Alzheimer's - Dementia, Author Interviews, Sleep Disorders / 21.06.2019
Sleep History as a Predictor For Late-Life Alzheimer’s Disease Later In Life
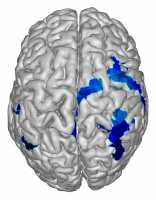
 Sleep patterns can predict the increase of Alzheimer’s pathology proteins tau and β-amyloid later in life, according to a June 2019 study published in the Journal of Neuroscience. The findings shed hope on earlier diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and the adoption of preventive measures earlier in life. Researchers found a decrease in sleep spindle synchronization, which is linked to higher tau levels. Reduced amplitude of slow wave activity, meanwhile, is closely related to higher β-amyloid levels. In younger people, both slow oscillations and sleep spindles are synchronized. This changes as people grow older, with less coordination between the two being visible. The researchers also noted that subjects who slept less had a higher chance of having Alzheimer’s proteins when they were older. The findings show that both reduced sleep quantity and quality can serve as important warnings of the onset of Alzheimer’s.
(more…)
Sleep patterns can predict the increase of Alzheimer’s pathology proteins tau and β-amyloid later in life, according to a June 2019 study published in the Journal of Neuroscience. The findings shed hope on earlier diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and the adoption of preventive measures earlier in life. Researchers found a decrease in sleep spindle synchronization, which is linked to higher tau levels. Reduced amplitude of slow wave activity, meanwhile, is closely related to higher β-amyloid levels. In younger people, both slow oscillations and sleep spindles are synchronized. This changes as people grow older, with less coordination between the two being visible. The researchers also noted that subjects who slept less had a higher chance of having Alzheimer’s proteins when they were older. The findings show that both reduced sleep quantity and quality can serve as important warnings of the onset of Alzheimer’s.
(more…)