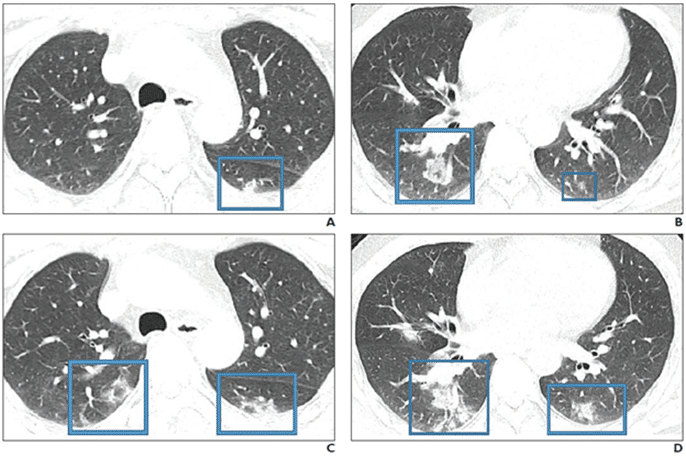
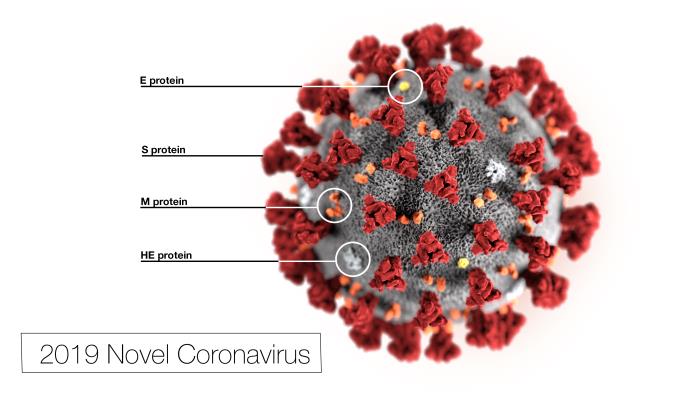
Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Coronavirus in Wuhan, China
Life Expectancy Increasing for Older, but Not Younger, Chinese with Diabetes
Significant PReP Gap Remains Among MSM in EU and Central Asia
How Do Painful Rituals Affect Psychological Wellbeing?
A Look At The State of Healthcare In Top Nations

Refugees at Higher Risk of Psychosis and Mental Illness
Children Living with Non-Citizen Parents May Lose Health Care Under New Rules
Bat Borne Nipah Virus Transmitted by Human Secretions
Little Consistency Among Leading Nations Regarding Drug Safety Warnings
TRAP: Traffic Related Air Pollution Linked to Millions of Pediatric Asthma Cases Worldwide
Ebola Fight Hampered by Misinformation and Mistrust
Melanoma Rates Stable in Australia but Rising in US
Venezuela: Rapid Rise in Infant Mortality Linked to Health Care System Collapse
 Ms Jenny García, PhD candidate
Institut National d’Études Démographiques INED
Institut de Démographie de l'université Paris 1 Panthéon Sorbonne IDUP
Paris, France
Prof Gerardo Correa, MSc
Instituto de Investigaciones Económicas y Sociales IIES
Universidad Católica Andrés Bello UCAB
Caracas, Venezuela
Prof Brenda Rousset, PhD
Departamento de Estadística, Escuela de Sociología (FaCES)
Universidad Central de Venezuela UCV
Caracas, Venezuela
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Venezuela, as many countries in Latin America, showed substantial improvements in infant mortality rates during the last 60 years. However, the decreasing pattern might be reversing. Recent socioeconomic and political events have led to a collapse in living standards, along with a breakdown of the health system. At the same time, a strict secrecy policy has ruled public institutions, and since 2013 the Venezuelan government stopped publishing mortality statistics.
This study attempts to fill this gap and estimate infant mortality using hospital and census data after 2013.
The main finding is that infant mortality rates in Venezuela may have stopped decreasing and started increasing in 2009 – around the time funding for the Venezuelan health system started to be substantially reduced. By 2016, the infant mortality rate was 21.1 deaths per 1000 live births, which is 1.4 times the rate in 2008 (15.0 deaths per 1000 live births), and equivalent to the rate recorded in the late 1990s, meaning 18 years of progress may have been lost. (more…)
Ms Jenny García, PhD candidate
Institut National d’Études Démographiques INED
Institut de Démographie de l'université Paris 1 Panthéon Sorbonne IDUP
Paris, France
Prof Gerardo Correa, MSc
Instituto de Investigaciones Económicas y Sociales IIES
Universidad Católica Andrés Bello UCAB
Caracas, Venezuela
Prof Brenda Rousset, PhD
Departamento de Estadística, Escuela de Sociología (FaCES)
Universidad Central de Venezuela UCV
Caracas, Venezuela
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Venezuela, as many countries in Latin America, showed substantial improvements in infant mortality rates during the last 60 years. However, the decreasing pattern might be reversing. Recent socioeconomic and political events have led to a collapse in living standards, along with a breakdown of the health system. At the same time, a strict secrecy policy has ruled public institutions, and since 2013 the Venezuelan government stopped publishing mortality statistics.
This study attempts to fill this gap and estimate infant mortality using hospital and census data after 2013.
The main finding is that infant mortality rates in Venezuela may have stopped decreasing and started increasing in 2009 – around the time funding for the Venezuelan health system started to be substantially reduced. By 2016, the infant mortality rate was 21.1 deaths per 1000 live births, which is 1.4 times the rate in 2008 (15.0 deaths per 1000 live births), and equivalent to the rate recorded in the late 1990s, meaning 18 years of progress may have been lost. (more…)All Travelers to Pakistan At Risk of Getting Drug Resistant Typhoid Fever
Scabies: For Community Control, Exam of Just Arms and Legs May Be Sufficient
Cost-effectiveness of Humanitarian Pediatric Cardiac Surgery
Female Genital Mutilation of Young Girls Declines in Africa, Not in Western Asia
 Professor Ngianga-Bakwin Kandala
Professor of Biostatistics
Department: Mathematics, Physics and Electrical Engineering
Northumbria University, UK
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The background “UNICEF (2014) estimates that worldwide more than two hundred million women have undergone some form of FGM/C, and approximately 3.3 million girls are cut each year. Recent estimates show that if FGM/C practices continue at current, 68 million girls will be cut between 2015 and 2030 in 25 countries where FGM is routinely practiced and more recent data are available (UNJP, 2018).”
Main findings: The prevalence of FGM/C among children varied greatly between countries and regions and also within countries over the survey periods. We found evidence of significant decline in the prevalence of FGM/C in the last three decades among children aged 0–14 years in most of the countries and regions, particularly in East, North and West Africa. We show that the picture looks different in Western Asia, where the practice remains and affects the same age group.
(more…)
Professor Ngianga-Bakwin Kandala
Professor of Biostatistics
Department: Mathematics, Physics and Electrical Engineering
Northumbria University, UK
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The background “UNICEF (2014) estimates that worldwide more than two hundred million women have undergone some form of FGM/C, and approximately 3.3 million girls are cut each year. Recent estimates show that if FGM/C practices continue at current, 68 million girls will be cut between 2015 and 2030 in 25 countries where FGM is routinely practiced and more recent data are available (UNJP, 2018).”
Main findings: The prevalence of FGM/C among children varied greatly between countries and regions and also within countries over the survey periods. We found evidence of significant decline in the prevalence of FGM/C in the last three decades among children aged 0–14 years in most of the countries and regions, particularly in East, North and West Africa. We show that the picture looks different in Western Asia, where the practice remains and affects the same age group.
(more…)Tens of Thousands Worldwide Die of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
 Dr Alessandro Cassini MD
Epidemiologist, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
Solna, Sweden
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We published an ECDC study estimating attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the European Union and the European Economic Area (EU/EEA). This study is based on 2015 data from the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net).
The study was developed by experts at ECDC and the Burden of AMR Collaborative Group, and published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
(more…)
Dr Alessandro Cassini MD
Epidemiologist, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
Solna, Sweden
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We published an ECDC study estimating attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the European Union and the European Economic Area (EU/EEA). This study is based on 2015 data from the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net).
The study was developed by experts at ECDC and the Burden of AMR Collaborative Group, and published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases.
(more…)Canadians Enjoy High Level of Health and Longevity
 Dr. Justin Lang, PhD
Research Analyst, Public Health Agency of Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: This study is based on the Global Burden of Disease Study, which is led by the Institute of Health Metrics at the University of Washington. In this study, we present estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study to describe the major causes of health loss among Canadians, and how these have changed from 1990 to 2016.
In 2016, cancers, cardiovascular diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and mental and substance use disorders, combined, resulted in over half of the total health loss among Canadians as measured by disability adjusted life years. Disability-adjusted life years is a measure that combines both mortality, through years of life lost, and morbidity, through years lived with disability, into a single measure that allows us to compare health loss from different causes using the same metric.
The all-cause age-standardized years of life lost rate declined 12% between 2006 and 2016, while the all-cause age-standardized years lived with disability rate remained stable (+1%) and the all-cause age-standardized disability-adjusted life year rate declined by 5%.
Finally, between 1990 and 2016, there has been a shift in what contributes to health loss in Canada from premature mortality to disability. In 1990, 45% of total all-cause disability-adjusted life years were due to years lived with disability. By 2016, this proportion grew to 52%. (more…)
Dr. Justin Lang, PhD
Research Analyst, Public Health Agency of Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: This study is based on the Global Burden of Disease Study, which is led by the Institute of Health Metrics at the University of Washington. In this study, we present estimates from the Global Burden of Disease Study to describe the major causes of health loss among Canadians, and how these have changed from 1990 to 2016.
In 2016, cancers, cardiovascular diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and mental and substance use disorders, combined, resulted in over half of the total health loss among Canadians as measured by disability adjusted life years. Disability-adjusted life years is a measure that combines both mortality, through years of life lost, and morbidity, through years lived with disability, into a single measure that allows us to compare health loss from different causes using the same metric.
The all-cause age-standardized years of life lost rate declined 12% between 2006 and 2016, while the all-cause age-standardized years lived with disability rate remained stable (+1%) and the all-cause age-standardized disability-adjusted life year rate declined by 5%.
Finally, between 1990 and 2016, there has been a shift in what contributes to health loss in Canada from premature mortality to disability. In 1990, 45% of total all-cause disability-adjusted life years were due to years lived with disability. By 2016, this proportion grew to 52%. (more…)Increase In Measles in Italy Linked to Austerity Measures
Did Billions in US AIDS Prevention Money Save Babies’ Lives in Kenya?
Multiple Myeloma Cases and Deaths Increase Worldwide
Solar Powered Oxygen Could Fill Critical Gap in Underserved Areas
- Pneumonia is the leading cause of mortality in children globally.
- Oxygen is an essential therapy for children with hypoxemic pneumonia, but is not available in many resource-limited and rural areas.
- Our innovation, solar powered oxygen delivery, harnesses freely available sun and air to delivery oxygen to patients independent of grid electricity.
- We performed a randomized controlled trial of solar powered oxygen delivery, compared to standard oxygen delivery using compressed oxygen cylinders in children with hypoxemia hospitalized at two centres in Uganda.
- Solar powered oxygen was non-inferior to cylinder oxygen with respect to clinical outcomes, and offers advantages in terms of reliability, simplicity, and cost.
Severely Malnourished Children May Benefit From Vitamin D Supplement
Trained Rats Detect TB Better Than Microscopy
US Free Trade Agreements Can Contribute to “Globesity”
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Pepita Barlow, MSc, Department of Sociology University of Oxford, Manor Road Building, Manor Road, Oxford, United Kingdom
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The escalating global prevalence of overweight and obesity, or “globesity,” is often described as a pandemic. Globalization via free trade agreements (FTAs) with the US has been implicated in this pandemic because of its role in spreading high-calorie diets rich in salt, sugar, and fat through the reduction of trade barriers like tariffs in the food and beverage sector.
We used a “natural experiment” design (that mimics a randomized controlled trial as closely as possible) and data from the United Nations Food and Agricultural Office to evaluate the impact of the 1989 Canada-US Free Trade Agreement on caloric availability in Canada (CUSFTA).
We found that CUSFTA was associated with an increase in caloric availability and likely intake of approximately 170 kilocalories per person per day in Canada. Additional models showed that this rise in caloric intake can contribute to weight gain of between 1.8-9.3 kg for men and 2.0-12.2 kg for women aged 40, depending on their physical activity levels and the extent to which availability affects caloric intake. (more…)
Study Finds Opportunities for Improvement to Pediatric Healthcare in Australia
With Increasing Westernization, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Becoming a Global Health Issue
The President’s Malaria Initiative Reduced All-Cause Childhood Mortality
- 1
- 2