MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Sara Saberi, MD, MS
Assistant Professor
Inherited Cardiomyopathy Program
Frankel Cardiovascular Center
University of Michigan Hospital
Michigan Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? Would you briefly explain what is meant by HCM?
How common is it and whom does it affect?
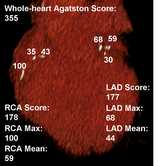
Response: HCM is short for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the most common genetic myocardial disorder. It occurs in 1:500 people worldwide and because it is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, it affects men and women equally. HCM is characterized by unexplained left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy, hypercontractility, myofibrillar disarray and myocardial fibrosis with associated abnormalities in LV compliance and diastolic function. In some patients, there is progressive adverse cardiac remodeling, associated with chronic heart failure and atrial fibrillation as a result of diastolic dysfunction, left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction, or less commonly, LV systolic dysfunction. Current medical management of obstructive HCM (oHCM) is limited to the use of beta blockers and non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, or disopyramide, none of which have been shown to modify disease expression or outcomes after onset.
Mavacamten is a first-in-class, small molecule, selective inhibitor of cardiac myosin specifically developed to target the underlying pathophysiology of HCM by reducing actin–myosin cross-bridge formation. The phase 3 EXPLORER-HCM trial showed that mavacamten improved exercise capacity, LVOT gradients, symptoms, and health status compared with placebo in patients with symptomatic oHCM. At selected study sites, participants were enrolled in a cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging substudy. CMR is the gold standard for measurement of ventricular mass, volumes and noninvasive tissue characterization, making it an ideal imaging modality to assess the effect of mavacamten on cardiac structure and function in patients with HCM.
(more…)



























 Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, FACC, FAHA, FASPC
Professor, Section of Cardiovascular Research
Director, Cardiology Fellowship Training Program
Baylor College of Medicine
Staff Cardiologist, Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Co-Director, VA Advanced Fellowship in Health Services Research & Development at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston, TX
Investigator, Health Policy, Quality and Informatics Program
Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center HSR&D Center of Innovation
Houston, TX @virani_md
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings? What do you think accounts for the gender differences?
Response: We know that women with ischemic heart disease (IHD) have lower prescription rates for statin and high-intensity statin therapy. In this study, we assessed whether the same trends hold true for women with other forms of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) i.e. women with peripheral artery disease (PAD) or ischemic cerebrovascular disease (ICVD). Maximally tolerated statin therapy is a Class-I indication in patients with clinical ASCVD which includes PAD and ICVD.
We also assessed statin adherence among men and women with PAD and ICVD.
Lastly, we performed exploratory analyses to assess whether statin therapy, statin intensity, and statin adherence in women with PAD and ICVD were associated with cardiovascular outcomes and/or mortality.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, FACC, FAHA, FASPC
Professor, Section of Cardiovascular Research
Director, Cardiology Fellowship Training Program
Baylor College of Medicine
Staff Cardiologist, Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Co-Director, VA Advanced Fellowship in Health Services Research & Development at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, Houston, TX
Investigator, Health Policy, Quality and Informatics Program
Michael E. DeBakey Veterans Affairs Medical Center HSR&D Center of Innovation
Houston, TX @virani_md
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings? What do you think accounts for the gender differences?
Response: We know that women with ischemic heart disease (IHD) have lower prescription rates for statin and high-intensity statin therapy. In this study, we assessed whether the same trends hold true for women with other forms of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) i.e. women with peripheral artery disease (PAD) or ischemic cerebrovascular disease (ICVD). Maximally tolerated statin therapy is a Class-I indication in patients with clinical ASCVD which includes PAD and ICVD.
We also assessed statin adherence among men and women with PAD and ICVD.
Lastly, we performed exploratory analyses to assess whether statin therapy, statin intensity, and statin adherence in women with PAD and ICVD were associated with cardiovascular outcomes and/or mortality. 
