Author Interviews, OBGYNE, Sleep Disorders, UCSF / 03.01.2018
Program Improves Sleep For Mothers Hospitalized For Delivery
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Kathryn A. Lee, RN, CBSM, PhD
Department of Family Health Care Nursing
University of California at San Francisco
San Francisco, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Sleep deprivation can adversely affect health and wellbeing in any patient population.
In pregnancy, adverse outcomes may include preterm birth, longer labor, cesarean birth, and depression.
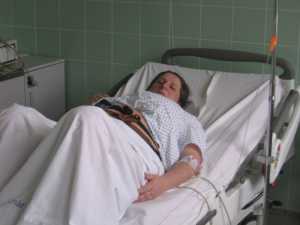
We found that women with high-risk pregnancies were sleep deprived even prior to hospitalization. Our sample averaged 29 weeks gestation, and half reported getting only between 5 and 6.5 hours of sleep at home before hospital admission. Our sleep hygiene intervention strategies gave them more control over the environment in their hospital room, and they self-reported significantly better sleep than controls. Interestingly, both groups increased their sleep time to almost 7 hours at night, on average, in the hospital before they were discharged home.
(more…)
Kathryn A. Lee, RN, CBSM, PhD
Department of Family Health Care Nursing
University of California at San Francisco
San Francisco, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Sleep deprivation can adversely affect health and wellbeing in any patient population.
In pregnancy, adverse outcomes may include preterm birth, longer labor, cesarean birth, and depression.
We found that women with high-risk pregnancies were sleep deprived even prior to hospitalization. Our sample averaged 29 weeks gestation, and half reported getting only between 5 and 6.5 hours of sleep at home before hospital admission. Our sleep hygiene intervention strategies gave them more control over the environment in their hospital room, and they self-reported significantly better sleep than controls. Interestingly, both groups increased their sleep time to almost 7 hours at night, on average, in the hospital before they were discharged home.
(more…)
 Kathryn A. Lee, RN, CBSM, PhD
Department of Family Health Care Nursing
University of California at San Francisco
San Francisco, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Sleep deprivation can adversely affect health and wellbeing in any patient population.
In pregnancy, adverse outcomes may include preterm birth, longer labor, cesarean birth, and depression.
We found that women with high-risk pregnancies were sleep deprived even prior to hospitalization. Our sample averaged 29 weeks gestation, and half reported getting only between 5 and 6.5 hours of sleep at home before hospital admission. Our sleep hygiene intervention strategies gave them more control over the environment in their hospital room, and they self-reported significantly better sleep than controls. Interestingly, both groups increased their sleep time to almost 7 hours at night, on average, in the hospital before they were discharged home.
(more…)
Kathryn A. Lee, RN, CBSM, PhD
Department of Family Health Care Nursing
University of California at San Francisco
San Francisco, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Sleep deprivation can adversely affect health and wellbeing in any patient population.
In pregnancy, adverse outcomes may include preterm birth, longer labor, cesarean birth, and depression.
We found that women with high-risk pregnancies were sleep deprived even prior to hospitalization. Our sample averaged 29 weeks gestation, and half reported getting only between 5 and 6.5 hours of sleep at home before hospital admission. Our sleep hygiene intervention strategies gave them more control over the environment in their hospital room, and they self-reported significantly better sleep than controls. Interestingly, both groups increased their sleep time to almost 7 hours at night, on average, in the hospital before they were discharged home.
(more…)