Author Interviews, Dental Research, Mental Health Research, NYU / 15.04.2021
Periodontal Bacteria Linked to Alzheimer’s Amyloid
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
ANGELA R. KAMER, DMD, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
Periodontology and Implant Dentistry
NYU Dentistry
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
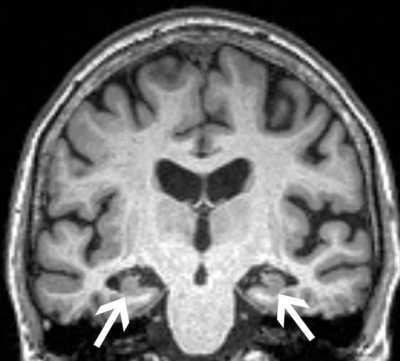
Response: The accumulation of amyloid β plaques and neurofibrillary pathology in the brain are pathognomonic to Alzheimer's disease (AD). Brain amyloid deposition begins decades before cognitive dysfunction and is thought to be the first AD pathological feature followed by tau tangle accumulations and other pathologies.
The mechanisms by which brain amyloid develops are incompletely understood although inflammation and bacterial imbalances (known as dysbiosis) of the gut and oral cavity may be involved. Periodontal disease affecting more than 50% of elderly is an inflammatory, chronic condition characterized by periodontal tissue destruction and bacterial imbalances. Using PET studies, we showed previously that measures of periodontal destruction were associated with brain amyloid retention in the brain [1]. In this study, we sought to investigate whether subgingival (under the gum line) bacteria associated with Alzheimer’s disease specific pathology, namely amyloidosis and tauopathy. (more…)