Author Interviews, CMAJ, Orthopedics, Rheumatology, Surgical Research / 02.02.2021
Knee Realignment Surgery May Delay or Prevent Some Knee Replacements
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Codie Primeau, MSc
Physical Therapy Student & Ph.D. Candidate (Combined MPT/Ph.D.)
Wolf Orthopaedic Biomechanics Lab, Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic
Western University
London, ON, Canada
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
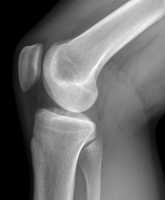
Response: High tibial osteotomy (HTO) is a surgery for patients with varus alignment (bowed legs) and earlier-stage knee osteoarthritis. By correcting alignment, HTO shifts load to less diseased parts of the knee. One of the goals of HTO is to delay or even prevent the need for knee replacement surgery later.
(more…)