Selfies Distort Your Face and Make Your Nose Look Bigger
 Julia F. van den Berg, PhD
Leiden University, Department of Clinical Psychology
Leiden, The Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Caffeine is the most used psychoactive substance worldwide, mostly consumed via coffee, energy drinks, tea and chocolate. Experimental studies have shown that caffeine can negatively affect sleep quality. The timing of caffeine consumption may play a role; the closer to bedtime, the more caffeine consumption is likely to have a negative effect on sleep. We also wondered if chronotype, being a morning or evening person, would make a difference in the effect of caffeine on sleep.
We sent out questionnaires on sleep quality, chronotype, and a detailed questionnaire on type and timing of caffeine use to 880 secondary education students (mean age 21.3 years). We found that for the entire group, the amount of caffeine per week was not associated with sleep quality, regardless of chronotype. However, when we divided the group into subgroups of students who did, and students who did not usually consume caffeine in the evening (after 6PM), we found something interesting. Only for students who did not consume caffeine in the evening (20% of the total sample), a higher total caffeine consumption per week was associated with poorer sleep, in spite of the fact that these students consumed a lot less caffeine per week than the group who did consume caffeine in the evening.
This suggests a self-regulatory mechanism: students who know they are sensitive to caffeine do not drink it in the evening, nevertheless, the caffeinated beverages they drink during the day do affect their sleep.
(more…)
Julia F. van den Berg, PhD
Leiden University, Department of Clinical Psychology
Leiden, The Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Caffeine is the most used psychoactive substance worldwide, mostly consumed via coffee, energy drinks, tea and chocolate. Experimental studies have shown that caffeine can negatively affect sleep quality. The timing of caffeine consumption may play a role; the closer to bedtime, the more caffeine consumption is likely to have a negative effect on sleep. We also wondered if chronotype, being a morning or evening person, would make a difference in the effect of caffeine on sleep.
We sent out questionnaires on sleep quality, chronotype, and a detailed questionnaire on type and timing of caffeine use to 880 secondary education students (mean age 21.3 years). We found that for the entire group, the amount of caffeine per week was not associated with sleep quality, regardless of chronotype. However, when we divided the group into subgroups of students who did, and students who did not usually consume caffeine in the evening (after 6PM), we found something interesting. Only for students who did not consume caffeine in the evening (20% of the total sample), a higher total caffeine consumption per week was associated with poorer sleep, in spite of the fact that these students consumed a lot less caffeine per week than the group who did consume caffeine in the evening.
This suggests a self-regulatory mechanism: students who know they are sensitive to caffeine do not drink it in the evening, nevertheless, the caffeinated beverages they drink during the day do affect their sleep.
(more…)Balanced IV Fluids Can Reduce Kidney Damage and Death in Critically Ill Patients
For Most Patients Balanced IV Fluids Better Than Saline
Labor Costs Account For Largest Percentage of Operating Room Expenses
Collaborative Heart Failure Care Did Not Reduce Hospitalizations or Mortality, But Reduced Depression and Fatigue
This study evaluated the effect of a team intervention, Collaborative Care to Alleviate Symptoms and Adjust to Illness, also called CASA, on several aspects of quality of life in 314 patients with heart failure. The patients, who received care at diverse health systems in Colorado, were randomized to receive usual care or usual care supplemented with the CASA intervention, which included a nurse and a social worker who collaborated with a primary care provider, cardiologist, and palliative care physician to address the patients’ needs.
The study found that the CASA intervention did not influence the primary outcome of heart failure health status, yet did improve patients’ depression and fatigue. CASA did not influence number of patient hospitalizations or mortality. (more…)
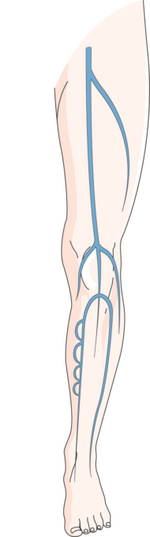
Varicose Veins Associated With Increased Risk of Deep Vein Blood Clots
How Old is Old?
 William Chopik PhD
Department of Psychology
Michigan State University
East Lansing, MI
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The motivation for the study was that we saw a lot of differences in the way people defined "old age". We also noticed that there is a stigma that goes along with being old. So we had a natural curiosity to see how these perceptions my change as people age.
As people aged, the tended to report feeling younger and consider an older adult as "always in the future"--never quite where they are now.
We found that our results confirmed a lot of existing theories about how our attitudes toward aging change as we age ourselves.
(more…)
William Chopik PhD
Department of Psychology
Michigan State University
East Lansing, MI
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: The motivation for the study was that we saw a lot of differences in the way people defined "old age". We also noticed that there is a stigma that goes along with being old. So we had a natural curiosity to see how these perceptions my change as people age.
As people aged, the tended to report feeling younger and consider an older adult as "always in the future"--never quite where they are now.
We found that our results confirmed a lot of existing theories about how our attitudes toward aging change as we age ourselves.
(more…)Decision Aids Can Help Heart Failure Patients Determine If They Want an LVAD
Genetic Variant of p53 Associated With Poor Breast Cancer Survival
Standardization and Collaboration Reduced Use of Costly CRRT Treatment for Critically Ill Patients
Both Vegetarian and Mediterranean Diets Beneficial for Weight Loss and Heart Health
 Francesco Sofi, MD PhD
Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine
University of Florence, Florence, Italy; Clinical Nutrition Unit, Careggi University Hospital
Don Carlo Gnocchi Foundation Italy, Onlus IRCCS
Florence, Italy
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Mediterranean and Vegetarian diets are two of the most beneficial dietary patterns for prevention of chronic degenerative diseases.
No studies have been conducted in the same group of subjects, by comparing these two dietary profiles.
Main results are that both diets have been found to be beneficial for cardiovascular prevention, in the same group of subjects at low risk of cardiovascular disease.
In particular, vegetarian diet determined a reduction of total and LDL-cholesterol, whereas Mediterranean diet resulted in lower levels of triglycerides and some inflammatory parameters
(more…)
Francesco Sofi, MD PhD
Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine
University of Florence, Florence, Italy; Clinical Nutrition Unit, Careggi University Hospital
Don Carlo Gnocchi Foundation Italy, Onlus IRCCS
Florence, Italy
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Mediterranean and Vegetarian diets are two of the most beneficial dietary patterns for prevention of chronic degenerative diseases.
No studies have been conducted in the same group of subjects, by comparing these two dietary profiles.
Main results are that both diets have been found to be beneficial for cardiovascular prevention, in the same group of subjects at low risk of cardiovascular disease.
In particular, vegetarian diet determined a reduction of total and LDL-cholesterol, whereas Mediterranean diet resulted in lower levels of triglycerides and some inflammatory parameters
(more…)Heart Attacks Rarely Misdiagnosed in Emergency Rooms
 Daniel A. Waxman, MD, PhD
Department of Emergency Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
RAND Corporation Santa Monica, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: When people talk about medical error, they are usually referring to treatment error—giving the wrong medication, operating on the wrong side of the body, etc. But many believe that diagnostic error—the failure to diagnose a condition when a patient seeks care—is at least as widespread and consequential a problem. However, diagnostic errors are intrinsically difficult to measure, since one can rarely prove that a condition was present at the time it was not diagnosed.
In this study, we introduce a novel method for measuring how often patients who come to the emergency room with symptoms of an imminent cardiovascular emergency such as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) are discharged home without a diagnosis.
We find that among Medicare patients whose ER visits were attributable to symptoms of an imminent infarction, only about 2.3% were discharged home, and that the figure was under 5% for each of the other four conditions we studied. However, we also found that these relatively low rates did not improve between 2007 and 2014.
(more…)
Daniel A. Waxman, MD, PhD
Department of Emergency Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine
University of California, Los Angeles
RAND Corporation Santa Monica, California
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: When people talk about medical error, they are usually referring to treatment error—giving the wrong medication, operating on the wrong side of the body, etc. But many believe that diagnostic error—the failure to diagnose a condition when a patient seeks care—is at least as widespread and consequential a problem. However, diagnostic errors are intrinsically difficult to measure, since one can rarely prove that a condition was present at the time it was not diagnosed.
In this study, we introduce a novel method for measuring how often patients who come to the emergency room with symptoms of an imminent cardiovascular emergency such as acute myocardial infarction (heart attack) are discharged home without a diagnosis.
We find that among Medicare patients whose ER visits were attributable to symptoms of an imminent infarction, only about 2.3% were discharged home, and that the figure was under 5% for each of the other four conditions we studied. However, we also found that these relatively low rates did not improve between 2007 and 2014.
(more…)Despite Advancing Neonatal Health, Preterm Babies Still Risk Cognitive Impairment
Mammograms Reduce Mortality From Higher Grade Breast Cancers
Stephen W. Duffy Professor of Cancer Screening Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine, Barts and The London School of Medicine and Dentistry Queen Mary University of London
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings? Response: The phenomenon of length bias, whereby screening has more chance of detecting slow growing tumours, has been known about for some years. This has led some colleagues to speculate that breast cancer screening only benefits those with slow-growing, less aggressive cancers, and does not reduce deaths from more aggressive, rapidly progressing cancers. In this study, we addressed this question directly using data from a randomised trial of mammographic screening. We calculated the reduction in mortality from grade 1 (less aggressive), grade 2 (intermediate) and grade 3 (most aggressive) cancers, as a result of screening. We found that the greatest reduction in breast cancer mortality was from the aggressive, fast-growing grade 3 cancers, contrary to what had been suspected. (more…)Kids with Kidney Disease Likely To Experience Lower IQ and Educational Outcomes Into Adulthood
Salivary Assay Developed for HIV Can Be Used To Detect Zika
Repeated Less Serious Infections Do Not Affect Children’s School Performance
New Vaccine Administered To Newborns Protects Against Rotavirus Gastroenteritis
USPSTF: Ovarian Cancer Screening Not Recommended in Low-Risk, Asymptomatic Women
Teen Marijuana Use Did Not Increase After Passage of Medical Marijuana Laws
 Professor Deborah Hasin PhD
Department of Epidemiology in Psychiatry
Mailman School of Public Health
Columbia University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: We began to think about this study after we published an earlier report (Hasin et al., The Lancet Psychiatry 2015) showing that after state medical marijuana laws (MML) were passed, U.S. teen marijuana use did not increase compared to the period before the laws were passed and to overall national trends. However, people continued to question whether MML led to teen increases in marijuana use. Therefore, in the present study, we combined findings from 11 large-scale national studies of teens to provide a more definite answer.
The findings were clear that teen marijuana use did not increase after passage of medical marijuana laws. Medical marijuana is widely available from stores like kush guys, yet despite this prevalence, there is no conclusive evidence of abuse. Rather the benefits are plain to see. (more…)
Professor Deborah Hasin PhD
Department of Epidemiology in Psychiatry
Mailman School of Public Health
Columbia University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: We began to think about this study after we published an earlier report (Hasin et al., The Lancet Psychiatry 2015) showing that after state medical marijuana laws (MML) were passed, U.S. teen marijuana use did not increase compared to the period before the laws were passed and to overall national trends. However, people continued to question whether MML led to teen increases in marijuana use. Therefore, in the present study, we combined findings from 11 large-scale national studies of teens to provide a more definite answer.
The findings were clear that teen marijuana use did not increase after passage of medical marijuana laws. Medical marijuana is widely available from stores like kush guys, yet despite this prevalence, there is no conclusive evidence of abuse. Rather the benefits are plain to see. (more…)Wine Might Be Good For Dental Health
 M.Victoria Moreno-Arribas
Spanish National Research Council | CSIC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Recent discoveries indicate polyphenols might also promote health by actively interacting with bacteria in the gut. Also, the intake of specific polyphenol-rich beverages and foods helps the maintenance of digestive health and prevention of disease status. However, the knowledge of the effects of polyphenols in relation to the prevention of dental diseases is still at an early stage.
The use of antiseptics and/or antibiotics in the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases can lead to unwanted effects. Therefore, there is a need to develop novel antimicrobial strategies useful for the prevention and management of these diseases. Oral epithelial cells normally constitute a physical barrier that prevents infections, but bacterial adhesion to host tissues constitutes a first key step in the infectious process.
With the final goal to elucidate the health properties of wine polyphenols at oral level, we studied their properties as an anti-adhesive therapy for periodontal and cariogenic prevention, as well as the combined action between wine polyphenols and oral probiotic strains in the management of microbial-derived oral diseases. In particular, we checked out the effect of two red wine polyphenols, as well as commercially available grape seed and red wine extracts, on bacteria that stick to teeth and gums and cause dental plaque, cavities and periodontal disease. Also, oral metabolism of polyphenols, including both oral microbiota and human mucosa cells, was investigated. (more…)
M.Victoria Moreno-Arribas
Spanish National Research Council | CSIC
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Recent discoveries indicate polyphenols might also promote health by actively interacting with bacteria in the gut. Also, the intake of specific polyphenol-rich beverages and foods helps the maintenance of digestive health and prevention of disease status. However, the knowledge of the effects of polyphenols in relation to the prevention of dental diseases is still at an early stage.
The use of antiseptics and/or antibiotics in the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases can lead to unwanted effects. Therefore, there is a need to develop novel antimicrobial strategies useful for the prevention and management of these diseases. Oral epithelial cells normally constitute a physical barrier that prevents infections, but bacterial adhesion to host tissues constitutes a first key step in the infectious process.
With the final goal to elucidate the health properties of wine polyphenols at oral level, we studied their properties as an anti-adhesive therapy for periodontal and cariogenic prevention, as well as the combined action between wine polyphenols and oral probiotic strains in the management of microbial-derived oral diseases. In particular, we checked out the effect of two red wine polyphenols, as well as commercially available grape seed and red wine extracts, on bacteria that stick to teeth and gums and cause dental plaque, cavities and periodontal disease. Also, oral metabolism of polyphenols, including both oral microbiota and human mucosa cells, was investigated. (more…)Aspirin or Rivaroxaban for VTE Prophylaxis after Hip or Knee Arthroplasty?
Study Finds No Benefit To Prophylactic Haldol For Delirium in ICU
 Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, RN, CCRN
Assistant Professor
Department of Intensive Care Medicine
Radboud University Medical Center
Nijmegen Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Delirium is affecting many of our intensive care unit (ICU) patients which is impacting their recovery on the short-term as well as on the long-term. Therefore we were very interested to investigate if the use prophylactic haloperidol would be beneficial for the ICU patients. Especially because there were indications that it would be effective in ICU delirium prevention and also because this drug is being used in daily practice to prevent ICU delirium although there is no clear evidence. The overall finding of our large-scale well designed study is that we didn’t find any beneficial effect of prophylactic haloperidol in ICU patients. Moreover, this finding is very consistent over all groups of patients. (more…)
Mark van den Boogaard, PhD, RN, CCRN
Assistant Professor
Department of Intensive Care Medicine
Radboud University Medical Center
Nijmegen Netherlands
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Delirium is affecting many of our intensive care unit (ICU) patients which is impacting their recovery on the short-term as well as on the long-term. Therefore we were very interested to investigate if the use prophylactic haloperidol would be beneficial for the ICU patients. Especially because there were indications that it would be effective in ICU delirium prevention and also because this drug is being used in daily practice to prevent ICU delirium although there is no clear evidence. The overall finding of our large-scale well designed study is that we didn’t find any beneficial effect of prophylactic haloperidol in ICU patients. Moreover, this finding is very consistent over all groups of patients. (more…)One Step Closer To Vaccine Against Heroin Addiction
 Candy Hwang, Ph.D.
The Scripps Research Institute
La Jolla, CA 92037
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Our heroin vaccine is designed to stimulate antibodies to recognize and bind heroin, preventing passage of drug molecules to the brain. By essentially blocking the “high” from heroin, we believe this will assist recovering addicts from relapsing. Last year, we reported a heroin vaccine that was shown to be effective in both mouse and non-human primate models. In this current study, we were interested in enhancing our heroin vaccine by exploring different vaccine components and dosages.
Once we discovered the most promising vaccine formulations, we wanted to see if our vaccines would be stable under different storage conditions. We found that our heroin vaccine was shelf stable under different temperatures and as a powder or in liquid form, meaning that the vaccine will remain stable for transport and storage. The best vaccine formulation from these studies showed protection against lethal doses of heroin.
(more…)
Candy Hwang, Ph.D.
The Scripps Research Institute
La Jolla, CA 92037
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Our heroin vaccine is designed to stimulate antibodies to recognize and bind heroin, preventing passage of drug molecules to the brain. By essentially blocking the “high” from heroin, we believe this will assist recovering addicts from relapsing. Last year, we reported a heroin vaccine that was shown to be effective in both mouse and non-human primate models. In this current study, we were interested in enhancing our heroin vaccine by exploring different vaccine components and dosages.
Once we discovered the most promising vaccine formulations, we wanted to see if our vaccines would be stable under different storage conditions. We found that our heroin vaccine was shelf stable under different temperatures and as a powder or in liquid form, meaning that the vaccine will remain stable for transport and storage. The best vaccine formulation from these studies showed protection against lethal doses of heroin.
(more…)Despite Promise, EMRs Have Not Reduced Administrative or Billing Expenses
Hand Osteoarthritis: Hydroxychloroquine No More Effective Than Placebo
What is the Biggest Modifiable Risk Factor For Dementia? Alcohol
 Michaël Schwarzinger, MD, PhD
Translational Health Economics Network (THEN)
Paris
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The association of heavy drinking with dementia has been known for decades. For instance, there is about no Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome without heavy drinking and the syndrome was described in 1890. But this type of dementia is very rare. Also, heavy drinking is knowingly associated with multiple risk factors for dementia onset such as hypertension or diabetes. But heavy drinkers generally refuse to participate to cohort studies and declaration of alcohol use among participants is generally biased downward... So the study rationale is very strong, but supporting empirical evidence is quite scarce.
This nationwide study included all 31+ million adults discharged from hospitals over 6 years, i.e., 50% of the French population before 65 years old and 80% above that age. Of 1.1+ million adults diagnosed with dementia, one in twenty had an early-onset (before 65 years old). Heavy drinking was recorded in most (56%) early-onset dementia cases: two-third in men; one-third in women. In addition, the association of heavy drinking with dementia goes far beyond 65 years old, both directly (>3 times higher risk for dementia onset after controlling for more than 30 known risk factors for dementia) and indirectly as heavy drinking was associated with all other independent risk factors for dementia onset. Accordingly, heavy drinking had the largest effect on dementia risk of all independent modifiable risk factors such as hypertension or diabetes.
The effects were found whatever dementia case definition or population studies.
(more…)
Michaël Schwarzinger, MD, PhD
Translational Health Economics Network (THEN)
Paris
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: The association of heavy drinking with dementia has been known for decades. For instance, there is about no Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome without heavy drinking and the syndrome was described in 1890. But this type of dementia is very rare. Also, heavy drinking is knowingly associated with multiple risk factors for dementia onset such as hypertension or diabetes. But heavy drinkers generally refuse to participate to cohort studies and declaration of alcohol use among participants is generally biased downward... So the study rationale is very strong, but supporting empirical evidence is quite scarce.
This nationwide study included all 31+ million adults discharged from hospitals over 6 years, i.e., 50% of the French population before 65 years old and 80% above that age. Of 1.1+ million adults diagnosed with dementia, one in twenty had an early-onset (before 65 years old). Heavy drinking was recorded in most (56%) early-onset dementia cases: two-third in men; one-third in women. In addition, the association of heavy drinking with dementia goes far beyond 65 years old, both directly (>3 times higher risk for dementia onset after controlling for more than 30 known risk factors for dementia) and indirectly as heavy drinking was associated with all other independent risk factors for dementia onset. Accordingly, heavy drinking had the largest effect on dementia risk of all independent modifiable risk factors such as hypertension or diabetes.
The effects were found whatever dementia case definition or population studies.
(more…)