MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Christina Lee Chung, MD, FAAD
Associate Professor of Dermatology
Director, Center for Transplant Patients
Drexel University College of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: It’s long been recognized immunosuppressed organ transplant recipients are at significantly increased risk for skin cancer and other types of skin disease.
But despite advances to improve skin cancer prevention for these patients, little is known about how skin conditions affect African-American, Asian and Hispanic transplant recipients. This is problematic given that, according to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than half of the 120,000 Americans on the waiting list for organs identify as nonwhite.
We compared medical records of 412 organ transplant recipients — including 154 white patients and 258 nonwhite (black, Asian or Hispanic) — who were referred to the Drexel Dermatology Center for Transplant Patients between 2011 and 2016. As one of the only models of its kind in the country, the center provides post-transplant dermatological care to every patient who is transplanted by and/or followed by the Drexel University and Hahnemann University Hospital Transplant Programs. That means that every patient, regardless of race, is screened annually for skin cancer, which provided a unique dataset for us to analyze.
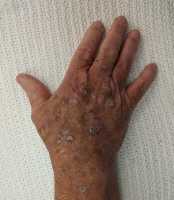
Two hundred eighty-nine transplant recipients exhibited malignant, infectious or inflammatory conditions during their evaluation, but their primary acute diagnoses differed greatly by race. In 82 white patients, skin cancer was the most common acute problem requiring attention at first visit. Black and Hispanic patients, by contrast, were most often diagnosed with inflammatory or infectious processes, such as fungal infections, warts, eczema, psoriasis, and rashes that required immediate medical attention.
Overall, squamous cell carcinoma in situ was the most common type of skin cancer diagnosed in each racial or ethnic group. But the location of the cancerous lesions again depended on the race of the patient. Most lesions in white and Asian patients occurred in sun-exposed areas of the body, like the scalp, neck, chest and back. For black patients, the lesions were primarily found in the groin. Moreover, six of the nine lesions found on black patients tested positive for high-risk HPV strains, suggesting an association between the virus and skin cancer for African Americans.
We also provided questionnaires to 66 organ transplant recipients to find out more about the patients’ awareness of skin cancer prevention. Seventy-seven percent of white patients were aware their skin cancer risk was increased, compared to 68 percent of nonwhites. Only 11 percent of nonwhite patients reported having regular dermatologic examinations, compared to 36 percent of whites. Finally, 45 percent of white patients but only 25 percent of nonwhite reported knowing the signs of skin cancer.
(more…)
 Howa Yeung, MD
Assistant Professor of Dermatology
Emory University School of Medicine
Atlanta, GA 30322
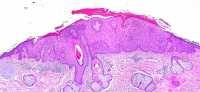
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you briefly explain what is meant by actinic keratoses?
Response: Actinic keratoses are common precancerous skin lesions caused by sun exposure. Because actinic keratoses may develop into skin cancers such as squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, they are often treated by various destructive methods. We used Medicare Part B billing claims to estimate the number and cost of treated actinic keratoses from 2007 to 2015.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: While the number of Medicare Part B beneficiaries increased only moderately, the number of actinic keratoses treated by destruction rose from 29.7 million in 2007 to 35.6 million in 2015. Medicare paid an average annual amount of $413.1 million for actinic keratosis destruction from 2007 to 2015. Independently billing non-physician clinicians, including advanced practice registered nurses and physician assistants, are treating an increasing proportion of actinic keratosis, peaking at 13.5% in 2015.
MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report?
Response: Readers should understand that the burden of actinic keratosis treatment is increasing in the Medicare population. There is also an increasing proportion of actinic keratoses being treated by advanced practice registered nurses and physician assistants. (more…)
Howa Yeung, MD
Assistant Professor of Dermatology
Emory University School of Medicine
Atlanta, GA 30322
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you briefly explain what is meant by actinic keratoses?
Response: Actinic keratoses are common precancerous skin lesions caused by sun exposure. Because actinic keratoses may develop into skin cancers such as squamous cell carcinoma and basal cell carcinoma, they are often treated by various destructive methods. We used Medicare Part B billing claims to estimate the number and cost of treated actinic keratoses from 2007 to 2015.
MedicalResearch.com: What are the main findings?
Response: While the number of Medicare Part B beneficiaries increased only moderately, the number of actinic keratoses treated by destruction rose from 29.7 million in 2007 to 35.6 million in 2015. Medicare paid an average annual amount of $413.1 million for actinic keratosis destruction from 2007 to 2015. Independently billing non-physician clinicians, including advanced practice registered nurses and physician assistants, are treating an increasing proportion of actinic keratosis, peaking at 13.5% in 2015.
MedicalResearch.com: What should readers take away from your report?
Response: Readers should understand that the burden of actinic keratosis treatment is increasing in the Medicare population. There is also an increasing proportion of actinic keratoses being treated by advanced practice registered nurses and physician assistants. (more…)