MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Mayesha Khan, M.A.
Research Coordinator
Staples Lab | Road Safety & Public Health Research
Dr. John A. Staples MD, FRCPC, MPH
Clinical Associate Professor
Department of Medicine
The University of British Columbia | VCH Research Institute
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: About one in thirty patients leave hospital before their inpatient medical treatment is complete. Before medically advised (BMA) discharge from hospital (also known as patient-initiated discharge) is associated with a several-fold increase in mortality in the following year compared to routine physician-advised discharge. The study’s senior author is a physician who works in the hospital (JS), and it’s the patients who initiate a BMA discharge that he often worries about the most.
We knew from past research that the rate of BMA discharge is much higher among people who use drugs. We suspected that the risk of drug overdose after BMA discharge was much higher than the risk of overdose after routine physician-advised discharge.
We also suspected that BMA discharge itself might create conditions that encourage drug use and increase the risk of overdose. A hospital stay can result in drug abstinence and reduced drug tolerance, and it can disrupt social routines and interfere with access to familiar/safer sources of drugs. BMA discharges sometimes occur suddenly, leaving little time to prescribe medications for opioid use disorder like methadone and Suboxone. Lingering illness or persistent pain after leaving hospital might prompt people to engage in heavier-than-usual drug use. All of these factors might increase the risk of overdose after BMA discharge.
(more…)
Alcohol, Author Interviews, CMAJ / 03.06.2024
Rare Auto-Brewery Syndrome Causes Intoxication Without Alcohol Consumption
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Rahel Zewude, MD FRCPC
Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology, PGY-5
University of Toronto
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you describe the syndrome of Auto-brewery syndrome?
Response: Auto-brewery syndrome refers to a syndrome where the gut ferments alcohol from carbohydrates leading to high blood alcohol levels and intoxication without any consumption of alcoholic drinks.
(more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, COVID -19 Coronavirus, Pediatrics / 27.09.2021
More Than Half of Children Admitted for COVID-19 in Early Pandemic Had No Co-Morbidities
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Shaun K. Morris MD, MPH, FRCPC, FAAP, DTM&H
Divisions of General Pediatrics
Clinician-Scientist, Division of Infectious Diseases
Division of Infectious Diseases at the Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids)
for the Canadian Paediatric Surveillance Program COVID-19 Study Team
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The SARS-CoV-2 virus can cause the disease we now call COVID-19. In early 2020, when the SARS-CoV-2 virus first spread outside of China, it quickly became apparent that cases may be seen in Canada. It was not known at the time how infection with the virus would affect children and youth. Because more severe disease from other respiratory viruses often disproportionally affect the very young, we expected that a similar pattern may be seen with SARS-CoV-2. We also did not know if children and youth with certain underlying medical conditions may be at higher risk for more severe disease.
Ultimately, this study was designed to get a better understanding of how often children and youth in Canada are hospitalized with SARS-CoV-2 infection, how often severe disease happens, and which children or youth may be at higher risk for severe disease. (more…)
Author Interviews, COVID -19 Coronavirus, Education, Pediatrics / 16.04.2021
COVID-19: Increasing Evidence Children Less Likely to Transmit Infection within Households or Schools
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Jared Bullard MD FRCPC
Associate Professor, Departments of Pediatrics & Child Health and Medical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases
Max Rady College of Medicine
Rady Faculty of Health Sciences
Cadham Provincial Laboratory
Children’s Hospital Research Institute of Manitoba
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Children are well known to transmit epidemic/endemic respiratory viruses like influenza. Initial public health policy was based on that children were likely to transmit SARS-CoV-2 effectively within a community and subsequently in-person school and extracurricular activities were suspended.
Initial research did not show a clear association with children driving transmission. The purpose of our study was to take respiratory samples from both children and adults with COVID-19 (all had SARS-CoV-2 detected by RT-PCR) and compare those samples by their ability to grow in cell culture and amount of virus in samples.
We took 175 samples from children (97 younger than 10 years of age and 78 between 11-17 years) and compared them to 130 adult samples from the same communities in Manitoba experiencing outbreaks of COVID-19. (more…)
Accidents & Violence, Author Interviews, Cannabis, CMAJ / 06.04.2021
Fatal Car Collisions After Marijuana Legalized
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Sarah Windle, MPH
PhD Student in Epidemiology
Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics, and Occupational Health
McGill University (Montréal, Québec, Canada)
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Concerns have been raised about the potential for increases in impaired driving following the legalization of recreational cannabis use in Canada in October 2018. Data from Statistics Canada suggest that cannabis use in the previous three months increased among adults (15 and older) from 14% before legalization in 2018 to 17% in 2019. Among those users with a driver’s license, 13% reported driving within two hours of cannabis use. While this proportion remained the same before and after legalization, this indicates that the absolute number of individuals who reported driving within two hours of use has increased following legalization (due to an increase in the number of users).
(more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, COVID -19 Coronavirus, OBGYNE / 19.03.2021
COVID-19: Potential Negative Impacts on Maternal and Infant Health Outcomes
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Nathalie Auger
Professeure agrégée de clinique
École de santé publique - Département de médecine sociale et preventive
University of Montreal
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: COVID-19, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), has been a major public health concern. The number of infected pregnant women continues to increase. Pregnant women and infants are particularly susceptible to COVID-19 because the physiologic changes of pregnancy involve cardiovascular, respiratory, and immune changes that may alter the response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Fetuses may be exposed to SARS-CoV-2 during critical periods of development. The nature of the association between COVID-19 and pregnancy outcomes remains unclear and meta-analyses of pregnant women with COVID-19 are lacking.
(more…)
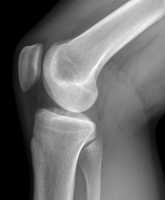
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Orthopedics, Rheumatology, Surgical Research / 02.02.2021
Knee Realignment Surgery May Delay or Prevent Some Knee Replacements
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Codie Primeau, MSc
Physical Therapy Student & Ph.D. Candidate (Combined MPT/Ph.D.)
Wolf Orthopaedic Biomechanics Lab, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic
Western University
London, ON, Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a surgery for patients with varus alignment (bowed legs) and earlier-stage knee osteoarthritis. By correcting alignment, HTO shifts load to less diseased parts of the knee. One of the goals of HTO is to delay or even prevent the need for knee replacement surgery later.
(more…)
Allergies, Author Interviews, CMAJ, Pediatrics / 23.09.2020
Childhood Peanut and Nut Allergies More Frequent at Halloween and Easter
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Melanie Leung, M.D.,C.M. candidate 2021
4th-year medical student at McGill University
Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Department of Pediatrics, Montreal Children’s Hospital
McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, QC, Canada
Dr. Moshe Ben-Shoshan, MD, MSc
Pediatric allergist and immunologist at the MCH (Montreal Children’s Hospital) and
Scientist at the Research Institute of the MUHC (McGill University Health Center)
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: In Canada, up to 9% of children have at least 1 food allergy. Anaphylaxis is the most severe and potential life-threatening manifestation of food allergy. Peanuts and tree nuts are the main culprits in food-induced anaphylaxis and account for most fatal cases in North America.
Public awareness about peanut and nut anaphylaxis can help to prevent and to act promptly, in the case of anaphylactic reaction. However, the best timing for public awareness campaigns remained unknown, as no previous study looked at the potential association between specific times of the year, such as public holidays, and the incidence of peanut and tree nut anaphylaxis. Our aim was to evaluate the risk of peanut and tree nut-induced anaphylaxis on Halloween, Christmas, Easter, Diwali, Chinese New Year, and Eid al-Adha.
Data was collected from 1390 pediatric cases of peanut or nut-induced anaphylaxis across Canada (Newfoundland & Labrador, Quebec, Ontario, and British Columbia), from 2011 to 2020. 62% of children were boys and the median age was 5.4 years. We compared the average daily number of cases during each holiday and compared it to the rest of the year (i.e.: non-holiday period). (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Ophthalmology, Pediatrics / 20.07.2020
About 10% of Kindergarten Children Have a Visual Problem
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Mayu Nishimura
Department of Ophthalmology and Vision Sciences
Director of Research
Kindergarten Vision Screening Program
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
 Response: Children's visual problems are difficult to identify without formal tests but most parents do not realize the importance of early eye checks nor are they aware that well-child visits to the family doctor/pediatrician are not enough. We are researchers at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) and SickKids Hospital (Toronto, ON) who examined if it is possible to implement a vision screening program for kindergartners in diverse Ontario communities. Below are the main findings:
Response: Children's visual problems are difficult to identify without formal tests but most parents do not realize the importance of early eye checks nor are they aware that well-child visits to the family doctor/pediatrician are not enough. We are researchers at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) and SickKids Hospital (Toronto, ON) who examined if it is possible to implement a vision screening program for kindergartners in diverse Ontario communities. Below are the main findings:
 Response: Children's visual problems are difficult to identify without formal tests but most parents do not realize the importance of early eye checks nor are they aware that well-child visits to the family doctor/pediatrician are not enough. We are researchers at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) and SickKids Hospital (Toronto, ON) who examined if it is possible to implement a vision screening program for kindergartners in diverse Ontario communities. Below are the main findings:
Response: Children's visual problems are difficult to identify without formal tests but most parents do not realize the importance of early eye checks nor are they aware that well-child visits to the family doctor/pediatrician are not enough. We are researchers at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON) and SickKids Hospital (Toronto, ON) who examined if it is possible to implement a vision screening program for kindergartners in diverse Ontario communities. Below are the main findings:
- We screened nearly 5000 kindergarten children in 15 communities and found that 11% of screened children had a visual problem, with 2/3 of the children being identified for the first time.
- There was great support for the program from the children, parents, teachers, and optometrists.
- Screening required 15-20 minutes per child and cost $10/child.
- When parents received a letter permitting them to opt out of screening, 4% did so. When parents were required to return a signed letter to opt in, 30% did not.
- Referral rates varied across schools but were higher for children in junior kindergarten (average 53%) than children in senior kindergarten (average 34%).
- Successful treatment depends on the parents’ awareness of the importance of eye exams and glasses, and access to optometrists and glasses without worrying about costs.
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Endocrinology, OBGYNE / 02.06.2020
Are Too Many Pregnant Women Being Diagnosed and Treated for Thyroid Disease?
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Lois Donovan MD FRCPC
Clinical Professor
Cumming School of Medicine
Division on Endocrinology and Metabolism and
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
University of Calgary
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
1) We observed in our clinical practices that minor TSH elevations in early pregnancy frequently normalized without intervention.
2) Recent randomized control trials have failed to show benefit of treating women with levothyroxine with minor TSH elevations in pregnancy (more…)
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Peter Jüni, MD, FESC
Director, Applied Health Research Centre
Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St Michael's Hospital
Department of Medicine
University of Toronto, Ontario
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: It is unclear whether seasonal changes, school closures or other public health interventions will result in a slowdown of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We studied 144 geopolitical areas around the world with more than 375,000 COVID-19 cases by March 27 to determine whether epidemic growth is globally associated with climate or public health interventions intended to reduce transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
(more…)
Peter Jüni, MD, FESC
Director, Applied Health Research Centre
Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St Michael's Hospital
Department of Medicine
University of Toronto, Ontario
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: It is unclear whether seasonal changes, school closures or other public health interventions will result in a slowdown of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We studied 144 geopolitical areas around the world with more than 375,000 COVID-19 cases by March 27 to determine whether epidemic growth is globally associated with climate or public health interventions intended to reduce transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
(more…)
 Peter Jüni, MD, FESC
Director, Applied Health Research Centre
Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St Michael's Hospital
Department of Medicine
University of Toronto, Ontario
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: It is unclear whether seasonal changes, school closures or other public health interventions will result in a slowdown of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We studied 144 geopolitical areas around the world with more than 375,000 COVID-19 cases by March 27 to determine whether epidemic growth is globally associated with climate or public health interventions intended to reduce transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
(more…)
Peter Jüni, MD, FESC
Director, Applied Health Research Centre
Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St Michael's Hospital
Department of Medicine
University of Toronto, Ontario
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: It is unclear whether seasonal changes, school closures or other public health interventions will result in a slowdown of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We studied 144 geopolitical areas around the world with more than 375,000 COVID-19 cases by March 27 to determine whether epidemic growth is globally associated with climate or public health interventions intended to reduce transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
(more…)
Allergies, Author Interviews, CMAJ, Environmental Risks, Pediatrics / 20.02.2020
Cleaning Products May Raise Risk of Wheezing and Asthma in Young Children
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Jaclyn Parks, B.Sc. Health Sciences
M.Sc. Health Sciences Candidate | Faculty of Health Sciences
Simon Fraser University
Burnaby, B.C
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Childhood asthma is a major public health concern, and many researchers are interested in determining environmental and modifiable exposures in early life so that we can recommend preventative measures. The findings of our study add to the understanding of which exposures in early life may be important to the development of childhood asthma and allergies and allows us to identify specific areas of intervention for parents and other stakeholders involved in protecting children’s health.
(more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Hematology / 13.01.2020
Incidental Low Lymphocyte Count Linked to Increased Mortality
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Stig E Bojesen
Professor, chief physician, dr.med.sci.
Dept of Clinical Biochemistry, Herlev Gentofte Hospital
Copenhagen University Hospital
Department of Clinical Medicine
University of Copenhagen
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Before this study, we did not know the value of an incidental finding of lymphopenia of an otherwise healthy individual from the general population. This is curious since lymphocyte count is a very simple measurement done almost every time you have a blood test done.
(more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Thyroid Disease / 18.11.2019
Is There A Clinical Benefit To Asymptomatic Thyroid Function Screening?
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Richard Birtwhistle, Professor
Departments of Family Medicine and Community Health and Epidemiology
Director of the Centre for Studies, Primary Care, Department of Family Medicine
Queen’s University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Testing for thyroid dysfunction is a commonly done by primary care practitioners. While the Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test is an easy blood test to perform results outside the normal range are often found and will revert to normal over time without treatment in patients without symptoms.
We wanted to see if there was any clinical benefit to patients by screening for thyroid dysfunction. (more…)
Alcohol, Author Interviews, CMAJ, Emergency Care / 22.07.2019
Young Adults Had Largest Increase in Alcohol-Related ER Visits
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, CCFP
Public Health & Preventive Medicine, PGY-5
University of Ottawa
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: We know that alcohol consumption results in enormous health and societal harms globally and in Canada.
While several studies have looked at changes in alcohol harms, such as Emergency Department (ED) visits and Hospitalizations due alcohol, this study is the first to examine in detail how harms related to alcohol have been changing over time in Canada.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Cancer Research, CMAJ, Emergency Care / 29.04.2019
Cancer Patients May Receive Better Emergency Care at Hospital Where They Receive Cancer Treatments
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Keerat Grewal, MD, MSc, FRCPC
Schwartz/Reisman Emergency Medicine Institute
Mount Sinai Hospital
Toronto, ON
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Patients with cancer have complex care requirements and often use the emergency department. The purpose of our study was to determine whether continuity of care, cancer expertise, or both, impact outcomes among cancer patients in the emergency setting. Using administrative data we looked at adult patients with cancer who received chemotherapy or radiation therapy in the 30 days prior to an emergency department visit. (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, OBGYNE / 19.02.2019
Risk of Spontaneous Abortion & Birth Defects with Oral Yeast Drug During Pregnancy
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Anick Bérard PhD FISPE
Research chair FRQS on Medications and Pregnancy
Director, Réseau Québécois de recherche sur le médicament
Professor, Research Chair on Medications, Pregnancy and Lactation
Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Montrealand
Director, Research Unit on Medications and Pregnancy
Research Center
CHU Ste-Justin
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Yeast infections are common during pregnancy (10%). Although topical treatments are first-line therapies, yeast infections during gestation are often more severe and are resistant to topical options. Hence, low dose oral fluconazole is often the treatment of choice for pregnant women (1 dose for 1 day).
Human and animal studies have shown that high dose of fluconazole is teratogenic.Few studies are available for the risk associated with low dose of fluconazole (the most used during pregnancy). Also, no one has studied the combined effect of low- and high-dose fluconazole use during pregnancy on overall adverse pregnancy outcomes (spontaneous abortions, stillbirths and major malformations). (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Fertility, McGill, OBGYNE / 04.02.2019
Absolute Risk Low, but Increased Maternal Morbidity Linked to IVF
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Natalie Dayan MD MSc FRCPC
General Internal Medicine and Obstetric Medicine,
Clinician-Scientist, Research Institute
Centre for Outcomes Research and Evaluation (CORE)
McGill University Health Centre
Montréal QC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Infertility treatment is rising in use and has been linked with maternal and perinatal complications in pregnancy, but the extent to which it is associated with severe maternal morbidity (SMM), a composite outcome of public health importance, has been less well studied. In addition, whether the effect is due to treatment or to maternal factors is unclear.
We conducted a propensity matched cohort study in Ontario between 2006 and 2012. We included 11 546 women who had an infertility-treated pregnancy and a singleton live or stillborn delivery beyond 20 weeks. Each woman exposed to infertility treatment was then matched using a propensity score to approximately 5 untreated pregnancies (n=47 553) in order to address confounding by indication. Poisson regression revealed on overall 40% increase in the risk of a composite of SMM (one of 44 previously validated indicators using ICD-10CA codes and CCI procedure codes) (30.3 per 1000 births vs. 22.8 per 1000 births, adjusted relative risk 1.39, 95% CI 1.23-1.56). When stratified according to invasive (eg., IVF) and non-invasive treatments (eg. IUI or pharmacological ovulation induction), women who were treated with IVF had an elevated risk of having any severe maternal morbidity, and of having 3 or more SMM indicators (adjusted odds ratio 2.28, 95% CI 1.56 – 3.33), when compared with untreated women, whereas women who were treated with non-invasive treatments had no increase in these risks.
(more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Heart Disease, Occupational Health, Social Issues, Stroke / 07.01.2019
Heart Attacks and Stroke Cause Blows to Financial Health
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Allan Garland, MD, MA
Professor of Medicine & Community
Health Sciences
Co-Head, Section of Critical Care Medicine
University of Manitoba
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Heart attacks, strokes and cardiac arrest are common acute health events. Most studies of serious acute health events look at outcomes such as death and how long is spent in the hospital. But for working age people, the ability to work and earn income are very important outcomes that have rarely been studied.
We set out to carefully measure, across Canada, how much heart attacks, strokes and cardiac arrests affect the ability of working age people to work and earn.
(more…)
Author Interviews, Breast Cancer / 11.12.2018
Canadian Task Force Updates Breast Cancer Screening Guidelines
MedicalResearch.com Interview with: Dr. Moore Dr. Ainsley Moore MD, CFPC, MSc(HB), MSc(CLinEpi) CandAssociate Professor,McMaster UniversityAssociate Editor,Canadian Medical Education JournalVice-Chair, Canadian Task Force on...
Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, CMAJ, Pharmacology / 26.11.2018
Aggression in Dementia: Alternatives to Antipsychotics Also Have Side Effects
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Jennifer Watt, PhD
Clinical Epidemiology and Health Care Research
Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation
University of Toronto
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (e.g. aggression, agitation) are common among persons living with dementia.
Pharmacological (e.g. antipsychotics) and non-pharmacological (e.g. reminiscence therapy) interventions are often used to alleviate these symptoms. However, antipsychotics are associated with significant harm among older adults with dementia (e.g. death, stroke). Regulatory agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Health Canada issued black box warnings to advise patients and clinicians of this potential for harm. And initiatives were championed to decrease the use of antipsychotics in persons living with dementia.
In response, we have seen a rise in the use of other pharmacological interventions, such as trazodone (an antidepressant). Its potential to cause harm in older adults with dementia is largely unknown. (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, HIV, Sexual Health / 20.11.2018
What is Risk of Sexual Transmission of HIV With Treatment-Suppressed Low Viral Load?
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Rachel Rodin
Centre for Communicable Diseases and Infection Control
Public Health Agency of Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: On December 1, 2016 (World AIDS Day), the Honourable Jody Wilson-Raybould, federal Minister of Justice, committed to working with provinces and territories, affected communities, and medical professionals to examine the criminal justice system’s response to non-disclosure of HIV status in the context of sexual relations.
To this end, Justice Canada worked with the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), provincial and territorial public health and justice counterparts, and a variety of other stakeholders to develop a comprehensive report on the issue of HIV non-disclosure. As part of this work, Justice Canada asked PHAC to provide an assessment of the most recent medical science on sexual HIV transmission risk.
In collaboration with external peer reviewers, PHAC undertook a systematic review of the full body of scientific evidence on sexual HIV transmission risk. The review found that the risk of sexual transmission of HIV is negligible when an individual is taking antiretroviral therapy as prescribed and maintains a suppressed viral load. The review also concluded that the risk remains low when the individual is on antiretroviral therapy with varying viral load, or is not on antiretroviral therapy but uses condoms. (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Pain Research, Pediatrics, Vaccine Studies / 22.10.2018
Program Can Help Parents Manage Kids’ Pain from Vaccines
Parents are less anxious about their children getting vaccinations. ...
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Cost of Health Care / 25.09.2018
Who Has the Highest Rate of Readmission After Hospital Discharge?
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Andrea Gruneir, PhD
Department of Family Medicine
University of Alberta
Edmonton, AB Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospital readmissions – when a patient is discharged from hospital but then returns to hospital in a short period of time – are known to be a problem, both for the patients and for the larger health system. Hospital readmissions have received considerable attention and there have been a number of initiatives to try to reduce them, but with mixed success. Older adults are among the most vulnerable group for hospital readmission. Older adults are also the largest users of continuing care services, such as home care and long-term care homes (also known as nursing homes). Yet, few large studies have really considered how older adults with different pathways through hospital compare on the risk of hospital readmission.
In our study, we take a population-level approach and use health administrative data to create a large cohort of older adults who were hospitalized in Ontario between 2008 and 2015. For each of the 701,527 patients in our study, we identified where they received care before the hospitalization (in the community or in long-term care) and where they received care after discharge (in the community, in the community with home care, or in long-term care). (more…)
Andrea Gruneir, PhD
Department of Family Medicine
University of Alberta
Edmonton, AB Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospital readmissions – when a patient is discharged from hospital but then returns to hospital in a short period of time – are known to be a problem, both for the patients and for the larger health system. Hospital readmissions have received considerable attention and there have been a number of initiatives to try to reduce them, but with mixed success. Older adults are among the most vulnerable group for hospital readmission. Older adults are also the largest users of continuing care services, such as home care and long-term care homes (also known as nursing homes). Yet, few large studies have really considered how older adults with different pathways through hospital compare on the risk of hospital readmission.
In our study, we take a population-level approach and use health administrative data to create a large cohort of older adults who were hospitalized in Ontario between 2008 and 2015. For each of the 701,527 patients in our study, we identified where they received care before the hospitalization (in the community or in long-term care) and where they received care after discharge (in the community, in the community with home care, or in long-term care). (more…)
 Andrea Gruneir, PhD
Department of Family Medicine
University of Alberta
Edmonton, AB Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospital readmissions – when a patient is discharged from hospital but then returns to hospital in a short period of time – are known to be a problem, both for the patients and for the larger health system. Hospital readmissions have received considerable attention and there have been a number of initiatives to try to reduce them, but with mixed success. Older adults are among the most vulnerable group for hospital readmission. Older adults are also the largest users of continuing care services, such as home care and long-term care homes (also known as nursing homes). Yet, few large studies have really considered how older adults with different pathways through hospital compare on the risk of hospital readmission.
In our study, we take a population-level approach and use health administrative data to create a large cohort of older adults who were hospitalized in Ontario between 2008 and 2015. For each of the 701,527 patients in our study, we identified where they received care before the hospitalization (in the community or in long-term care) and where they received care after discharge (in the community, in the community with home care, or in long-term care). (more…)
Andrea Gruneir, PhD
Department of Family Medicine
University of Alberta
Edmonton, AB Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Hospital readmissions – when a patient is discharged from hospital but then returns to hospital in a short period of time – are known to be a problem, both for the patients and for the larger health system. Hospital readmissions have received considerable attention and there have been a number of initiatives to try to reduce them, but with mixed success. Older adults are among the most vulnerable group for hospital readmission. Older adults are also the largest users of continuing care services, such as home care and long-term care homes (also known as nursing homes). Yet, few large studies have really considered how older adults with different pathways through hospital compare on the risk of hospital readmission.
In our study, we take a population-level approach and use health administrative data to create a large cohort of older adults who were hospitalized in Ontario between 2008 and 2015. For each of the 701,527 patients in our study, we identified where they received care before the hospitalization (in the community or in long-term care) and where they received care after discharge (in the community, in the community with home care, or in long-term care). (more…)
Aging, Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, CMAJ, Genetic Research / 06.09.2018
Age, Sex and Genetics Can Identify Groups at Higher Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Ruth Frikke-Schmidt, Professor, Chief Physician, MD, DMSc, PhD
Department of Clinical Biochemistry
Rigshospitalet, Blegdamsvej &
Deputy Head
Department of Clinical Medicine
Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences
University of Copenhagen
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia are devastating, neurodegenerative disorders affecting more than 47 million people in 2015, a number projected to triple by 2050 (1,2). Available curative treatments are lacking, and no useful risk prediction tools exist. The potential for prevention is however substantial, emphasized by the recently observed incidence decline in Western societies, likely caused by improved treatment and prevention of vascular risk factors (1,3,4). Population growth and aging, will however triple dementia prevalence by 2050, if no action is taken. Acting now with ambitious preventive interventions, delaying onset of disease by five years, is estimated to halve the prevalence globally (1,5).
Despite important preventive efforts over the last decades - resulting in decreased smoking, lower blood pressure and lower cholesterol levels in the general population - physical inactivity, overweight, and diabetes remain threats for our health care system, and in particular for cardiovascular disease and dementia. Intensifying preventive efforts in general is thus of crucial importance, and especially for those patients at highest risk who most likely will benefit the most from early and targeted prevention. Risk stratification and specific treatment goals according to the estimated absolute 10-year risk, has been implemented in cardiovascular disease for years (6,7). There is an un-met need for similar strategies in dementia, underscored by the publication of several randomized multicomponent trials that seem to improve or maintain brain function in at-risk elderly people from the general population (8-10) (more…)
Author Interviews, Biomarkers, CMAJ, Heart Disease / 20.08.2018
Clinical Chemistry Score Helps Rule Out Diagnosis of Heart Attack
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Peter Kavsak, PhD, FCACB, FAACC, FCCS
Professor, Pathology and Molecular Medicine
McMaster University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: For patients who present to the hospital with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) the preferred blood test to help physicians in making a diagnosis is cardiac troponin.
Recent studies have demonstrated that a very low or undetectable cardiac troponin level when measured with the newest generation of blood tests (i.e., the high-sensitivity cardiac troponin tests) in this population may rule-out myocardial infarction (MI or a heart attack) on the initial blood sample collected in the emergency department, thus enabling a faster decision and foregoing the need for subsequent serial measurements of cardiac troponin over several hours as recommended by the guidelines. The problem with this approach, however, is that using high-sensitivity cardiac troponin alone to do this has not reliably been demonstrated to achieve a sensitivity >99% for detecting MI, which is the estimate that most physicians in this setting consider as safe for discharge.
Our study goal was to compare the diagnostic performance of a simple laboratory algorithm using common blood tests (i.e., a clinical chemistry score (CCS) consisting of glucose, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and either high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I or T) to high-sensitivity cardiac troponin alone for predicting MI or death within the first month following the initial blood work. (more…)
Author Interviews, CMAJ, Vaccine Studies / 26.09.2016
Immunity to the Acellular Whooping Cough Vaccine Wanes With Time
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Kevin Schwartz, MD MSc
Infection Prevention and Control Physician
Infection Prevention and Control
Public Health Ontario | Santé publique Ontario
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: There has been a resurgence of pertussis, or ‘whooping cough’, in several countries and regions since the introduction of the new “acellular” pertussis vaccine in the 1990s to replace the older “whole cell” vaccine. In Ontario, we have not seen large increases but observed a small outbreak in 2012 that affected both unvaccinated people, as well as in those who have been vaccinated against pertussis. Our objective was to evaluate the effectiveness of the current acellular vaccine used in Ontario. We wanted to find out whether immunity wanes with time in the same way as had been previously observed during a large outbreak in California. We also wanted to study the impact of receiving the older ‘whole cell’ vaccine, which we used in Ontario until 1997.
(more…)