MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Joshua D. Wallach, MS, PhD
Assistant Professor of Epidemiology (Environmental Health Sciences)
Yale School of Public Health
New Haven, CT
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Over the past few years, there has been growing interest in the potential health benefits of cannabidiol (CBD), a chemical compound in cannabis. Although only one CBD-derived prescription drug has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of epilepsy, I recently started seeing products containing CBD advertised and sold across the US (e.g. CBD in foods, beverages, dietary supplements, and cosmetics). I noticed that many of these products were being marketed with unproven claims to prevent, cure, and treat various conditions, and became interested in learning more about the research supporting the use of CBD, the potential for misleading claims, and impact that the CBD-industry may be having on research that is being generated and disseminated to the public.
Research funding sources and other author conflicts of interests (e.g. consulting fees, honoraria, travel expenses) can influence the way that research is designed, conducted, and reported. Previous studies have consistently demonstrated associations between authors' conflicts of interest and proindustry conclusions in clinical research.
Given the growing number of companies invested in CBD's commercial success, we decided to analyze the disclosed funding sources, conflicts of interest statements, author employment details, and CBD-related conclusions in a large sample of published articles on the characteristics, use, and therapeutic effects of cannabidiol.
(more…)





 Brett King, MD, PhD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Yale School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
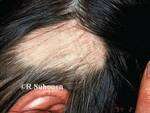
Response: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder marked by disfiguring, non-scarring hair loss, and there are no therapies approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of the disease. JAK inhibitors are showing promise for treatment of severe alopecia areata. In this work, the pooled results of two phase 3 clinical trials of the JAK inhibitor baricitinib were reported out to 52 weeks.
Brett King, MD, PhD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Yale School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder marked by disfiguring, non-scarring hair loss, and there are no therapies approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treatment of the disease. JAK inhibitors are showing promise for treatment of severe alopecia areata. In this work, the pooled results of two phase 3 clinical trials of the JAK inhibitor baricitinib were reported out to 52 weeks.