Author Interviews, Brigham & Women's - Harvard, Cost of Health Care, JAMA, Surgical Research, Weight Research / 24.02.2019
Bariatric Surgery Could be a Cost-Effective Intervention in Patients with NASH Cirrhosis who are Overweight or Obese.
MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
Jagpreet Chhatwal PhD
Assistant Professor, Harvard Medical School
Senior Scientist, Institute for Technology Assessment
Massachusetts General Hospital
Chin Hur, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
Harvard Medical School
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
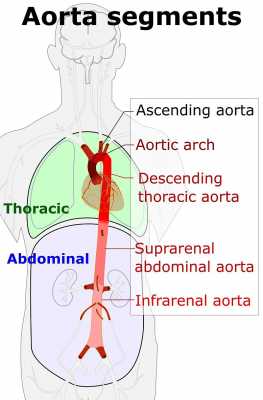
Response: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, is one of the leading causes of liver transplantation. Because of increasing prevalence of obesity in the United States, NASH-related cirrhosis cases are expected to increase in the near future. Unfortunately, there are few pharmacological treatments for NASH, and none with proven long-term benefit. Weight loss can be effective in managing NASH but not many patients can lose the sufficient weight necessary to impact NASH and/or maintain long-term weight loss. In contrast, bariatric surgery can provide long-term weight loss and thus potentially reverse liver damage in cirrhosis. However, bariatric surgery is associated with mortality and morbidity associated with the procedure.
(more…)




















 Faiz Gani, PhD
Postdoctoral research fellow
Department of Surgery
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Firearm related injuries are a leading cause of injury and death in the United States, yet, due to combination of factors, limited data exist that evaluate these injuries, particularly among younger patients (patients younger than 18 years).
The objective of this study was to describe emergency department utilization for firearm related injuries and to quantitate the financial burden associated with these injuries.
In our study of over 75,000 emergency department visits, we observed that each year, over 8,300 children and adolescents present to the emergency department for the treatment / management of a gunshot injury. Within this sub-population of patients, we observed that these injuries are most frequent among patients aged 15-17 years and while these injuries decreased over time initially, were observed to increase again towards the end of the time period studied.
In addition to describing the clinical burden of these injuries, we also sought to describe the financial burden associated with these injuries. For patients discharged from the emergency department, the average (median) charge associated with their care was $2,445, while for patients admitted as inpatients for further care, the average (median) charge was $44,966.
Collectively these injuries resulted in $2.5 billion in emergency department and hospital charges over the time period studied. This translates to an annual financial burden of approximately $270 million.
Faiz Gani, PhD
Postdoctoral research fellow
Department of Surgery
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Firearm related injuries are a leading cause of injury and death in the United States, yet, due to combination of factors, limited data exist that evaluate these injuries, particularly among younger patients (patients younger than 18 years).
The objective of this study was to describe emergency department utilization for firearm related injuries and to quantitate the financial burden associated with these injuries.
In our study of over 75,000 emergency department visits, we observed that each year, over 8,300 children and adolescents present to the emergency department for the treatment / management of a gunshot injury. Within this sub-population of patients, we observed that these injuries are most frequent among patients aged 15-17 years and while these injuries decreased over time initially, were observed to increase again towards the end of the time period studied.
In addition to describing the clinical burden of these injuries, we also sought to describe the financial burden associated with these injuries. For patients discharged from the emergency department, the average (median) charge associated with their care was $2,445, while for patients admitted as inpatients for further care, the average (median) charge was $44,966.
Collectively these injuries resulted in $2.5 billion in emergency department and hospital charges over the time period studied. This translates to an annual financial burden of approximately $270 million. 

 Dr. Janey Pratt, MD
Clinical Associate Professor, Surgery
Stanford University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: In 2013 obesity became recognized as a disease. The rate of pediatric obesity continues to rise. Severe pediatric obesity is rising at a even faster rate than obesity in pediatrics. Despite this Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (MBS) remains underutilized in the treatment of severe pediatric obesity. There is a significant amount of adult data and now pediatric data about effective treatments for severe obesity. These support the use of MBS as a primary treatment for severe obesity in children. (BMI > 120% of 95th percentile with a comorbidity or BMI > 140% of 95th percentile).
Dr. Janey Pratt, MD
Clinical Associate Professor, Surgery
Stanford University
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: In 2013 obesity became recognized as a disease. The rate of pediatric obesity continues to rise. Severe pediatric obesity is rising at a even faster rate than obesity in pediatrics. Despite this Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (MBS) remains underutilized in the treatment of severe pediatric obesity. There is a significant amount of adult data and now pediatric data about effective treatments for severe obesity. These support the use of MBS as a primary treatment for severe obesity in children. (BMI > 120% of 95th percentile with a comorbidity or BMI > 140% of 95th percentile).