Author Interviews, Biomarkers, Heart Disease, JAMA / 05.11.2018
New Biomarker Allows ‘Liquid Biopsy’ of Heart Muscle
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Robin M. Shaw, MD, PhD
Wasserman Foundation Chair in Cardiology
in honor of S. Rexford Kennamer MD
Division of Cardiology, Smidt Heart Institute
Department of Medicine, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center,
Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine
University of California,
Los Angeles, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
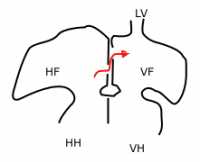
Response: At present, doctors do not have a clinical tool that assesses the biochemical health of heart muscle. Biomarkers are available that tests the amount of fluid in the heart, and whether a heart is overloaded (which can be resolved with diuretics). However, we don’t have biomarkers that assess the state of heart muscle itself. As a result, doctors can use biomarkers to determine whether, when a patient has trouble breathing, there is heart failure present.
However, biomarkers do not work when the patient does not have symptoms or when we already know the patient has heart failure and are trying to make clinical management decisions about the condition.
Current biomarkers also don’t work to assess the health of the heart before symptoms develop which is to detect cellular changes in muscle before overall heart function is impaired. The new biomarker, CS, address the above unmet needs. CS is based on cBIN1 which is a heart muscle protein that is essential for the heart to both contract and relax. cBIN1 decrease when hearts are stressed such as in heart failure. cBIN1 is also released into the blood stream, so it can be detected from a simple blood draw. CS is determined from the inverse of cBIN1, so low cBIN1 in blood will give a high CS signal. A low cBIN1, or a high CS, indicates failing heart muscle, and an increased likelihood for being admitted to the hospital with acute heart failure within the next twelve months. (more…)