MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Matthew H. Law, PhD
Senior Research Officer, Statistical Genetics
QIMR Berghofer
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: A large genetic study of melanoma involving a global collaboration of scientists, co-led by QIMR Berghofer, the University of Leeds in the UK, and the National Cancer Institute in the US which is part of the National Institutes of Health, has been published in the prestigious journal
Nature Genetics.
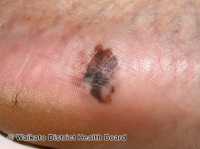
Melanoma is a sometimes-deadly skin cancer, with an estimated 350,000 cases worldwide in 2015, resulting in nearly 60,000 deaths. Melanoma begins in melanocytes, cells in the skin responsible for making the pigment melanin that gives colour to the skin. Melanin is able to block some of the harmful effects of UV radiation, which is why people with pale skin are at a higher risk of skin cancer, but the protection is not complete. Moles also develop from melanocytes, and having a high number of moles is a risk factor for melanoma.
UK based co-lead author, Dr Mark Iles from the University of Leeds’s Institute for Data Analytics, said the researchers examined DNA from 37,000 people who had been diagnosed with melanoma and compared their genetic information to that of nearly 400,000 people with no history of the disease.”
Joint study leader and QIMR Berghofer statistical geneticist Associate Professor Matthew Law said the researchers identified 33 new regions of the genome and confirmed another 21 previously reported regions that are linked to a person’s risk of developing melanoma of the skin. Two of the new regions we’ve discovered that are linked to melanoma have previously been linked to autoimmune disorders. This provides further evidence that the immune system plays an important role in a person developing melanoma. We also found an association between melanoma and common genetic variants in the gene TP53, which is a gene critical in controlling DNA repair when cells divide, and in suppressing cancer.”
Co-lead author on the study and senior investigator at the National Cancer Institute, Dr Maria Teresa Landi, said the research also uncovered other important clues to the genetic causes of melanoma. We used the relationship between moles, pigmentation, and melanoma to identify 31 additional gene regions that potentially influence melanoma risk. For example, one of the regions we identified is involved in melanocyte growth,” Dr Landi said. “Moreover, we also included people from Mediterranean populations involved in the MelaNostrum Consortium. Most studies of melanoma use people with northern or western European ancestry (e.g. British) and by expanding our analysis to include Mediterranean populations, we will gain a greater understanding of the genetics of melanoma in this highly sun exposed group.”
(more…)