Medical Imaging Continues to Rise in US Hospitals
MRIs Improve Targeting of Biopsies for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Risk Prediction Nodule Helps Determine Cancer Risk of Pulmonary Nodule Found on CT Scan
Cinematic Rendering of CT Scans Can Assist Surgeons in Preparation for Surgery
Non-Invasive Echocardiograms Can Be Overused Leading To Increased Costs
Canadian ERs Use Less Pediatric Diagnostic Imaging Than US
Combat-Related Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: Magnetoencephalography Can Detect Abnormal Gamma Band
Lung Cancer: AI Can Reduce False Positives on Low-Dose CT Screening
Lung Cancer: Screening Model Including Low-Dose CT Can Improve Risk Prediction
Radiomics Plus Machine Learning Can Optimize Prostate Cancer Classification
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Study Finds No Benefit to MRI-Guided Treatment
 Philippe Henrot, MD
Radiology Department
Institut de Cancerologie de Lorraine
Vandoeuvre-les-Nancy
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The initial observation was that daily practice of mammography shows a substantial proportion of women that report a negative experience after having a mammogram. Compression of the breast before delivering X-rays is mandatory to achieve the best image quality and to detect small cancers. Unfortunately, compression is uncomfortable, even sometimes painful.
We took into consideration a study of PJ Kornguth et al. published in 1993 reporting the self-compression technique. In this study one breast was compressed by the radiographer and the other with self-compression. The author reported a high level of patient satisfaction, and a lower discomfort, without compromising image quality. We performed a multicenter prospective randomized trial to demonstrate the feasibility of the self-compression technique in condition similar to routine screening or follow-up, compared with standard compression. The primary outcome was to demonstrate that self-compression did not lead to compress the breast less than standard compression, and that was done. The secondary outcomes were to evaluate pain, compression force and image quality.
The results indicated that compression force was higher when the women controlled themselves the compression of their breast, and the pain measured on a visual analogue scale was lower. Moreover, image quality was not compromised compared with standard compression. (more…)
Philippe Henrot, MD
Radiology Department
Institut de Cancerologie de Lorraine
Vandoeuvre-les-Nancy
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The initial observation was that daily practice of mammography shows a substantial proportion of women that report a negative experience after having a mammogram. Compression of the breast before delivering X-rays is mandatory to achieve the best image quality and to detect small cancers. Unfortunately, compression is uncomfortable, even sometimes painful.
We took into consideration a study of PJ Kornguth et al. published in 1993 reporting the self-compression technique. In this study one breast was compressed by the radiographer and the other with self-compression. The author reported a high level of patient satisfaction, and a lower discomfort, without compromising image quality. We performed a multicenter prospective randomized trial to demonstrate the feasibility of the self-compression technique in condition similar to routine screening or follow-up, compared with standard compression. The primary outcome was to demonstrate that self-compression did not lead to compress the breast less than standard compression, and that was done. The secondary outcomes were to evaluate pain, compression force and image quality.
The results indicated that compression force was higher when the women controlled themselves the compression of their breast, and the pain measured on a visual analogue scale was lower. Moreover, image quality was not compromised compared with standard compression. (more…)Safety of MRIs in Patients with Tattoos
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Dr. Martina Callaghan PhD Head of Physics & Senior Lecturer Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging Institute of Neurology University College London London
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: As mirrors the situation in the general population, we found that an increasing number of volunteers who were seeking to enter cognitive neuroscience studies at our Centre had tattoos. However, the magnetic fields used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) pose a potential safety risk for people with tattoos. A number of case reports have described such incidents. However, as these describe isolated cases retrospectively, there was not enough information to objectively assess the risk of tattoo-related adverse reactions for persons having an MRI scan. Therefore, in 2011, we decided to embark upon this first prospective study to quantitatively assess this risk.
(more…)Computer Simulation Study Favors Tomosynthesis over Digital Mammography
 Aldo Badano, Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Division of Imaging, Diagnostics, and Software Reliability
Office of Science and Engineering Laboratories
Center for Devices and Radiological Health Silver Spring, MD 20993
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Expensive and lengthy clinical trials can delay regulatory evaluation of innovative technologies, affecting patient access to high-quality medical products. Although computational modeling is increasingly being used in product development, it is rarely at the center of regulatory applications.
Within this context, the VICTRE project attempted to replicate a previously conducted imaging clinical trial using only computational models. The VICTRE trial involved no human subjects and no clinicians. All trial steps were conducted in silico. The fundamental question the article addresses is whether in silico imaging trials are at a mature development stage to play a significant role in the regulatory evaluation of new medical imaging systems. The VICTRE trial consisted of in silico imaging of 2986 virtual patients comparing digital mammography (DM) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) systems.
The improved lesion detection performance favoring DBT for all breast sizes and lesion types was consistent with results from a comparative trial using human patients and radiologists. (more…)
Aldo Badano, Ph.D.
Deputy Director, Division of Imaging, Diagnostics, and Software Reliability
Office of Science and Engineering Laboratories
Center for Devices and Radiological Health Silver Spring, MD 20993
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Expensive and lengthy clinical trials can delay regulatory evaluation of innovative technologies, affecting patient access to high-quality medical products. Although computational modeling is increasingly being used in product development, it is rarely at the center of regulatory applications.
Within this context, the VICTRE project attempted to replicate a previously conducted imaging clinical trial using only computational models. The VICTRE trial involved no human subjects and no clinicians. All trial steps were conducted in silico. The fundamental question the article addresses is whether in silico imaging trials are at a mature development stage to play a significant role in the regulatory evaluation of new medical imaging systems. The VICTRE trial consisted of in silico imaging of 2986 virtual patients comparing digital mammography (DM) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) systems.
The improved lesion detection performance favoring DBT for all breast sizes and lesion types was consistent with results from a comparative trial using human patients and radiologists. (more…)Women Benefit from Mammography Screening Beyond Age 75
Newer MRIs May Predict Alzheimer’s Disease Before Any Symptoms
Pulsed Radiofrequency For Acute Back Pain and Sciatica
AI: Deep Learning Algorithms Can Detect Critical Head CT Findings
 Sasank Chilamkurthy
AI Scientist,
Qure.ai
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Head CT scan is one of the most commonly used imaging protocols besides chest x-ray. They are used for patients with symptoms suggesting stroke, rise in intracranial pressure or head trauma. These manifest in findings like intracranial haemorrhage, midline shift or fracture.
Scans with these critical findings need to be read immediately. But radiologists evaluate the scans on first-come-first-serve basis or based on stat/routine markers set by clinicians. If the scans with critical findings are somehow pushed to the top of radiologists’ work list, it could substantially decrease time to diagnosis and therefore decrease mortality and morbidity associated with stroke/head trauma.
(more…)
Sasank Chilamkurthy
AI Scientist,
Qure.ai
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Head CT scan is one of the most commonly used imaging protocols besides chest x-ray. They are used for patients with symptoms suggesting stroke, rise in intracranial pressure or head trauma. These manifest in findings like intracranial haemorrhage, midline shift or fracture.
Scans with these critical findings need to be read immediately. But radiologists evaluate the scans on first-come-first-serve basis or based on stat/routine markers set by clinicians. If the scans with critical findings are somehow pushed to the top of radiologists’ work list, it could substantially decrease time to diagnosis and therefore decrease mortality and morbidity associated with stroke/head trauma.
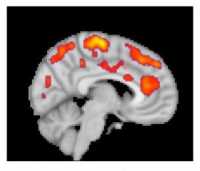
(more…)Fibromyalgia: Scan Reveals Increased Brain Activation in Pain, Emotion and Affect Areas
“Head CT Choice” Educates Parents of Children with Mild Head Injury
Using Tau PET Scan to Distinguish Alzheimer Disease from Other Neurodegenerative Disorders
 Rik Ossenkoppele -PhD
Lund University & VU University Medical Center
Oskar Hansson - Lund University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: [18F]flortaucipir is a relatively novel PET tracer that can be used to detect tau pathology in the living human brain. Previous studies have shown a robust signal in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, but in patients with other types of dementia the signal was more variable.
We aimed to assess the ability of [18F]flortaucipir PET to distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from other neurodegenerative disease in more than 700 study participants. T
he main finding was that [18F]flortaucipir discriminated Alzheimer’s disease patients from patients with other neurodegenerative diseases with high accuracy. Furthermore, [18F]flortaucipir PET outperformed established MRI markers and showed higher specificity than amyloid-β PET. (more…)
Rik Ossenkoppele -PhD
Lund University & VU University Medical Center
Oskar Hansson - Lund University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: [18F]flortaucipir is a relatively novel PET tracer that can be used to detect tau pathology in the living human brain. Previous studies have shown a robust signal in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, but in patients with other types of dementia the signal was more variable.
We aimed to assess the ability of [18F]flortaucipir PET to distinguish Alzheimer’s disease from other neurodegenerative disease in more than 700 study participants. T
he main finding was that [18F]flortaucipir discriminated Alzheimer’s disease patients from patients with other neurodegenerative diseases with high accuracy. Furthermore, [18F]flortaucipir PET outperformed established MRI markers and showed higher specificity than amyloid-β PET. (more…)Coronary CT Angiography May Be Best Approach to Chest Pain
Routine Mammography Screening Recommendations Do Not Apply To Women With History of Breast Cancer
How Common is Overdiagnosis of Lung Cancer with Low Dose CT Screening?
 Dr. Bruno Heleno MD PhD
Assistant Professor | Professor Auxiliar
NOVA Medical School | Faculdade de Ciências Médicas
Universidade Nova da Lisboa
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The Danish Lung Cancer Screening Trial (DLCST) is a randomized controlled trial which enrolled 4104 participants (aged 50-70 years; current or former smokers; ≥20 pack years; former smokers must have quit <10 years before enrollment) to either 5 rounds of screening for lung cancer with low-dose CT-scans or to no screening.
After 10 years of follow-up, there was a 2.10 percentage points lung cancer absolute risk increase with low-dose CT-screening. Overdiagnosis, i.e. the detection of cancer that would not progress to symptoms or death, was estimated at 67.2% of the screen-detected cancers.
(more…)
Dr. Bruno Heleno MD PhD
Assistant Professor | Professor Auxiliar
NOVA Medical School | Faculdade de Ciências Médicas
Universidade Nova da Lisboa
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The Danish Lung Cancer Screening Trial (DLCST) is a randomized controlled trial which enrolled 4104 participants (aged 50-70 years; current or former smokers; ≥20 pack years; former smokers must have quit <10 years before enrollment) to either 5 rounds of screening for lung cancer with low-dose CT-scans or to no screening.
After 10 years of follow-up, there was a 2.10 percentage points lung cancer absolute risk increase with low-dose CT-screening. Overdiagnosis, i.e. the detection of cancer that would not progress to symptoms or death, was estimated at 67.2% of the screen-detected cancers.
(more…)