MedicalResearch.com Interview with:
 Kathryn R. Tringale, MAS
Kathryn R. Tringale, MAS
Department of Radiation Medicine and Applied Sciences
University of California San Diego, La Jolla
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study? What are the main findings?
Response: Financial relationships between biomedical industry and physicians are common, and previous work has investigated the potential conflicts of interest that can arise from these interactions.
Data show that even small payments in the form of industry sponsored lunches can influence physician prescribing patterns. Given the concern for the potential influence of biomedical industry over practice patterns and potentially patient care, the Open Payments program was implemented under the Affordable Care Act to shed light on these interactions and make reports of these financial transactions publicly available. We recently published a paper in JAMA on industry payments to physicians that found that men received a higher value and greater number of payments than women physicians and were more likely to receive royalty or licensing payments when grouped by type of specialty (surgeons, primary care, specialists, interventionalists).
The purpose of the Research Letter discussed here was to further examine differences in the value of payments received by male and female physicians within each individual specialty. The main takeaway from this study is that male physicians, across almost every specialty, are receive more money from biomedical industry compared to female physicians. At first glance, this finding can be interpreted as merely another example of gender disparities in the workplace, which we have seen before with gender gaps in physician salaries and research funding. Indeed, this gender gap may be a product of industry bias leading to unequal opportunity for women to engage in these profitable relationships. Alternatively, these data may be more representative of gender differences in physician decision-making. Previous data has shown that industry engagement can lead to changes in practice patterns, so maybe female physicians acknowledge these conflicts of interest and actively choose not to engage with industry. Unfortunately, we cannot tease out these subtleties from our results, but our paper does reveal a remarkable gender difference among physician engagement with industry. With this being said, whether male or female, everyone needs a bit of help sometimes. The use of loans is a possibility for many people who need a little financial assistance. Regardless of whether men are getting paid a little more than women, they may all need help just as equally. The type of loans that would be worth looking into if this is your current situation is
physician loans, which basically allows medical professionals to purchase a home with a low/little down payment while avoiding mortgage insurance. A little bit of help goes a long way, especially when it involves your future.
(more…)




 Lauren C. Davis, MBS
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA 19409
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
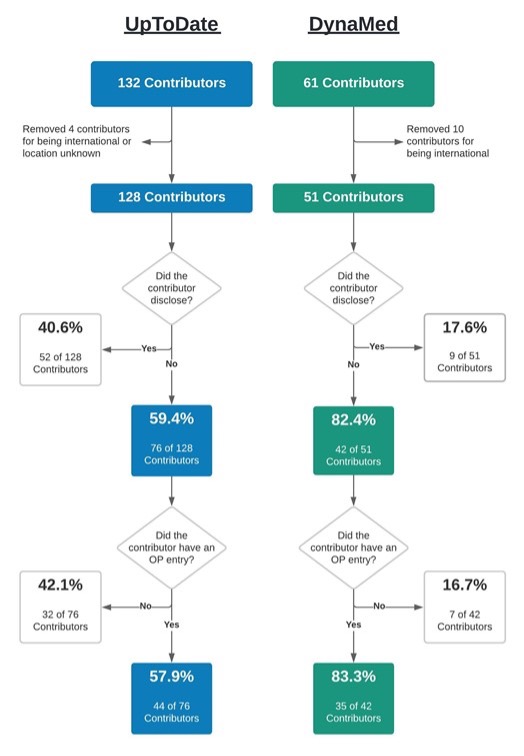
Response: Financial conflicts of interest (COIs) resulting from ties between academia and industry have been under scrutiny for their potential to hinder the integrity of medical research. COIs can lead to implicit bias, compromise the research process, and erode public trust (1-6). The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), standardizes symptom criteria and codifies psychiatric disorders. This manual contributes to the approval of new drugs, extensions of patent exclusivity, and can influence payers and mental health professionals seeking third-party reimbursements. Given the implications of the DSM on public health, it is paramount that it is free of industry influence. Previous research has shown a high prevalence of industry ties among panel and task force members of the DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5, despite the implementation of a disclosure policy for the DSM-5 (7,8). This study (9) determined the extent and type of COIs received by panel and task-force members of the DSM-5-TR (2022) (10). As the DSM-5-TR did not disclose COI, we used the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments (OP) database (11) to quantify them.
Lauren C. Davis, MBS
Department of Medical Education
Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
Scranton, PA 19409
MedicalResearch.com: What is the background for this study?
Response: Financial conflicts of interest (COIs) resulting from ties between academia and industry have been under scrutiny for their potential to hinder the integrity of medical research. COIs can lead to implicit bias, compromise the research process, and erode public trust (1-6). The American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), standardizes symptom criteria and codifies psychiatric disorders. This manual contributes to the approval of new drugs, extensions of patent exclusivity, and can influence payers and mental health professionals seeking third-party reimbursements. Given the implications of the DSM on public health, it is paramount that it is free of industry influence. Previous research has shown a high prevalence of industry ties among panel and task force members of the DSM-IV-TR and DSM-5, despite the implementation of a disclosure policy for the DSM-5 (7,8). This study (9) determined the extent and type of COIs received by panel and task-force members of the DSM-5-TR (2022) (10). As the DSM-5-TR did not disclose COI, we used the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services Open Payments (OP) database (11) to quantify them.