Author Interviews, Heart Disease, Lancet, Mayo Clinic, Technology / 02.08.2019
AI-Trained EKG Can Detect New or Impending Atrial Fibrillation
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Paul Friedman, M.D.
Professor of Medicine
Norman Blane & Billie Jean Harty Chair
Mayo Clinic Department of Cardiovascular Medicine
Honoring Robert L. Frye, M.D.
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
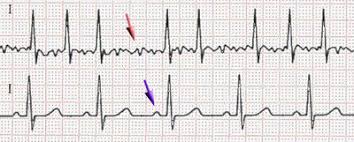
Response: Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heart rhythm that is often intermittent and asymptomatic. It is estimated to affect 2.7–6.1 million people in the United States, and is associated with increased risk of stroke, heart failure and mortality. It is difficult to detect and often goes undiagnosed. After an unexplained stroke, it is important to accurately detect atrial fibrillation so that patients with it are given anticoagulation treatment to reduce the risk of recurring stroke, and other patients (who may be harmed by this treatment) are not. Currently, detection in this situation requires monitoring for weeks to years, sometimes with an implanted device, potentially leaving patients at risk of recurrent stroke as current methods do not always accurately detect atrial fibrillation, or take too long.
We hypothesized that we could train a neural network to identify the subtle findings present in a standard 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) acquired during normal sinus rhythm that are due to structural changes associated with a history of (or impending) atrial fibrillation. Such an AI enhanced ECG (AI ECG) would be inexpensive, widely available, noninvasive, performed in 10 seconds, and immensely useful following embolic stroke of unknown source to guide therapy. To test this hypothesis, we trained, validated, and tested a deep convolutional neural network using a large cohort of patients from the Mayo Clinic Digital Data Vault.
(more…)