Author Interviews, Medical Imaging / 05.12.2024
AI-Enhanced Routine Abdominal CT Scans Detected Cardiovascular Disease Risk
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Miriam A. Bredella, MD, MBA
Bernard and Irene Schwartz Professor of Radiology & Vice Chair for Strategy
Associate Dean for Translational Science
Director, Clinical and Translational Science Institute
NYU Grossman School of Medicine
NYU Langone Health
Translational Research Building 743
New York, NY 10016
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
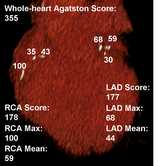
Response: We perform >80 million CTs every year in the US, and there is a lot of information on these CTs that is not used and “thrown away.” Opportunistic imaging or opportunistic screening with the help of AI takes advantage of this information and automatically detects and quantifies vascular calcification, bone mineral density, abdominal fat or muscle mass. In our study, we wanted to detect whether calcification of the abdominal aorta, quantified using AI, could predict coronary artery calcification and major cardiovascular events (e.g. myocardial infarction, cardiac revascularization, stroke, or death).
(more…)










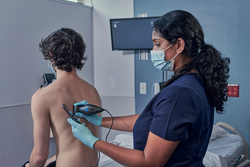
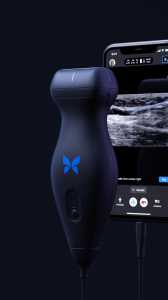 Response: Point-of-care ultrasound is one of the most significant advances in bedside patient care, and its use is expanding across nearly all fields of medicine. In order to best prepare medical students for residency and beyond, it is imperative to begin POCUS training as early as possible. At the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, we introduced POCUS education over a decade ago and have expanded it since then.
By providing each student with a Butterfly iQ device, we can augment our curriculum significantly. In addition to our robust pre-clinical sessions, now we will expand into the clinical years highlighting the utility of POCUS with actual patients.
This gift was made possible by the incredible generosity of Dr. Ronald Salvitti, MD ’63.
Response: Point-of-care ultrasound is one of the most significant advances in bedside patient care, and its use is expanding across nearly all fields of medicine. In order to best prepare medical students for residency and beyond, it is imperative to begin POCUS training as early as possible. At the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, we introduced POCUS education over a decade ago and have expanded it since then.
By providing each student with a Butterfly iQ device, we can augment our curriculum significantly. In addition to our robust pre-clinical sessions, now we will expand into the clinical years highlighting the utility of POCUS with actual patients.
This gift was made possible by the incredible generosity of Dr. Ronald Salvitti, MD ’63.