Author Interviews, Dermatology, JAMA, Salt-Sodium / 12.06.2024
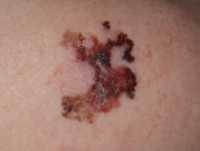
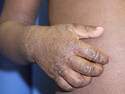
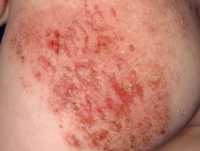
UCSF Study Finds Salt Intake May Be Associated with Eczema Severity
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Katrina Abuabara, MD, MA, MSCE
Associate Professor of Dermatology, UCSF
Associate Adjunct Professor of Epidemiology
UC Berkeley School of Public Health
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) has become increasingly common over recent decades, especially in industrialized countries, suggesting that environmental or lifestyle factors like diet could impact rates of disease. It is well established that sodium, consumed primarily in the form of salt, increases the risk of hypertension and heart disease through pro-inflammatory mechanisms. The role of sodium on other chronic inflammatory conditions like eczema has been less well-studied.
(more…)