25 women ate 50 grams of Camembert for 6 weeks. The Camembert was manufactured with a starting culture not producing Vitamin K2. The fat, protein, and energy content of the daily consumption of Jarlsberg® and Camembert is approximately the same. After 6 weeks, Camembert was replaced with 57 grams of Jarlsberg® per day for another 6 weeks. (more…)