Study Emphasizes Need to Establish Optimal Pressure Combination Therapies by Ethnicity
Genetic Evidence Suggests New LDL-C Lowering Drug May Decrease Cardiovascular Events and Have Additive Effect with Statins
Number of Opioid Prescriptions for New Users Has Dropped More Than 50%
Ultrashort TB Therapy Found Just As Effective as 6 Month Course
Bempedoic Acid Lowers LDL When Statins Alone Aren’t Enough
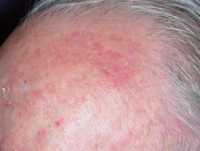
Actinic Keratosis: What is the Best Treatment for Pre-Skin Cancers?
Prostate Cancer: Novel Androgen Blocker Darolutamide Has Potential to Delay Mets and Extend Survival
Antibody–Drug Conjugate in Refractory Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Safety of MRIs in Patients with Tattoos
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Martina Callaghan PhD Head of Physics & Senior Lecturer Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging Institute of Neurology University College London London
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: As mirrors the situation in the general population, we found that an increasing number of volunteers who were seeking to enter cognitive neuroscience studies at our Centre had tattoos. However, the magnetic fields used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) pose a potential safety risk for people with tattoos. A number of case reports have described such incidents. However, as these describe isolated cases retrospectively, there was not enough information to objectively assess the risk of tattoo-related adverse reactions for persons having an MRI scan. Therefore, in 2011, we decided to embark upon this first prospective study to quantitatively assess this risk.
(more…)Single-Dose Tafenoquine to Prevent Malaria Relapse
A significantly greater proportion of patients in the tafenoquine group did not have malaria relapses compared to patients in the...
Esophageal Cancer: HMIE Procedure Reduces Morbidity Without Sacrificing Efficacy
Parents: Vaping is Drawing Adolescents into Nicotine Use
Pancreatic Cancer: mFOLFIRINOX After Surgery Improves Survival
Reclast, Zometa (zoledronate) Reduced Fractures in Osteopenic Older Women
Probiotics Found Unhelpful in Kids With Outpatient Diarrhea
New Drug Class Holds Promise Against Antibiotic Resistant Gonorrhea
Critical Illness: Haloperidol and Ziprasidone for Treatment of Delirium
Genetic Variant is Risk Factor for Two Different Types of Interstitial Lung Disease
Do Antipsychotics Shorten Duration of Delirium in ICU Patients?
Brain Change in Addiction as Learning, Not Disease
Most Overweight or Obese Children Will Stay So
Obesity Sets In At Very Early Age...
Zoledronate (Reclast, Zometa) Reduced Fractures in Older Women with Osteopenia
NEJM: Rivaroxaban (XARELTO®) For Thromboembolism Prevention after Medical Illness
Outbreak of Synthetic Cannabinoid–Associated Bleeding Disorders in Illinois
What Happens When Pay for Performance Incentives Are Withdrawn?
Subcutaneous Emicizumab Reduces Number of Injections Needed to Control Hemophilia
Ibudilast Slowed Brain Atrophy Progressive Multiple Sclerosis in Phase 2 Study
Percutaneous Repair or Medical Treatment for Secondary Mitral Regurgitation?
 Jean François Obadia MD PhD
Adult Cardiovascular Surgery and Transplantation
Louis Pradel Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
-By definition a secondary MR concerns a normal valve or sub normal valve inside a dilated heart with poor LV function in a population of Heart failure patients. It is perfectly established today that secondary MR is a predictor of poor clinical outcomes of thissevere population.
-Therefore,it has been proposed to treat those regurgitation either by surgery (mainly the downsizing anuloplasty) or by percutaneous technique like the mitraclipwhich has been used more and more frequently recently.
-However, a beneficial effect on hardclinical outcomes has never been provedandwe still don’t know if those regurgitations need to be corrected or not, We still don’t Know if the regurgitation is the cause, the consequence or just a marker of poor prognosis.
-In this context according to the guidelines, there is a low level of evidence to support those treatments, and Europe and US Guidelines call for prospective randomized studies in this severe population.
And this excatly what we have done with MITRA-FR
(more…)
Jean François Obadia MD PhD
Adult Cardiovascular Surgery and Transplantation
Louis Pradel Hospital
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
-By definition a secondary MR concerns a normal valve or sub normal valve inside a dilated heart with poor LV function in a population of Heart failure patients. It is perfectly established today that secondary MR is a predictor of poor clinical outcomes of thissevere population.
-Therefore,it has been proposed to treat those regurgitation either by surgery (mainly the downsizing anuloplasty) or by percutaneous technique like the mitraclipwhich has been used more and more frequently recently.
-However, a beneficial effect on hardclinical outcomes has never been provedandwe still don’t know if those regurgitations need to be corrected or not, We still don’t Know if the regurgitation is the cause, the consequence or just a marker of poor prognosis.
-In this context according to the guidelines, there is a low level of evidence to support those treatments, and Europe and US Guidelines call for prospective randomized studies in this severe population.
And this excatly what we have done with MITRA-FR
(more…)