Author Interviews, Heart Disease, JACC, Surgical Research, Technology / 20.11.2018
Comparison of the Evolut R™TAVR Valve with the Evolut PRO™
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Dr. Shazia Afzal MD
University Hospital Düsseldorf, Medical Faculty, Division of Cardiology, Pulmonology and Vascular Medicine, Düsseldorf, Germany
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Since its introduction in 2002, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) emerged to an increasingly important interventional procedure in the field of structural heart disease. Widespread use in Europe, the USA and Canada lead to continuous technological development and improved patient’s safety, procedural success and clinical outcome.
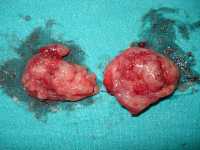
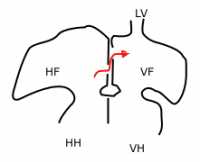
In 08/2017 one of the market leaders introduced its latest generation valve model -the CoreValve Evolut PROTM- which was especially designed to mitigate paravalvular leakage after valve deployment. We conducted the first prospective study which directly compares the Evolut PROTM with its direct predecessor the Evolut RTM as a head-to-head analysis especially focusing on hemodynamic performance and clinical outcome in a real-world setting. To ensure comparability between groups, we performed propensity score matching with special interest in CT-derived data to guarantee equitable anatomical conditions.
Since both valves are on the market but sold at different prices the pivotal question is whether the Evolut PROTM reaches its target. In a highly budget restricted health care system with limited refunding cost-effectiveness evolves to a substantial discussion point in daily clinical practice. Our results may not be marketing friendly but we think of relevance for the interventional community. (more…)
Dr. Shazia Afzal MD
University Hospital Düsseldorf, Medical Faculty, Division of Cardiology, Pulmonology and Vascular Medicine, Düsseldorf, Germany
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Since its introduction in 2002, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) emerged to an increasingly important interventional procedure in the field of structural heart disease. Widespread use in Europe, the USA and Canada lead to continuous technological development and improved patient’s safety, procedural success and clinical outcome.
In 08/2017 one of the market leaders introduced its latest generation valve model -the CoreValve Evolut PROTM- which was especially designed to mitigate paravalvular leakage after valve deployment. We conducted the first prospective study which directly compares the Evolut PROTM with its direct predecessor the Evolut RTM as a head-to-head analysis especially focusing on hemodynamic performance and clinical outcome in a real-world setting. To ensure comparability between groups, we performed propensity score matching with special interest in CT-derived data to guarantee equitable anatomical conditions.
Since both valves are on the market but sold at different prices the pivotal question is whether the Evolut PROTM reaches its target. In a highly budget restricted health care system with limited refunding cost-effectiveness evolves to a substantial discussion point in daily clinical practice. Our results may not be marketing friendly but we think of relevance for the interventional community. (more…)
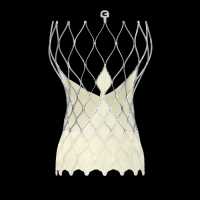 Dr. Shazia Afzal MD
University Hospital Düsseldorf, Medical Faculty, Division of Cardiology, Pulmonology and Vascular Medicine, Düsseldorf, Germany
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Since its introduction in 2002, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) emerged to an increasingly important interventional procedure in the field of structural heart disease. Widespread use in Europe, the USA and Canada lead to continuous technological development and improved patient’s safety, procedural success and clinical outcome.
In 08/2017 one of the market leaders introduced its latest generation valve model -the CoreValve Evolut PROTM- which was especially designed to mitigate paravalvular leakage after valve deployment. We conducted the first prospective study which directly compares the Evolut PROTM with its direct predecessor the Evolut RTM as a head-to-head analysis especially focusing on hemodynamic performance and clinical outcome in a real-world setting. To ensure comparability between groups, we performed propensity score matching with special interest in CT-derived data to guarantee equitable anatomical conditions.
Since both valves are on the market but sold at different prices the pivotal question is whether the Evolut PROTM reaches its target. In a highly budget restricted health care system with limited refunding cost-effectiveness evolves to a substantial discussion point in daily clinical practice. Our results may not be marketing friendly but we think of relevance for the interventional community. (more…)
Dr. Shazia Afzal MD
University Hospital Düsseldorf, Medical Faculty, Division of Cardiology, Pulmonology and Vascular Medicine, Düsseldorf, Germany
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Since its introduction in 2002, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) emerged to an increasingly important interventional procedure in the field of structural heart disease. Widespread use in Europe, the USA and Canada lead to continuous technological development and improved patient’s safety, procedural success and clinical outcome.
In 08/2017 one of the market leaders introduced its latest generation valve model -the CoreValve Evolut PROTM- which was especially designed to mitigate paravalvular leakage after valve deployment. We conducted the first prospective study which directly compares the Evolut PROTM with its direct predecessor the Evolut RTM as a head-to-head analysis especially focusing on hemodynamic performance and clinical outcome in a real-world setting. To ensure comparability between groups, we performed propensity score matching with special interest in CT-derived data to guarantee equitable anatomical conditions.
Since both valves are on the market but sold at different prices the pivotal question is whether the Evolut PROTM reaches its target. In a highly budget restricted health care system with limited refunding cost-effectiveness evolves to a substantial discussion point in daily clinical practice. Our results may not be marketing friendly but we think of relevance for the interventional community. (more…)








 Faiz Gani, PhD
Postdoctoral research fellow
Department of Surgery
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Firearm related injuries are a leading cause of injury and death in the United States, yet, due to combination of factors, limited data exist that evaluate these injuries, particularly among younger patients (patients younger than 18 years).
The objective of this study was to describe emergency department utilization for firearm related injuries and to quantitate the financial burden associated with these injuries.
In our study of over 75,000 emergency department visits, we observed that each year, over 8,300 children and adolescents present to the emergency department for the treatment / management of a gunshot injury. Within this sub-population of patients, we observed that these injuries are most frequent among patients aged 15-17 years and while these injuries decreased over time initially, were observed to increase again towards the end of the time period studied.
In addition to describing the clinical burden of these injuries, we also sought to describe the financial burden associated with these injuries. For patients discharged from the emergency department, the average (median) charge associated with their care was $2,445, while for patients admitted as inpatients for further care, the average (median) charge was $44,966.
Collectively these injuries resulted in $2.5 billion in emergency department and hospital charges over the time period studied. This translates to an annual financial burden of approximately $270 million.
Faiz Gani, PhD
Postdoctoral research fellow
Department of Surgery
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Firearm related injuries are a leading cause of injury and death in the United States, yet, due to combination of factors, limited data exist that evaluate these injuries, particularly among younger patients (patients younger than 18 years).
The objective of this study was to describe emergency department utilization for firearm related injuries and to quantitate the financial burden associated with these injuries.
In our study of over 75,000 emergency department visits, we observed that each year, over 8,300 children and adolescents present to the emergency department for the treatment / management of a gunshot injury. Within this sub-population of patients, we observed that these injuries are most frequent among patients aged 15-17 years and while these injuries decreased over time initially, were observed to increase again towards the end of the time period studied.
In addition to describing the clinical burden of these injuries, we also sought to describe the financial burden associated with these injuries. For patients discharged from the emergency department, the average (median) charge associated with their care was $2,445, while for patients admitted as inpatients for further care, the average (median) charge was $44,966.
Collectively these injuries resulted in $2.5 billion in emergency department and hospital charges over the time period studied. This translates to an annual financial burden of approximately $270 million. 

 Dr. Janey Pratt, MD
Clinical Associate Professor, Surgery
Stanford University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: In 2013 obesity became recognized as a disease. The rate of pediatric obesity continues to rise. Severe pediatric obesity is rising at a even faster rate than obesity in pediatrics. Despite this Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (MBS) remains underutilized in the treatment of severe pediatric obesity. There is a significant amount of adult data and now pediatric data about effective treatments for severe obesity. These support the use of MBS as a primary treatment for severe obesity in children. (BMI > 120% of 95th percentile with a comorbidity or BMI > 140% of 95th percentile).
Dr. Janey Pratt, MD
Clinical Associate Professor, Surgery
Stanford University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: In 2013 obesity became recognized as a disease. The rate of pediatric obesity continues to rise. Severe pediatric obesity is rising at a even faster rate than obesity in pediatrics. Despite this Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (MBS) remains underutilized in the treatment of severe pediatric obesity. There is a significant amount of adult data and now pediatric data about effective treatments for severe obesity. These support the use of MBS as a primary treatment for severe obesity in children. (BMI > 120% of 95th percentile with a comorbidity or BMI > 140% of 95th percentile).