Author Interviews, Dermatology, Diabetes, JAMA / 15.01.2019
Increase Risk of Blistering Disorder with Diabetes Medication
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dong Hyun Kim M.D.
Associate professor
Department of Dermatology
CHA Bundang Medical Center
CHA University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
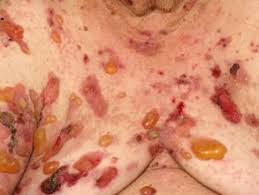
Response: As a dermatologist, we see many patients with newly diagnosed with bullous pemphigoid (BP), many of whom have diabetes.
The use of DPP-4 inhibitors is a common treatment for diabetes, we have noted previous case reports that DPP-4 inhibitors may be the cause of BP. For this reason, we started this study.
The most important thing in my article is DPP-4 inhibitors, particularly vildagliptin, may be associated with the development of bullous pemphigoid in male patients with diabetes. We have confirmed these points based on the nationwide, population-based study. It is very meaningful because there have been few studies using large sample sizes so far.
(more…)