Improving family dynamics takes time, patience, and consistent effort. Therapeutic techniques such as active listening, setting boundaries, and practicing mindfulness...
Navigating Legal Compliance: Why Healthcare Businesses Must Understand Business Law
Compliance with Healthcare-Specific Regulations
Healthcare is one of the most heavily regulated industries, and for good reason. The stakes are high, with patient safety, privacy, and well-being on the line. Regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards, and the Anti-Kickback Statute are designed to protect patients, employees, and the integrity of the healthcare system. However, these regulations can be complex and challenging to navigate, especially for businesses without dedicated legal expertise. Noncompliance can have severe consequences. Fines for HIPAA violations, for example, can range from thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the severity of the breach. Similarly, failing to meet OSHA standards can result in hefty penalties and even shutdowns. Beyond financial costs, legal violations can damage a healthcare business’s reputation, eroding patient trust and making it harder to attract and retain clients. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, healthcare businesses can avoid these pitfalls and build a foundation of trust and reliability. (more…)How Healthcare Technology is Reducing Physician Burnout
 Physician burnout is a growing crisis in the healthcare industry, with many doctors facing overwhelming workloads, excessive administrative burdens, and emotional exhaustion. According to recent studies, nearly 50% of physicians experience symptoms of burnout, leading to reduced job satisfaction, increased medical errors, and even early retirement. Fortunately, advances in healthcare technology are helping to alleviate these stressors, allowing doctors to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork.
Let's explore how modern healthcare technology is playing a crucial role in reducing physician burnout and improving overall well-being for healthcare providers.
Physician burnout is a growing crisis in the healthcare industry, with many doctors facing overwhelming workloads, excessive administrative burdens, and emotional exhaustion. According to recent studies, nearly 50% of physicians experience symptoms of burnout, leading to reduced job satisfaction, increased medical errors, and even early retirement. Fortunately, advances in healthcare technology are helping to alleviate these stressors, allowing doctors to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork.
Let's explore how modern healthcare technology is playing a crucial role in reducing physician burnout and improving overall well-being for healthcare providers.
1. Electronic Health Records (EHRs) that Prioritize Physician Efficiency
One of the biggest contributors to physician burnout is the time spent on administrative tasks, particularly electronic documentation. Traditional EHR systems have often been complex, time-consuming, and frustrating, but newer platforms are designed with physician efficiency in mind.- Streamlined User Interfaces Modern EHRs now feature intuitive designs that make navigating patient records easier.
- Voice-to-Text Documentation AI-powered dictation tools allow doctors to document notes quickly without typing.
- Automated Workflows Features like auto-populating fields and predictive text reduce the time spent on repetitive data entry.
Cerebral Palsy: Understanding the Complexities Involved in Treatment and Diagnosis
A Major Issue Related to the Treatment of Cerebral Palsy
While you must educate yourself about diagnosis and treatment options, you must acknowledge a troubling aspect surrounding CP first: the potential for medical negligence. A large number of cerebral palsy cases are unfortunately linked to errors and omissions in medical care during labor, pregnancy, or delivery. These errors may include delayed or inappropriate C-sections, failure to monitor fetal distress, negligence in managing neonatal complications, and misuse of vacuum extractors or forceps. (more…)Buckle Up
Seatbelts remain the single most effective safety feature in preventing serious injuries. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), wearing a seatbelt reduces the risk of fatal injury by 45% in passenger cars and by 60% in SUVs and trucks. Drivers and passengers should always ensure they use seatbelts when traveling in a vehicle to reduce the risk of being injured in a crash. (more…)Revitalising Energy and Function: Science-Backed Regenerative Therapies for Men
Understanding Styes
Styes are one of the most frequent eye conditions encountered by people of all ages. These painful, red bumps on the eyelid are typically caused by a bacterial infection in the oil glands or hair follicles of the eyelid.What is a Stye?
A stye, or hordeolum, often appears as a swollen, pus-filled bump near the edge of the eyelid. They are usually localized and can cause significant discomfort, especially if the affected area is touched or rubbed frequently. Although styes generally resolve on their own, their presence can be a signal that the eye’s natural defense mechanisms are under stress. (more…)While prostate cancer can be serious, most patients can be managed with the proper treatment. With the use of medications,...
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, from treatment methods to medical equipment and systems. In this regard, health professions educators...
What is sleep apnoea?
Sleep apnoea is a sleep disorder that causes repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. These pauses, known as apnoeas, can last from a few seconds to minutes and may occur multiple times an hour. This condition disrupts normal sleep patterns, leading to poor rest and long-term health risks. Sleep apnoea is generally classified into three main types. Obstructive sleep apnoea: Obstructive sleep apnoea is the most common form. It occurs when the throat muscles relax excessively, temporarily blocking the airway. This results in disrupted breathing patterns and frequent awakenings throughout the night. Central sleep apnoea: Central sleep apnoea is less common and occurs when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Unlike obstructive sleep apnoea this type is not caused by airway obstruction but rather by a failure of the central nervous system to regulate breathing. Complex sleep apnoea syndrome: Complex Sleep Apnoea Syndrome, also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnoea, is a combination of both obstructive sleep apnoea and central sleep apnoea. Individuals with this form of sleep apnoea experience characteristics of both conditions, making diagnosis and treatment more complex. (more…)Diversity of Cells Allow Colon Cancer to Resist Treatment and To Metastasize
UMichigan Study Reveals Gender Differences in Online Physician Reviews
NYU Study Finds No Link Between Maternal Illness and Autism
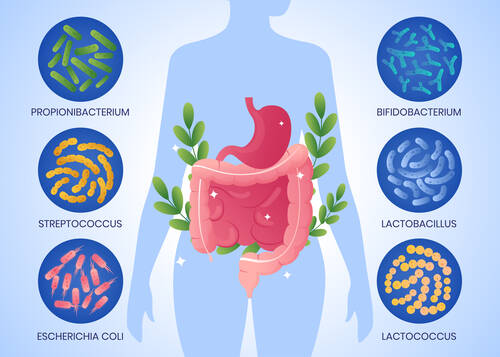
Why Your Gut Feelings Are Actually in Your Gut: The Microbiome-Mood Connection
The Hidden Conversation Between Gut and Brain
Your digestive system contains over 100 million neurons - more than your spinal cord. This extensive neural network, called the enteric nervous system, communicates directly with your brain through the vagus nerve, creating a two-way street of chemical messages that affect everything from stress levels to emotional resilience. Recent studies show that 90% of serotonin, often called the "happiness hormone," is produced in your gut, not your brain. This explains why digestive issues often accompany anxiety and depression, and why dietary changes can sometimes be as effective as traditional treatments for mood disorders. (more…)How to Identify and Minimize Long-Term Effects of Whiplash
Understanding Whiplash and Its Long-Term Effects
Whiplash occurs when your neck muscles and ligaments are suddenly stretched and torn, usually due to a rapid back-and-forth movement of the head. Think of it like a sudden jolt to your neck. Common causes include rear-end car collisions, contact sports, and falls. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may not appear immediately after the injury. You might experience neck pain, stiffness, limited range of motion, headaches, dizziness, and even tingling or numbness in your arms. If left untreated, whiplash can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and a reduced quality of life. It's important to take whiplash seriously and seek medical attention as soon as possible. You might be wondering, how long does whiplash last? The answer varies, but early intervention is key to a faster recovery. (more…)How Antibody Drug Discovery is Transforming Rare Disease Research
Precision Targeting for Effective Treatment
A key advantage of antibody-based therapies is their ability to achieve precision targeting, which is essential for treating rare diseases. Since many rare diseases stem from genetic mutations or protein dysregulation, they are well-suited for highly specific and targeted interventions. Antibodies can be designed to target disease-causing molecules like misfolded proteins, overactive receptors, or harmful cells while preserving healthy tissues. This precision improves treatment effectiveness and minimizes side effects, which is essential for patients with complex or fragile health conditions. To harness this potential, researchers are increasingly relying on advanced antibody discovery services. These services employ advanced technologies like phage display, single B-cell screening, and AI modeling to identify and refine high-affinity, specific antibodies for rare diseases. Partnering with specialized antibody discovery services helps researchers fast-track tailored therapies, offering hope to patients with untreatable conditions. This collaborative approach is revolutionizing rare disease research, leading to innovative treatments that target the root causes of complex disorders. Alloy Therapeutics recommends collaborating with an expert team to develop ranked bispecific candidates tailored to specific targets. Their comprehensive approach combines advanced technologies with proprietary workflows. This ensures the delivery of precise, high-quality bispecific leads for effective therapeutic development. (more…)Lupus and Blood Disorders: Understanding Lupus Anticoagulant Syndrome
Lupus anticoagulant syndrome is a serious but manageable condition that increases blood clotting risks in individuals with lupus autoimmune disease....
Routine eye exams are essential to preventative eye care, typically recommended every one to two years. However, it is advised...
Natural Pain Relief Without Risks from Opioids
Many countries have been grappling with an opioid crisis, which has motivated patients to seek cannabis as a much safer alternative. Medicinal cannabis minimizes the risks of addiction associated with opioids due to misuse and gives little risk of an overdose. To obtain medicinal cannabis legally, there are options like medical marijuana cards you can obtain from providers such as Leafy Doc Mississippi. Regarding how cannabis works in terms of pain relief, cannabinoids like THC bind to receptors in the brain and the immune system, modulating the experience of pain. The endocannabinoid system engages with trauma states mainly on account of pain, mood regulation, and inflammation. However, for long-term relief, medicinal cannabis is viewed as a considerably safer alternative compared to opioids. (more…)The Cognitive Effects of a TBI You Should Know About
Common Cognitive Effects of Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI)
According to the NIH, approximately 1.5 million Americans sustain a TBI each year, and 65% of survivors experience long-term cognitive impairments. Some common impairments to look for include:Memory Problems
One of the most common cognitive effects of a TBI is memory loss. This can manifest in both short- and long-term memory issues. Learning new information can become a challenge. For instance, someone with a TBI may struggle to recall names, appointments, or important events. These memory issues can significantly disrupt daily routines and relationships. (more…)The health risks associated with improper pet waste disposal extend far beyond simple inconvenience. From bacterial infections to pest infestations,...
Exploring the Cornerstones of an Effective Knowledge Management Strategy
Understanding Knowledge Management Strategy and Its Importance
 What is knowledge management strategy? It is a framework organizations use to manage knowledge assets systematically, ensuring information is accessible to those who need it. By fostering collaboration and sharing knowledge, companies can streamline processes, innovate, and make smarter decisions. This strategy emphasizes connecting people with both information and each other, focusing on active management of corporate knowledge, including the tacit expertise employees hold.
A strong knowledge management strategy is vital in today’s fast-paced industries. It helps retain critical knowledge during staff turnover, supports succession planning, and drives innovation by leveraging internal skills. By creating an environment of shared intelligence, businesses can exceed customer expectations, stand out in the market, and achieve operational excellence.
(more…)
What is knowledge management strategy? It is a framework organizations use to manage knowledge assets systematically, ensuring information is accessible to those who need it. By fostering collaboration and sharing knowledge, companies can streamline processes, innovate, and make smarter decisions. This strategy emphasizes connecting people with both information and each other, focusing on active management of corporate knowledge, including the tacit expertise employees hold.
A strong knowledge management strategy is vital in today’s fast-paced industries. It helps retain critical knowledge during staff turnover, supports succession planning, and drives innovation by leveraging internal skills. By creating an environment of shared intelligence, businesses can exceed customer expectations, stand out in the market, and achieve operational excellence.
(more…)Clinical Trials CRO: The Backbone of Successful Clinical Research
What is a Clinical Trials CRO?
A Clinical Research Organization (CRO) is a specialized service provider that assists pharmaceutical companies, biotech firms, and medical device manufacturers in conducting clinical trials. These organizations offer comprehensive services, including study design, patient recruitment, monitoring, regulatory compliance, data collection, and statistical analysis. CROs streamline the clinical trial process, reducing time and costs while ensuring compliance with regulatory authorities such as the FDA and EMA.Key Services Offered by Clinical Trials CROs
- Protocol Development – Designing a scientifically sound and regulatory-compliant study protocol.
- Regulatory Compliance – Ensuring adherence to FDA, EMA, and other global regulatory requirements.
- Patient Recruitment and Management – Identifying and enrolling eligible patients for clinical trials.
- Site Selection and Monitoring – Identifying qualified research sites and ensuring compliance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP).
- Data Management and Biostatistics – Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting trial data.
- Safety Monitoring – Assessing adverse events and ensuring patient safety throughout the trial.
- Quality Assurance – Conducting audits and inspections to maintain data integrity and protocol adherence.
- Medical Writing and Reporting – Preparing regulatory submissions, study reports, and scientific publications.
5 Main Scalp Issues Causing Hair Loss in Men and How to Address Them
Key Takeaways
- Scalp issues can contribute significantly to hair loss in men beyond genetic factors.
- Treating underlying scalp conditions is crucial for maintaining healthy hair growth.
- Various treatment options, including specialized products and medical interventions, can help combat hair loss.
Mount Sinai Study Emphasizes Importance of Personalizing Peanut Allergy Immunotherapy in Children
For many individuals, noticing blood in their urine is the initial sign that something may be wrong. Sometimes, people notice...