Single Higher Dose Radiation Treatment Effective for Metastatic Cancer Pain Relief
Cancer Patients May Receive Better Emergency Care at Hospital Where They Receive Cancer Treatments
Occupational Exposure to Pesticides: Poor Prognosis for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients
Gene Linked to Colon Cancer in Younger Patients Identified
“Magic Mouthwash” Can Decrease Mouth Pain from Radiation Therapy
RNA Genetic Testing Improves Analysis of Hereditary Cancer Genes
 Rachid Karam, PhD
Director, Ambry Translational Genomics Lab
Ambry Genetics
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: DNA genetic testing (DGT) for hereditary cancer genes is now a well accepted clinical practice; however, the interpretation of DNA variation remains a challenge to laboratories and medical providers.
RNA genetic testing (RGT) as a supplement to DGT is a means to clarify the clinical actionability of variants in hereditary cancer genes, improving our ability to accurately apply known strategies for cancer risk reduction.
(more…)
Rachid Karam, PhD
Director, Ambry Translational Genomics Lab
Ambry Genetics
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: DNA genetic testing (DGT) for hereditary cancer genes is now a well accepted clinical practice; however, the interpretation of DNA variation remains a challenge to laboratories and medical providers.
RNA genetic testing (RGT) as a supplement to DGT is a means to clarify the clinical actionability of variants in hereditary cancer genes, improving our ability to accurately apply known strategies for cancer risk reduction.
(more…)Sentinel Lymph Node Drainage Can Be Used to Test For Marker of Melanoma Relapse Risk
Surgical Outcomes Found to be Better at ‘Brand Name’ than Affiliate Cancer Hospitals
How Many Cancer Patients Use Complementary or Alternative Medicine Treatments?
Cancer Drug Trials: Does Changing the Endpoint from Overall Survival Hasten the Approval Process?
Opioid-Related Hospitalizations Among Cancer Patients are Rare
The Word ‘Cancer’ Still Affects How Patients Feel About Their Disease, Even if Low Risk
Genetic Mutation May Predict Outcomes of Prostate Cancer Treated With Androgen-Deprivation Therapy or Abiraterone
Younger Generations at Much Higher Risk of Obesity Related Cancers
Female Radiation Oncologists Less Likely to Receive Industry Payments
Younger Cancer Survivors Face Greater Financial Burdens
First Patient Dosed in Phase 3 AGENT Study for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Esophageal Cancer: HMIE Procedure Reduces Morbidity Without Sacrificing Efficacy
WHO: Profits Outweigh R&D Costs of New Cancer Drugs
Cancers Attributable to Obesity Vary by State
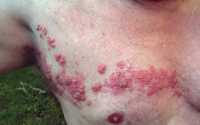
Chemo and Some Cancers Raise Risk of Shingles
Some Anti-Tumor Drugs May Promote Delayed Aggressive Cancers
MedicalResearch.comInterview with:
Alexandra Avgustinova PhD
Postdoctoral fellow at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRBBarcelona)

MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The basis of this study was the strong association between closed chromatin and high mutation rate reported several years ago. We were surprised to see this observation being widely interpreted as a causal association, as it was largely based on correlative studies without experimental backing. Therefore we decided to experimentally test for the first time whether indeed altering chromatin opening would affect mutation rate or distribution within tumours.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: We found that, despite significantly increasing chromatin opening, loss of the histone methyltransferase G9a did not have any major influence on the mutation rate or distribution within cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas. These results demonstrate that chromatin opening does not play a major role in determining the mutation rate within tumours, and we speculate that other, confounded factors (e.g. replication timing or H3K36me3 levels) are likely causal for the observed association. This, however, remains to be proven experimentally.
Another major conclusion of our study was that although tumour initiation was delayed and tumour burden decreased in the absence of G9a, the tumours that did develop were highly aggressive due to selection for more aggressive tumour clones. This finding was contrary to many published reports suggesting G9a as a good candidate for clinical targeting, highlighting the need for long-term follow-up in pre-clinical studies.
(more…)Immunotherapy Gel Sprayed on Surgical Site May Reduce Cancer Recurrence
MedicalResearch.comInterview with:

Zhen Gu, Ph.D.
Professor, Department of Bioengineering
University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA)
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Despite improvements in surgical techniques, local residual tumor micro infiltration and circulating tumor cells continue causing tumor recurrence after resection.
Calcium carbonate nanoparticles could scavenge H+ in the surgical wound, reserving the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and promoting the antitumor immuneresponses.
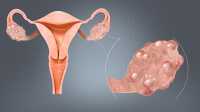
(more…)Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Linked to Increased Risk of Some Cancer Types
Daily Drinking is Dangerous
 Sarah Hartz, MD PhD
Assistant Professor
Department of Psychiatry
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: This study is the first to show that daily drinking is dangerous. Specifically, drinking four or more times weekly, even if it’s only 1-2 drinks at a time, increases risk of mortality. This is in line with recent studies published in the Lancet, but we were able to break down their lowest drinking categories (up to 12.5 drinks weekly in one and up to 5.6 drinks weekly in the other) and found that the frequency is important, not just the average number of drinks per week. It looks like the increased mortality is predominantly due to cancer-related deaths.
(more…)
Sarah Hartz, MD PhD
Assistant Professor
Department of Psychiatry
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: This study is the first to show that daily drinking is dangerous. Specifically, drinking four or more times weekly, even if it’s only 1-2 drinks at a time, increases risk of mortality. This is in line with recent studies published in the Lancet, but we were able to break down their lowest drinking categories (up to 12.5 drinks weekly in one and up to 5.6 drinks weekly in the other) and found that the frequency is important, not just the average number of drinks per week. It looks like the increased mortality is predominantly due to cancer-related deaths.
(more…)Can an Organic Diet Reduce Cancer Risk?
 Julia Baudry &
Emmanuelle Kesse-Guyot PhD
Centre de Recherche Epidémiologie et Statistique Sorbonne Paris Cité, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM) U1153, Institut National de la Recherche
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Among the environmental risk factors for cancer, there are concerns about exposure to different classes of pesticides, notably through occupational exposure. Organic foods are less likely to contain pesticide residues than conventional foods, and studies have showed that an organic diet reduces exposure to certain pesticides (Baudry et al 2018, Oates et al 2014, Curl et al 2015). In the general population, the primary route of exposure is diet, especially intake of conventionally grown fruits and vegetables. However, few studies have examined the association of organic food consumption with cancer risk.
In a population of 68 946 French adults from the NutriNet-Santé study, we found a reduction of 25% of cancer risk among consumers with a high frequency of organic foods compared to consumers with a low frequency, after accounting for many factors (such as lifestyle, diet and sociodemographic factors). Specifically a 34% and 76% decrease in risk was observed for post-menopausal breast cancer and all lymphomas, respectively, among frequent organic food consumers compared to consumers with a low organic food consumption frequency.
(more…)
Julia Baudry &
Emmanuelle Kesse-Guyot PhD
Centre de Recherche Epidémiologie et Statistique Sorbonne Paris Cité, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM) U1153, Institut National de la Recherche
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Among the environmental risk factors for cancer, there are concerns about exposure to different classes of pesticides, notably through occupational exposure. Organic foods are less likely to contain pesticide residues than conventional foods, and studies have showed that an organic diet reduces exposure to certain pesticides (Baudry et al 2018, Oates et al 2014, Curl et al 2015). In the general population, the primary route of exposure is diet, especially intake of conventionally grown fruits and vegetables. However, few studies have examined the association of organic food consumption with cancer risk.
In a population of 68 946 French adults from the NutriNet-Santé study, we found a reduction of 25% of cancer risk among consumers with a high frequency of organic foods compared to consumers with a low frequency, after accounting for many factors (such as lifestyle, diet and sociodemographic factors). Specifically a 34% and 76% decrease in risk was observed for post-menopausal breast cancer and all lymphomas, respectively, among frequent organic food consumers compared to consumers with a low organic food consumption frequency.
(more…)TumorScan May Become a Universal Screening Blood Test For Cancer
Breast Cancer: Gene Expression of Receptors on a Chip Can Enhance Precision Diagnosis
 Univ.- Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Schreiner
Section Biosimulation and Bioinformatics
Center for Medical Statistics, Informatics, and Intelligent Systems
Medical University of Vienna
General Hospital
WIEN / AUSTRIA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The choice of correct individualized therapy for breast cancer depends on correct diagnosis: receptors for estrogen, progesterone and HER2 are determined routinely. However 5-10% of these routine diagnostics are inaccurate and may entail suboptimal therapy.
We have paved the way for additional diagnostics from gene expression data so as to increase precision of diagnostics. (more…)
Univ.- Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Schreiner
Section Biosimulation and Bioinformatics
Center for Medical Statistics, Informatics, and Intelligent Systems
Medical University of Vienna
General Hospital
WIEN / AUSTRIA
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The choice of correct individualized therapy for breast cancer depends on correct diagnosis: receptors for estrogen, progesterone and HER2 are determined routinely. However 5-10% of these routine diagnostics are inaccurate and may entail suboptimal therapy.
We have paved the way for additional diagnostics from gene expression data so as to increase precision of diagnostics. (more…)