Author Interviews, Dermatology / 05.04.2021
Mechanism of Horrible Itching of Liver Disease Identified in Superficial Skin Cells
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Wolfgang Liedtke, M.D., Ph.D.
Professor (tenured) of Neurology, Anesthesiology and Neurobiology
Attending Physician, Duke Neurology Clinics for Headache, Head-Pain and Trigeminal Sensory Disorders
Attending Physician, Duke Clinics for Innovative Pain Therapy at Brier Creek (Dept of Anesthesiology)
Duke University School of Medicine, Center for Translational Neuroscience
Durham NC 27710 Since April 2021 Chair of Neurology Global Development Scientific Council Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Tarrytown NY 10591 MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: There are systemic diseases that are characterized by intense itching, yet without inflammation of the skin and not associated with allergic inflammation. For example and importantly, liver disease with non-functional secretion of bile (cholestatic liver disease, most common primary biliary cholangitis, an autoimmune disease), but also chronic end-stage renal disease (also certain lymphomas and pruritic psoriasis where the itch is whole-body, not only restricted to diseased skin). We thought that these diseases might be great starting points to better understand itch because there is no inflamed skin and no allergies. Thus, there must be some systemic factor that causes itch, and we were intent on discovering such factors, and with them, molecular mechanisms how they cause itch. For cholestatic liver disease, one of the best candidates to fit this profile has been lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), since the pioneering discoveries of Andreas Kremer, one of our co-authors. My research laboratory at Duke has been rooted in my discovery of TRPV4 ion channels 20 years ago, out of the Friedman Lab at The Rockefeller University in NYC. Over the years, with my colleague Yong Chen out of my lab, now leading his own independent research operation, we focused on the role of TRPV4 ion channels in skin. 5 years ago Yong and I published a paper that provided some evidence for TRPV4 in skin perhaps playing a role in itch. Working with phospholipids, we made the serendipitous discovery that lysophosphatidyl choline (LPC) is a more potent itch-inducing lipid molecule than LPA. Of note, LPC is the metabolic precursor of LPA. We then found that LPA does not depend on TRPV4 to elicit itch. The more robust itch evoked by LPC was significantly reduced when we knocked down TRPV4 in skin keratinocytes. Itch was NOT affected when TRPV4 was deleted from sensory nerve cells that innervate the skin. In terms of background, my long-term goal has been to elucidate how innervating peripheral nerve cell and innervated organ, such as skin, talk to one another so that the sensation that is felt is regulated or modulated, e.g how can skin influence itch or pain, how can joint cells influence pain. That became the exciting bedrock of our study, and we took it from there, 5 years of hard work with collaborations spanning the globe, and a final stretch of exhausting work during the pandemic. (more…)
Attending Physician, Duke Neurology Clinics for Headache, Head-Pain and Trigeminal Sensory Disorders
Attending Physician, Duke Clinics for Innovative Pain Therapy at Brier Creek (Dept of Anesthesiology)
Duke University School of Medicine, Center for Translational Neuroscience
Durham NC 27710 Since April 2021 Chair of Neurology Global Development Scientific Council Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Tarrytown NY 10591 MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: There are systemic diseases that are characterized by intense itching, yet without inflammation of the skin and not associated with allergic inflammation. For example and importantly, liver disease with non-functional secretion of bile (cholestatic liver disease, most common primary biliary cholangitis, an autoimmune disease), but also chronic end-stage renal disease (also certain lymphomas and pruritic psoriasis where the itch is whole-body, not only restricted to diseased skin). We thought that these diseases might be great starting points to better understand itch because there is no inflamed skin and no allergies. Thus, there must be some systemic factor that causes itch, and we were intent on discovering such factors, and with them, molecular mechanisms how they cause itch. For cholestatic liver disease, one of the best candidates to fit this profile has been lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), since the pioneering discoveries of Andreas Kremer, one of our co-authors. My research laboratory at Duke has been rooted in my discovery of TRPV4 ion channels 20 years ago, out of the Friedman Lab at The Rockefeller University in NYC. Over the years, with my colleague Yong Chen out of my lab, now leading his own independent research operation, we focused on the role of TRPV4 ion channels in skin. 5 years ago Yong and I published a paper that provided some evidence for TRPV4 in skin perhaps playing a role in itch. Working with phospholipids, we made the serendipitous discovery that lysophosphatidyl choline (LPC) is a more potent itch-inducing lipid molecule than LPA. Of note, LPC is the metabolic precursor of LPA. We then found that LPA does not depend on TRPV4 to elicit itch. The more robust itch evoked by LPC was significantly reduced when we knocked down TRPV4 in skin keratinocytes. Itch was NOT affected when TRPV4 was deleted from sensory nerve cells that innervate the skin. In terms of background, my long-term goal has been to elucidate how innervating peripheral nerve cell and innervated organ, such as skin, talk to one another so that the sensation that is felt is regulated or modulated, e.g how can skin influence itch or pain, how can joint cells influence pain. That became the exciting bedrock of our study, and we took it from there, 5 years of hard work with collaborations spanning the globe, and a final stretch of exhausting work during the pandemic. (more…)











![MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Selin Tokez, PhD Student Department of Dermatology Erasmus MC, Rotterdam MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is the second most common skin cancer worldwide with still increasing incidence rates. Given these high incidence rates together with the associated health costs and possibility of fatal progression, it is extremely important to have accurate and complete data on the epidemiology of this disease. Nevertheless, national cancer registries in many countries do not routinely record cSCC cases and therefore currently known numbers are mainly based on incomplete data sources. Additionally, if cSCC cases are registered, this usually only concerns the first cSCC per patient while we know that, contrary to many other malignant neoplasms, patients may develop numerous cSCCs over time. MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings? Response: In the present study, we analyzed Dutch nationwide data comprising about 145,000 patients with a first invasive cSCC diagnosis between the years 1989 and 2017. We found that the incidence rates of a first cSCC per patient almost tripled in male patients and increased about fivefold in female patients in this 30-year time period. Also, we had data on all cSCCs per patient for the year 2017 and could therefore compare this with the data on only the first cSCC per patient: incidence rates increased by 58% for men and 35% for women when multiple cSCCs were considered. In absolute numbers, this resulted in an increase of 45% in cSCC diagnoses in 2017. Lastly, we extended our analyses by predicting future cSCC incidence rates up to 2027. Given that no substantially effective measures are undertaken in the near future, current cSCC incidence rates will increase with 23% in males and 29% in females in the next decade. MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report? Response: We could summarize our main message in two points: while people generally know that cSCC is a very common disease with increasing incidence rates, it is not taken into account that these numbers are often based on incomplete data registries and that the real numbers are even higher. In this paper, we provided these numbers for a period of 30 years based on highly accurate data from the Netherlands Cancer Registry. On top of that, as a second main finding, we showed that the real burden caused by cSCC is approximately 50% higher (taken males and females together) when all cSCC diagnoses in 1 year are registered instead of only the first tumor per patient. Together with our prediction analyses that showed an on average 26% further increase for the coming decade, this will have enormous implications for the dermato-oncological health care planning and cost management. Our results urgently call for revision of skin cancer health policies to be able to cope with this rising burden of cSCC management. Ultimately, primary prevention will remain the key strategy to halt the increasing trend in cSCC incidence and the occurrence of multiple cSCCs per patient, which we hope to further stimulate with our paper as well. MedicalResearch.com: What recommendations do you have for future research as a result of this work? Response: As we had data on multiple cSCCs for only one year, we would suggest to perform trend analyses for multiple cSCCs per patient as well when a longer follow-up duration has been reached. Furthermore, it would be very relevant to identify high-risk cSCCs or patients at risk for multiple cSCCs in order to be able to establish efficient follow-up regimens and take these high risk groups into account when revising skin cancer health policies. MedicalResearch.com: Is there anything else you would like to add? Response: The authors of this study have no conflicts of interest that are relevant to this article. Citation: Tokez S, Hollestein L, Louwman M, Nijsten T, Wakkee M. Incidence of Multiple vs First Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma on a Nationwide Scale and Estimation of Future Incidences of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Dermatol. Published online October 28, 2020. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.3677 [subscribe] Last Modified: [last-modified] The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.](https://medicalresearch.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/squamous-cell-cancer-dermnetnz-image.jpg)







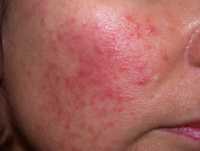
![MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Dr Herman Anne Service de Dermatologie Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc Avenue Hippocrate, 10 1200 Bruxelle MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Response: In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, several cases of acro-located lesions (on foot or hands) suggestive of chilblains have been reported and were possibly related to COVID-19. We wanted to determine if chilblains, observed in many patients recently referred to our department, are indicative of COVID-19. MedicalResearch.com: Would you briefly explain what is meant by chilblains? Response: Chilblains are frequent cold induced inflammatory lesions. Chilblains are typically seen in winter and occur after repeated exposure to cold temperatures. Clinical presentation includes erythema and swelling on toes and/or digits followed by red-purple macules or patches. However, given the large number of patients affected, and the exceptionally high outdoor temperatures for the spring season over the past month and at the time of case-observation, cold-exposure seemed unlikely. These lesions were, therefore, suspected to be associated with COVID-19. However, to date, no study has proven a pathological link between these lesions and COVID-19. MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings? Response: In our series of 31 patients who recently developed chilblains, negative nasopharyngeal swabs and the absence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 blood immunoglobulin (Ig)M and IgG antibodies in all patients included in your study suggested that these patients had not been infected with COVID-19. These lesions appeared not to be directly related to COVID-19. MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report? Response: One hypothesis points to an indirect consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic due to imposed community containment and lockdown measures. Indeed, all patients in this study had either been working from home or were home-schooled since the beginning of containment measures in Belgium (March 11, 2020) or were temporarily unemployed. As a result of containment measures, the majority (64.5%) of patients reported a decrease in their physical activity and significantly more time spent in sedentary positions in front of screens. Most of the patients declared that they remained barefoot or in socks most of the day. All these lifestyle changes can be considered as risk factors for developing chilblains. Therefore, it seems plausible that containment, through its collateral effects, may induce chilblains. Interestingly also, the mean BMI of the patients included was relatively low, suggesting that thin people may be more at risk of developing chilblains. MedicalResearch.com: What recommendations do you have for future research as a result of this work? Response: During the current pandemic, several reports have suggested a possible link between cutaneous manifestations including aural lesions such as chilblains, and COVID-19, however, only few patients were tested for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR and no serologic tests were performed. Therefore, reliable testings (RT-PCR and serologic testing) are essential to confirm a potential association with COVID-19. Citation: Herman A, Peeters C, Verroken A, et al. Evaluation of Chilblains as a Manifestation of the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Dermatol. Published online June 25, 2020. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2368 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/2767774 [subscribe] Last Modified: [last-modified] The information on MedicalResearch.com is provided for educational purposes only, and is in no way intended to diagnose, cure, or treat any medical or other condition. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health and ask your doctor any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. In addition to all other limitations and disclaimers in this agreement, service provider and its third party providers disclaim any liability or loss in connection with the content provided on this website.](https://medicalresearch.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/chilblain-example-dermnet-nz.jpg)